A Burning Legacy
Greek fire is a great mystery that humans have lost to time and secrecy. It’s one of the ancient world’s greatest puzzles, to which we have so few pieces, that scholars have spent centuries trying to figure out. Here’s what we know about it so far.
Its Purpose Was Nefarious
Greek fire was an incendiary substance meant to start fires on enemy ships. It was intentionally difficult to put out, and the substance earned a dangerous and terrifying reputation.
 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
It Didn’t Have Many Weaknesses
The substance was unaffected by water, which would put out a regular fire. There were also rumors that it was ignited by contact with water. Historians changed the list of Greek fire’s ingredients based on this quality.
 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
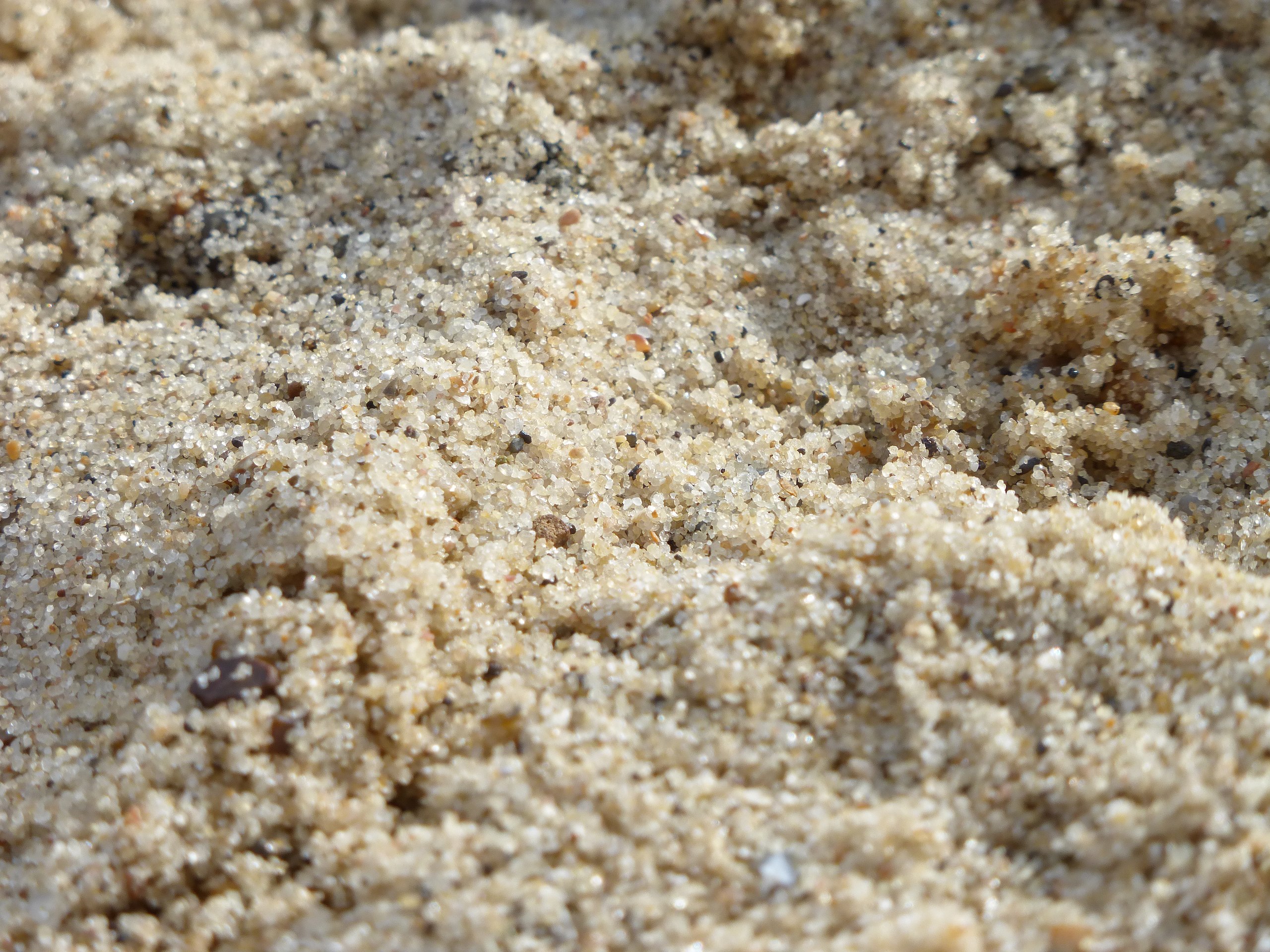
You Needed Special Tactics To Extinguish The Fire
According to many reports and extant writings, the flames were only extinguishable using unconventional methods. They would use urine, sand, and strong vinegar, and likely needed to create a specific chemical reaction to put out Greek fire.
 Annajohepworth, Wikimedia Commons
Annajohepworth, Wikimedia Commons
This Empire Was The Only One To Use It
Greek fire was invented and used in naval conflicts by the Byzantine Empire. They used it from the seventh to fourteenth centuries in many, many nautical battles with other empires.
 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
It Went By Many Names
According to sources at the time, it was also called “sea fire”, “Roman fire”, “war fire”, “liquid fire”, “sticky fire”, “manufactured fire”, or “Median fire”. This is quite the list of nicknames for such a powerful substance.
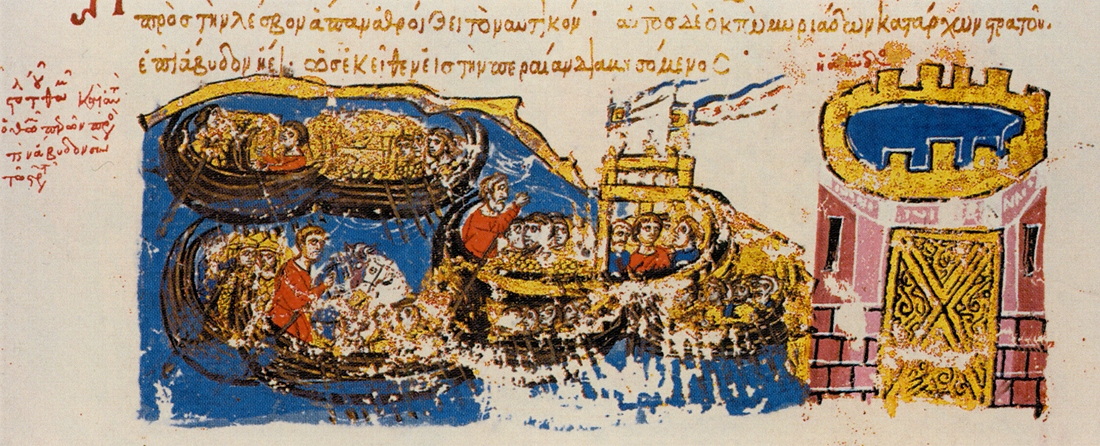
Many Tried To Replicate It
Many of the Byzantine Empire’s enemies tried to replicate the mixture. Unfortunately, they couldn’t fight fire with fire—they never figured out how to copy the recipe.
 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
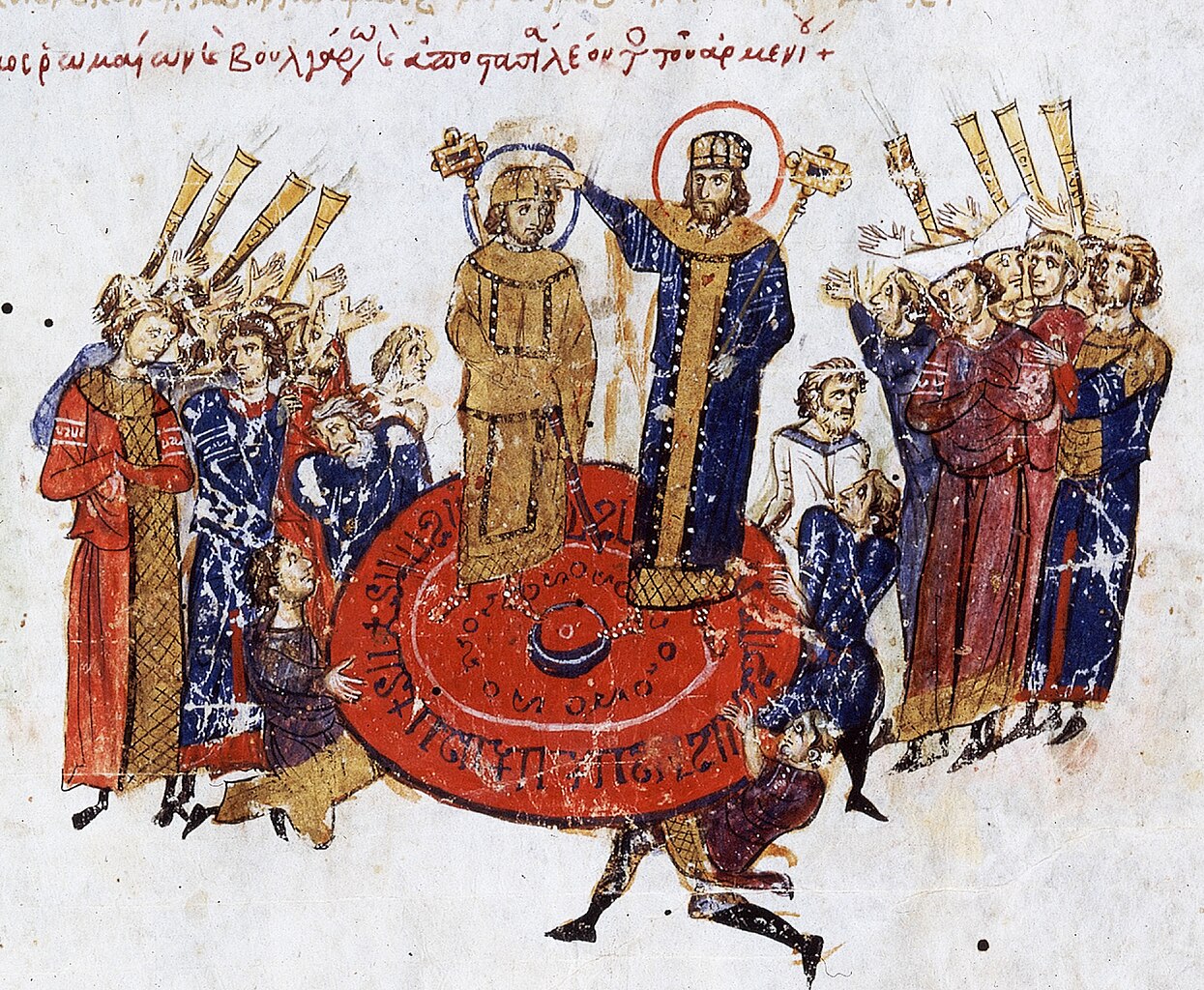
It Was A Tightly Monitored Secret
The Byzantine government didn’t want their rivals to have the recipe for Greek fire. It was one of the closest kept secrets, so much so that they let the recipe disappear with those who knew of it.
 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
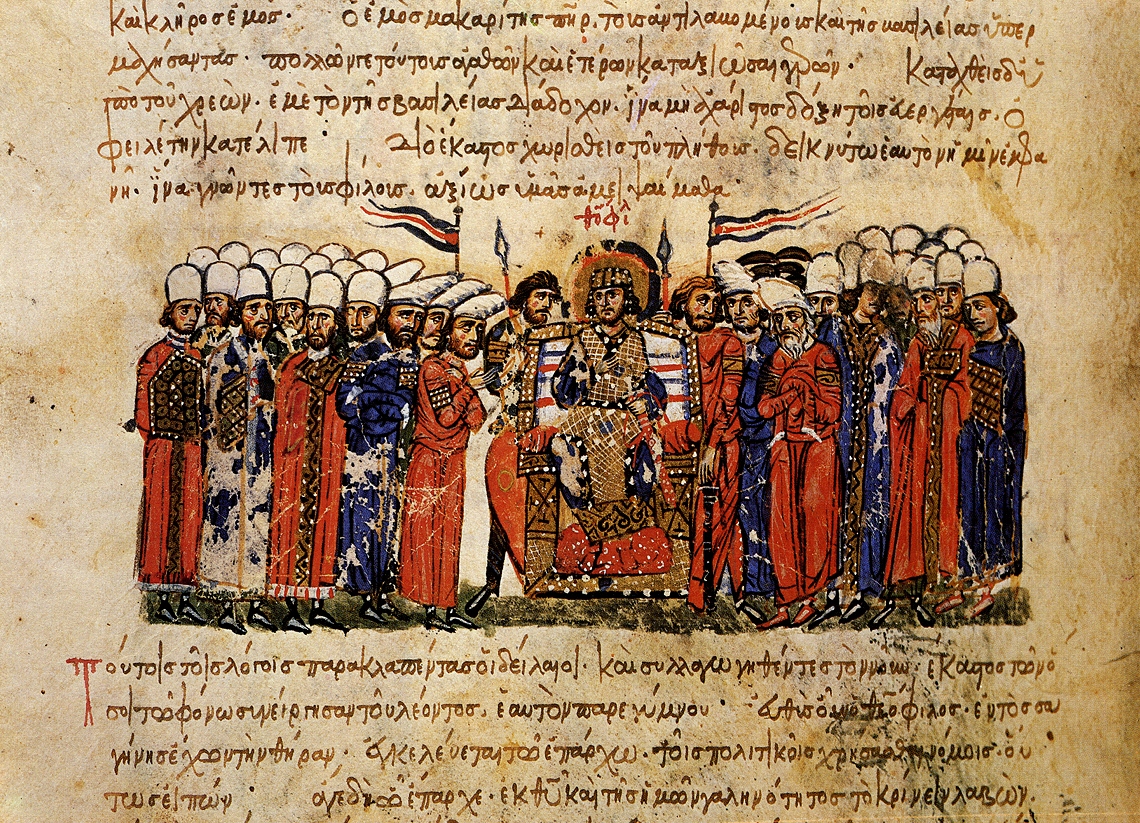
It Was A Wolf Among Coyotes
There were other flame strategies used for centuries prior to Greek fire’s invention. None were as powerful or as dangerous as the so-called “sea fire”.
 Skylitzes Chrinicle, Wikimedia Commons
Skylitzes Chrinicle, Wikimedia Commons

Sign up to our newsletter.
History’s most fascinating stories and darkest secrets, delivered to your inbox daily. Making distraction rewarding since 2017.
The Mystery Of The Creator
The original inventor of Greek fire is unknown. No one is credited with the initial creation of the substance, despite how widespread its use was in the Byzantine Navy. Some claimed its source was far stranger than mere invention.
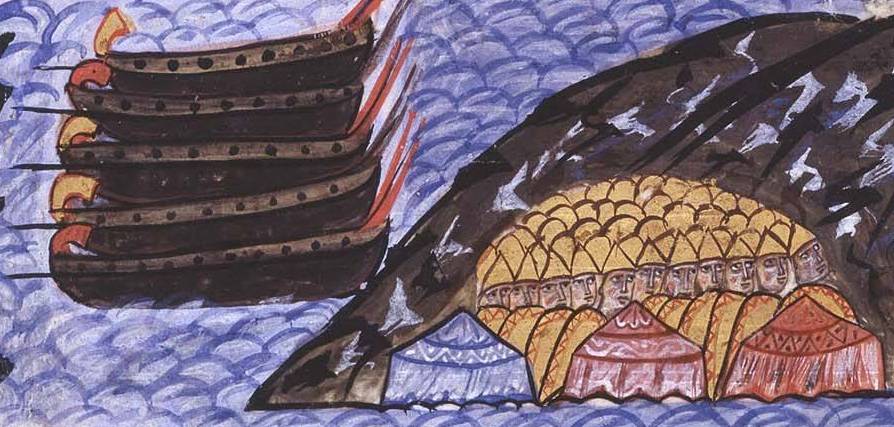 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
A Religious Gift
Emperor Constantine Porphyrogenetos claimed the recipe was “shown and revealed by an angel to the great and holy first Christian emperor Constantine” and the angel bound him “not to prepare this fire but for Christians, and only in the imperial city”.
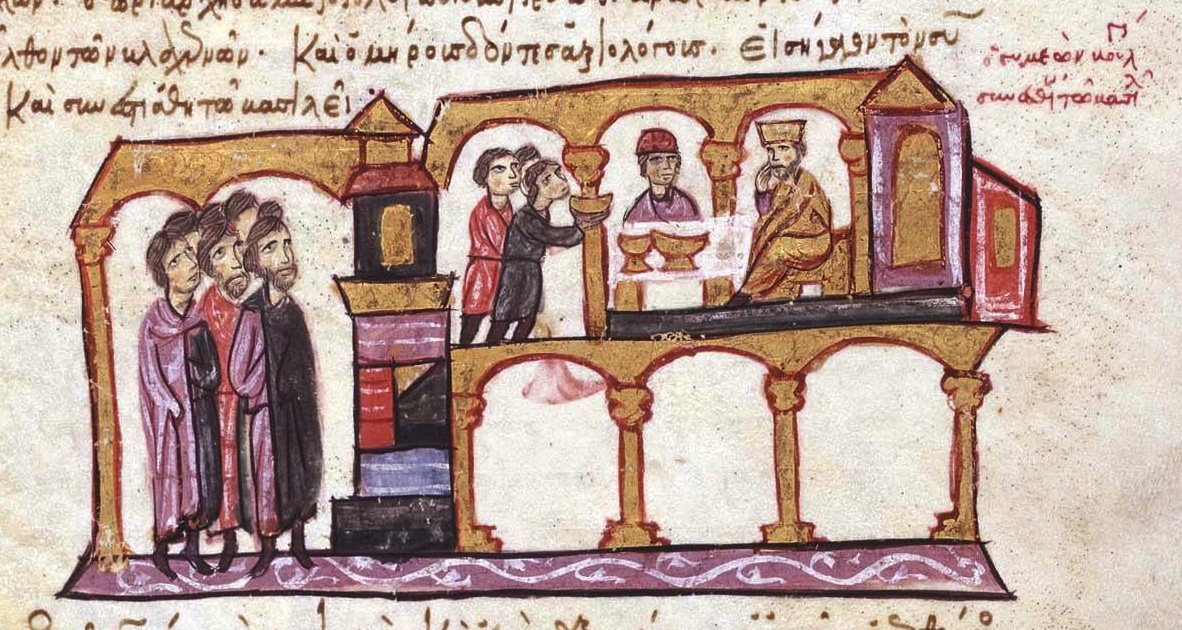 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Room For Improvement
A few years after it was first used, artificer Kallinikos of Heliopolis fled his home and joined the Byzantine Empire. Once there, he improved the recipe for Greek fire, and was partially credited as its creator. What he used in it is still up for debate.
 Gts-tg, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Gts-tg, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
A Change In Fate
Once the recipe was finished, the Byzantine Empire was unstoppable. They were able to use the new Greek fire to their advantage. But this would be to the detriment of all they fought against.
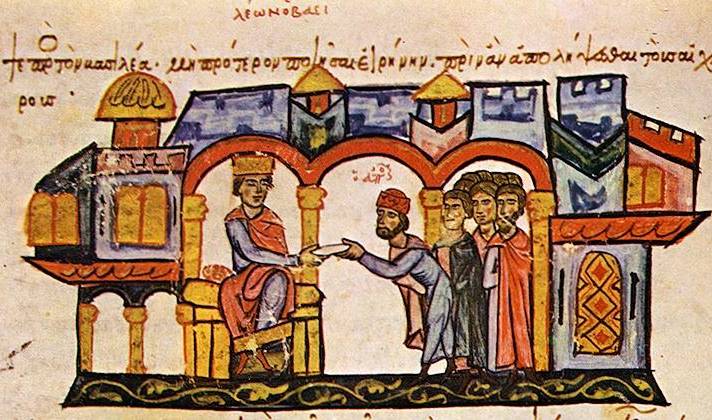 John Skylitzes, Wikimedia Commons
John Skylitzes, Wikimedia Commons
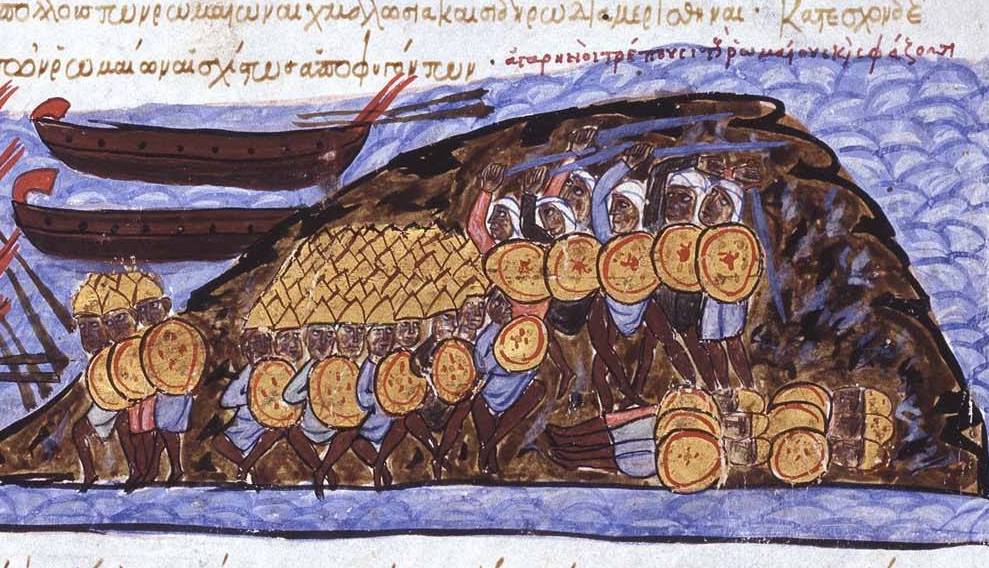
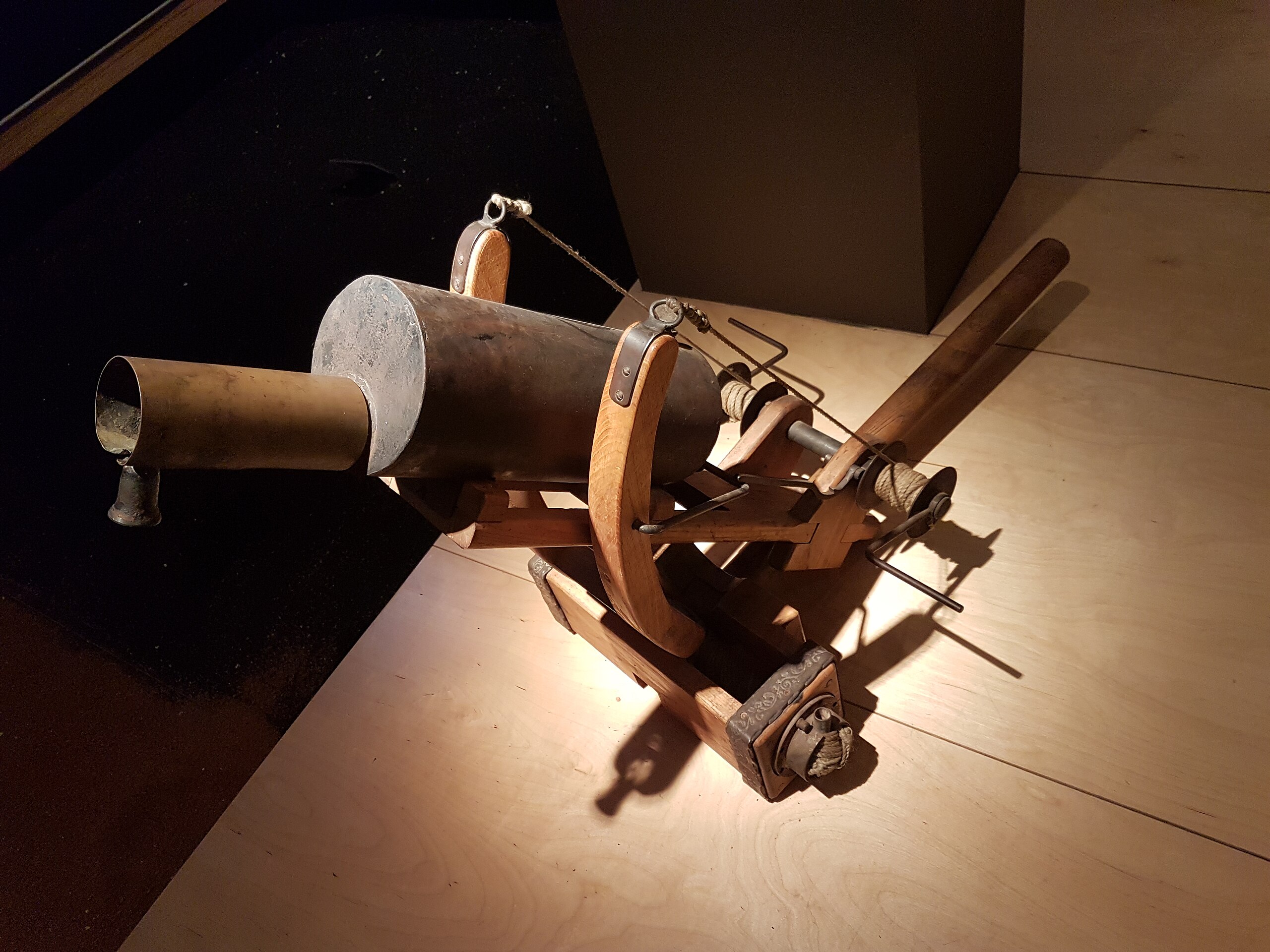
It Was An Explosive Addition To Combat
One of the ways Greek fire was deployed was through grenades. Byzantine sailors would toss them onto enemy ships, where they would ignite and explode, flames roaring across the decks.
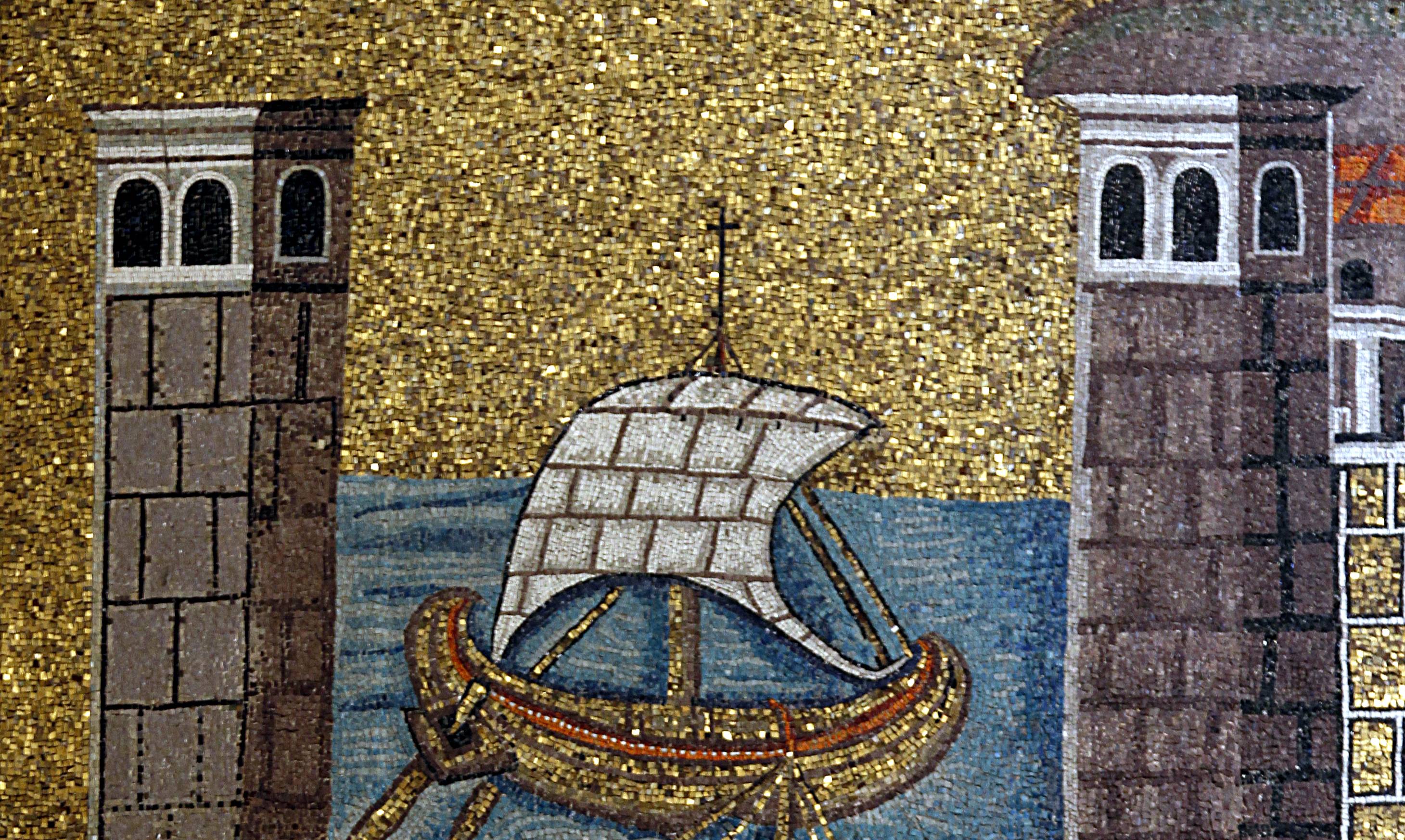 José Luiz Bernardes Ribeiro, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
José Luiz Bernardes Ribeiro, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
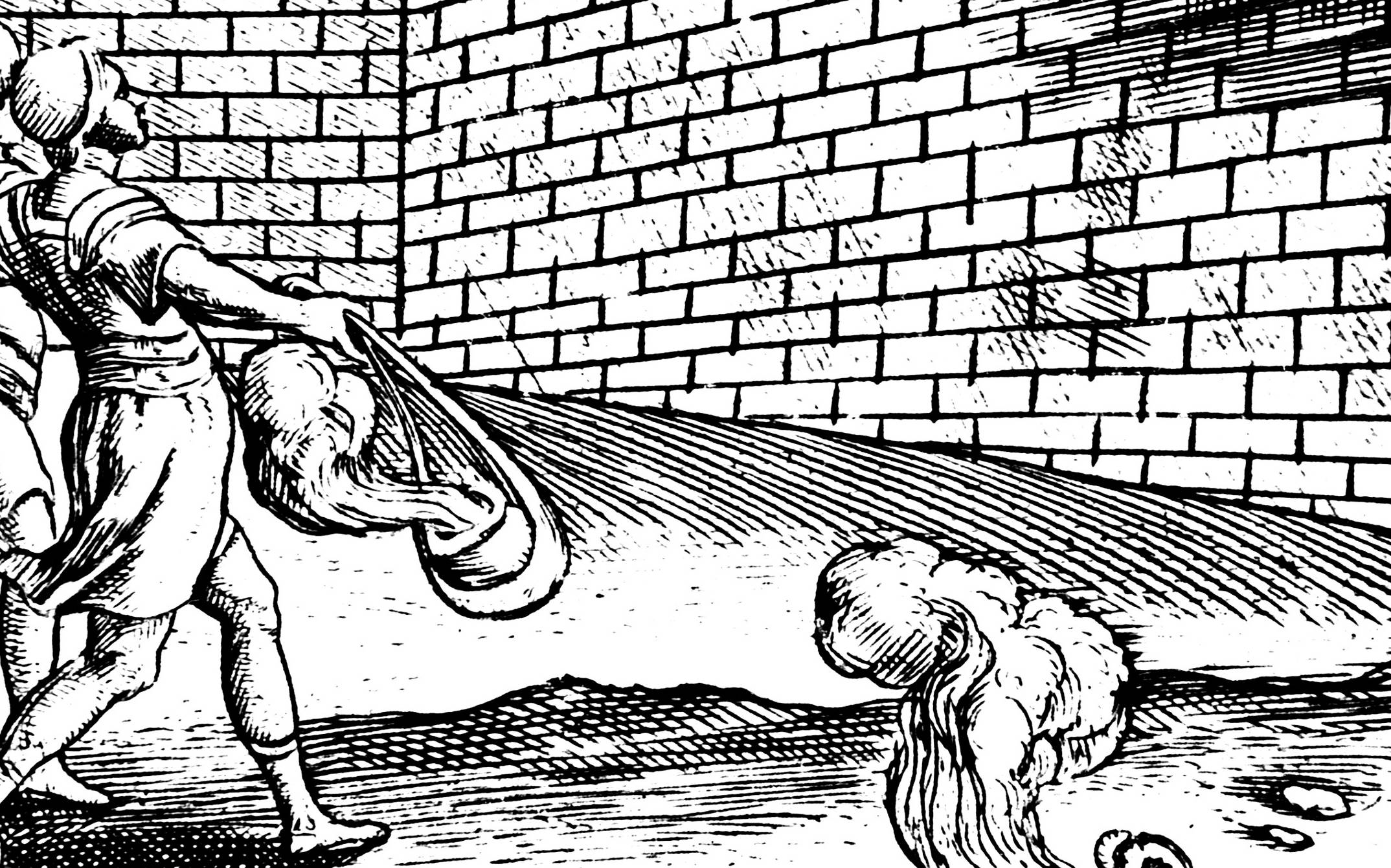
A Literal Fire Hose
Another method of launching the substance toward enemy ships was through long types, called siphons. This relied on shorter-range encounters. Once the enemy ship was further away, the siphon wasn’t as effective. That wasn’t their only method of attack, though.
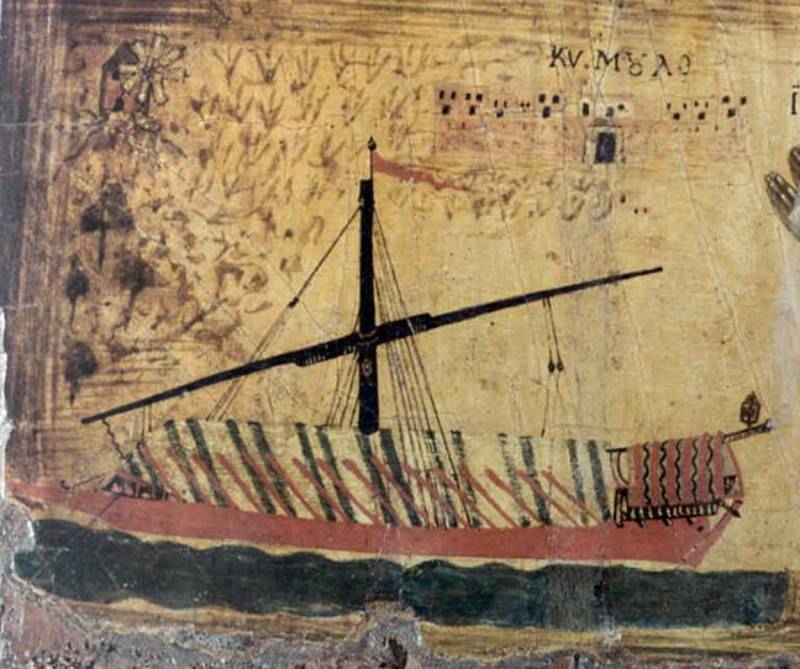 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
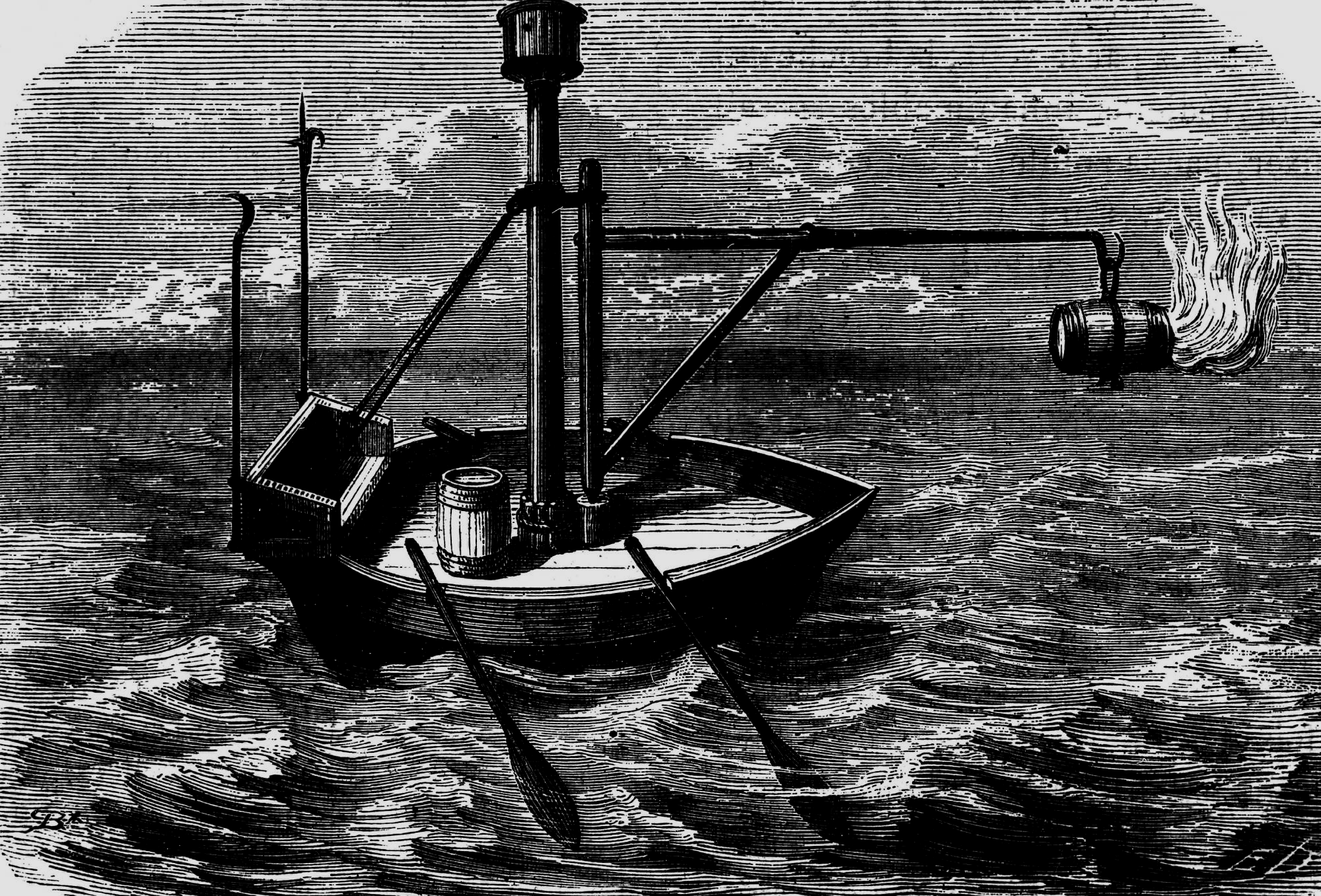
An Unexpected Early Innovation
Greek fire was also launched out of hand-held projection devices. These are dubbed as being early versions of what we know as a flame-thrower. This wouldn’t be the last time Greek fire inspired other inventions.
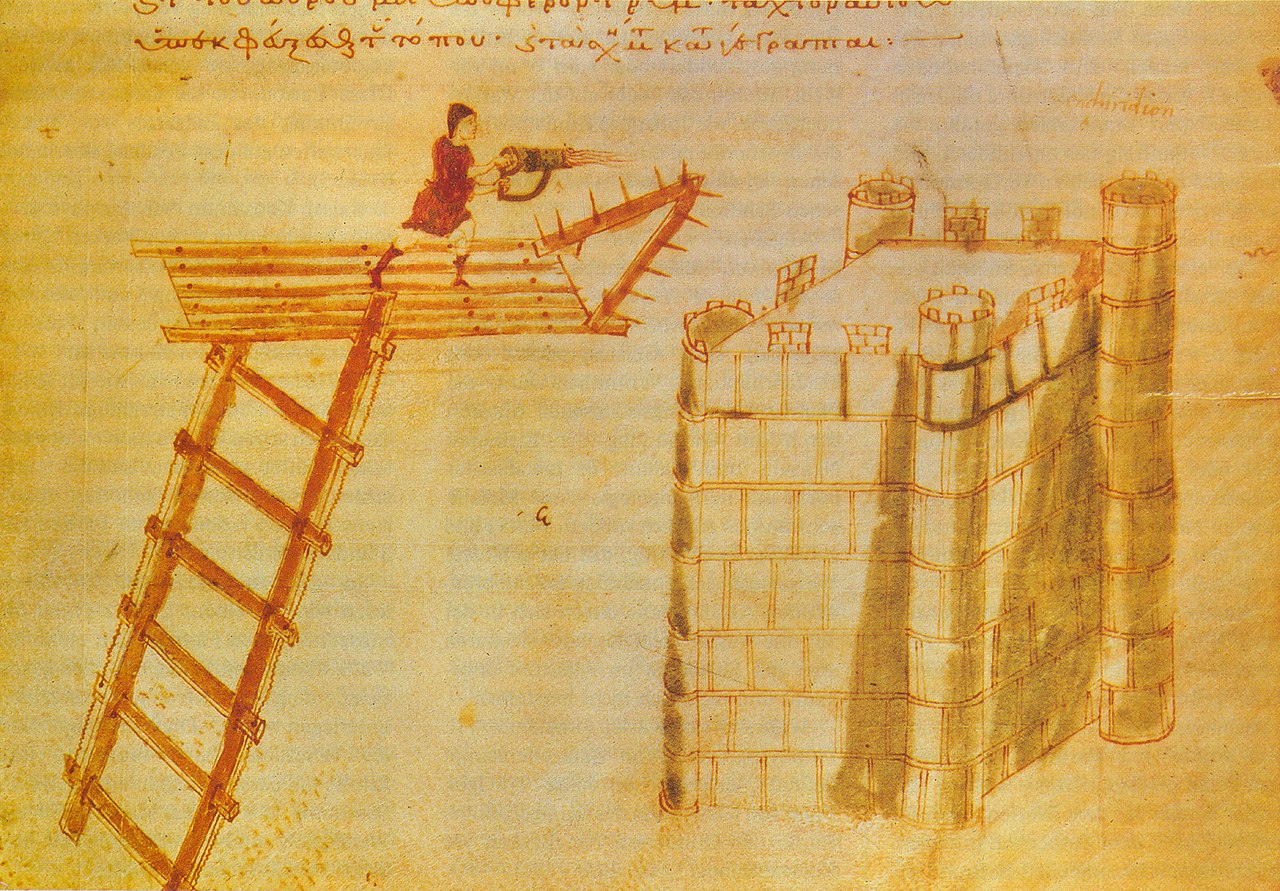 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
The Byzantine Empire Faced Horrible Trials
The Byzantine Empire spent long years in the midst of conflict with empires in the East, especially Sassanid Persia. And the Byzantine Empire was at a disadvantage.
 Carole Raddato, CC BY-SA 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
Carole Raddato, CC BY-SA 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
The Forces To Rome’s East Were A Huge Threat
The Byzantine Empire had a difficult time fighting against the Persian conquest. And they weren’t the only country struggling to escape the attacks from the east. It didn’t look good for the empire, but luckily, an innovation changed that for them.
 Constantine Manasses, Wikimedia Commons
Constantine Manasses, Wikimedia Commons
In Steps Their Greatest Strategy
Greek fire changed the landscape of naval battles. It was highly effective against attacking fleets, and covered vast swathes of ships in flames. But the horrors of Greek fire didn’t stop there.
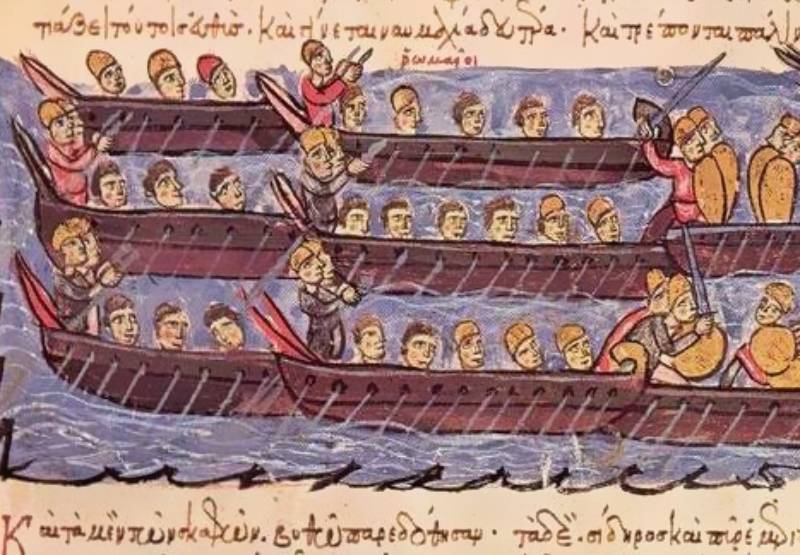 John Skylitzes, Wikimedia Commons
John Skylitzes, Wikimedia Commons
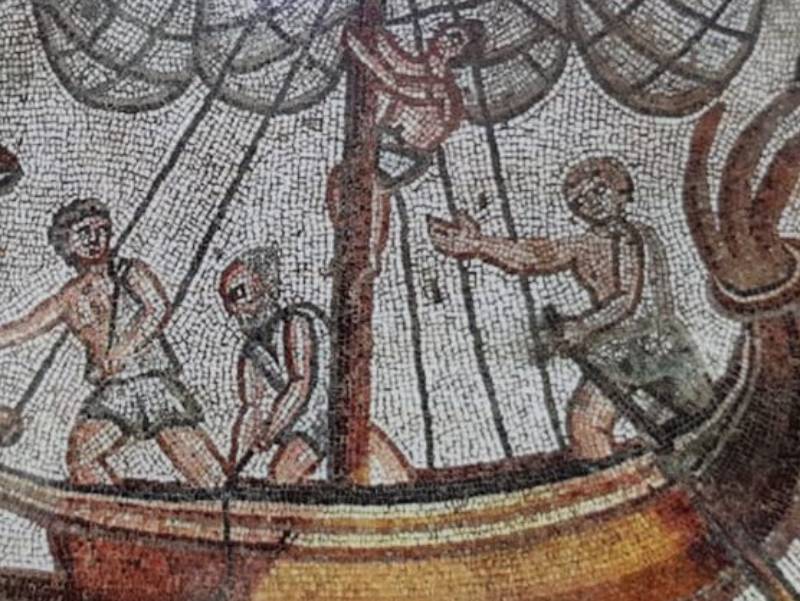
The Recovery Of Byzantine Power
Greek fire enabled the Byzantine Empire to win several battles and expand their empire during the late ninth and early tenth centuries. They were on a roll with this new substance at their disposal.
 Alon Palzor, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Alon Palzor, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
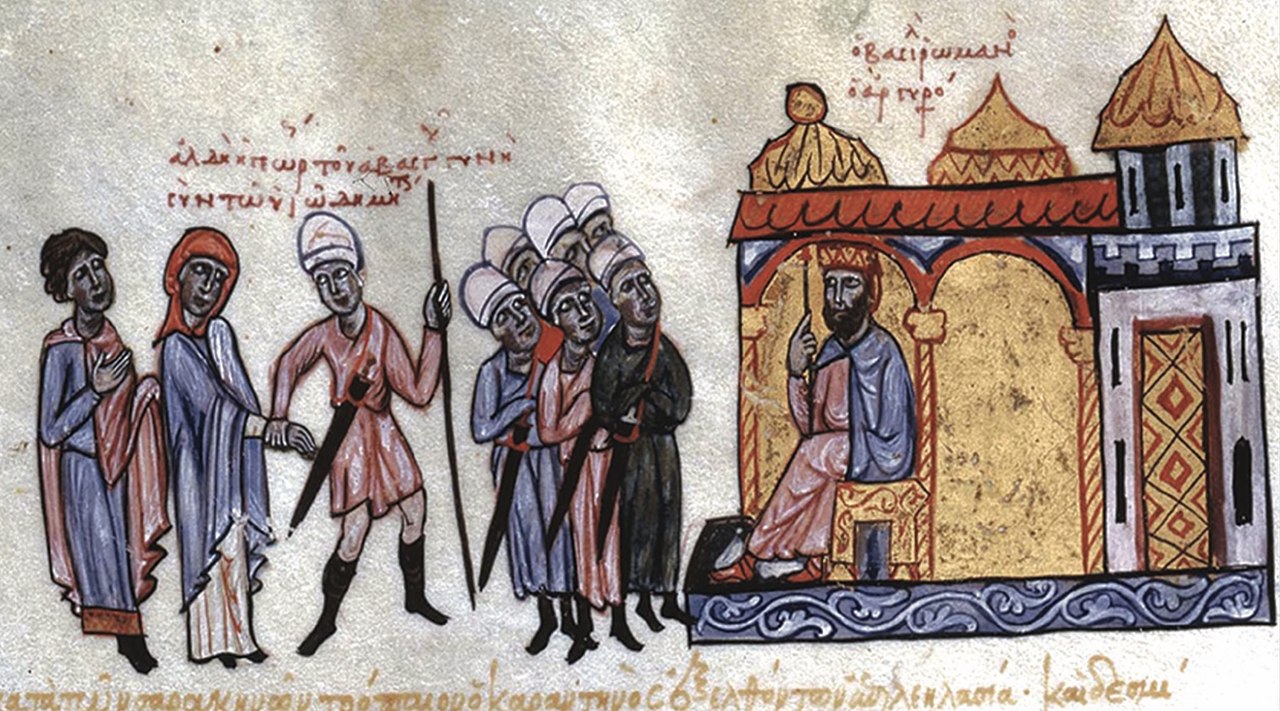
The Flames Turned Inward
The leaders of the Byzantine Empire needed to use Greek fire closer to home. They used this substance to quell several civil conflicts and rebellions throughout the eighth and ninth century.
 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Raiding Forces Felt The Burn
In addition to internal conflicts and forces attacking from the east, the Byzantine Empire also used their Greek fire against northern invaders. Rus’ invaded from the north, in what is now Sweden, and faced down Greek fire.
 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
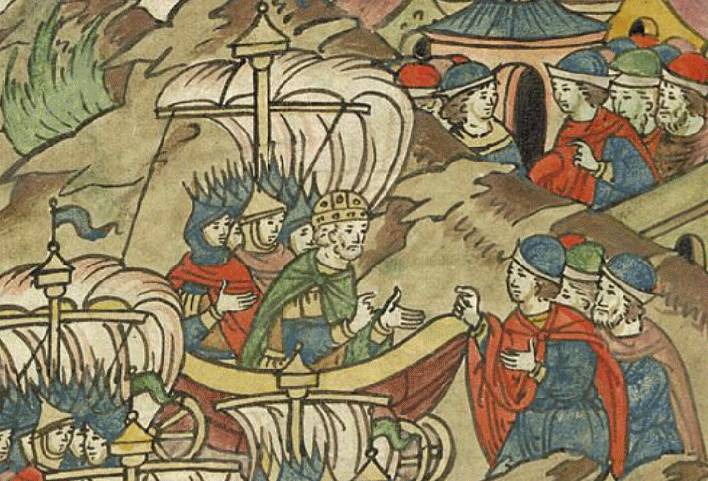
The Devastation Was Immense
The flames of Greek fire were devastating. It cannot be emphasized enough that the substance would wreak havoc on fleets of ships, and could single-handedly devastate attacking forces. Which is why this next fact holds a lot of weight.
 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
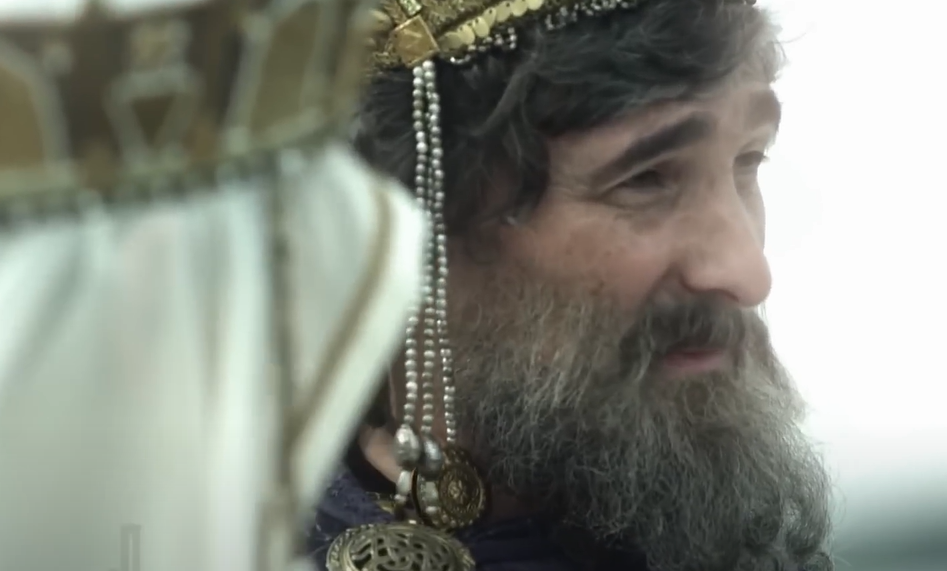
The Divine Consequences
The recipe was held in such high regard, and was such an intense secret that Emperor Constantine made a wild claim. He said that someone who intended to reveal the secret was struck down by a “flame from heaven”.
 Star Media, The Rurik Dynasty (2019)
Star Media, The Rurik Dynasty (2019)
A Coveted Secret
One of the empire’s enemies, the Bulgars, tried to replicate the recipe. They captured ships that carried the substance, but despite the amount of it they obtained, they weren’t able to discern the recipe.
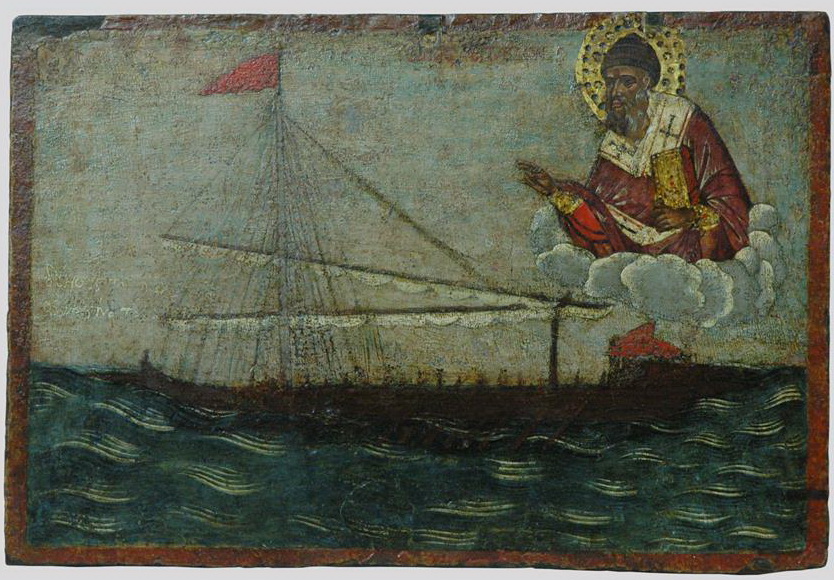 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
There Were Many Attempts At Recreation
The Bulgars weren’t the only enemies to try and replicate the substance. And while some of them got close to replicating it, none were able to create something that had the same explosive power as Greek fire.
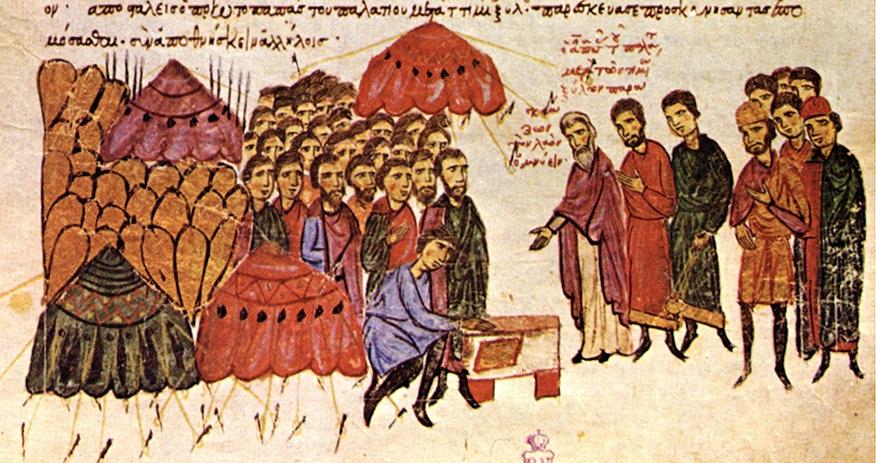 John Skylitzes, Wikimedia Commons
John Skylitzes, Wikimedia Commons
Disappearing As Quickly As It Appeared
In a shocking turn, Greek fire wasn’t used during what was a pivotal moment for the imperial capital, Constantinople. It was distinctly absent during the 1203 siege of Constantinople when they were assailed by the Fourth Crusade. The reason why can’t be confirmed, but there are a couple of theories.
The Fractures In The Empire
One of the theories why it wasn’t present is that the empire had lost some of its physical power. There was a disarmament in the two decades leading up to the siege, and this could have affected their ability to use the substance.
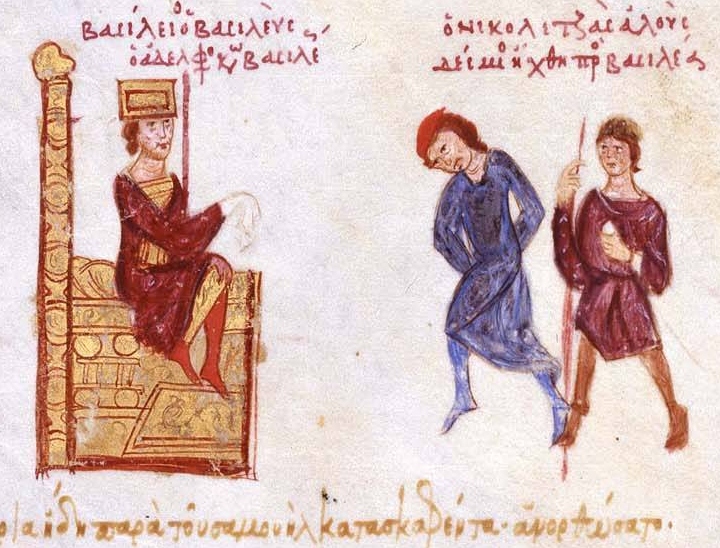 John Skylitzes, Wikimedia Commons
John Skylitzes, Wikimedia Commons
A Loss Of Territory
It could have also been due to losing access to ingredients as other empires took back territory, or the Byzantine Empire was forced out of their land. But the next theory fits with what we know today.
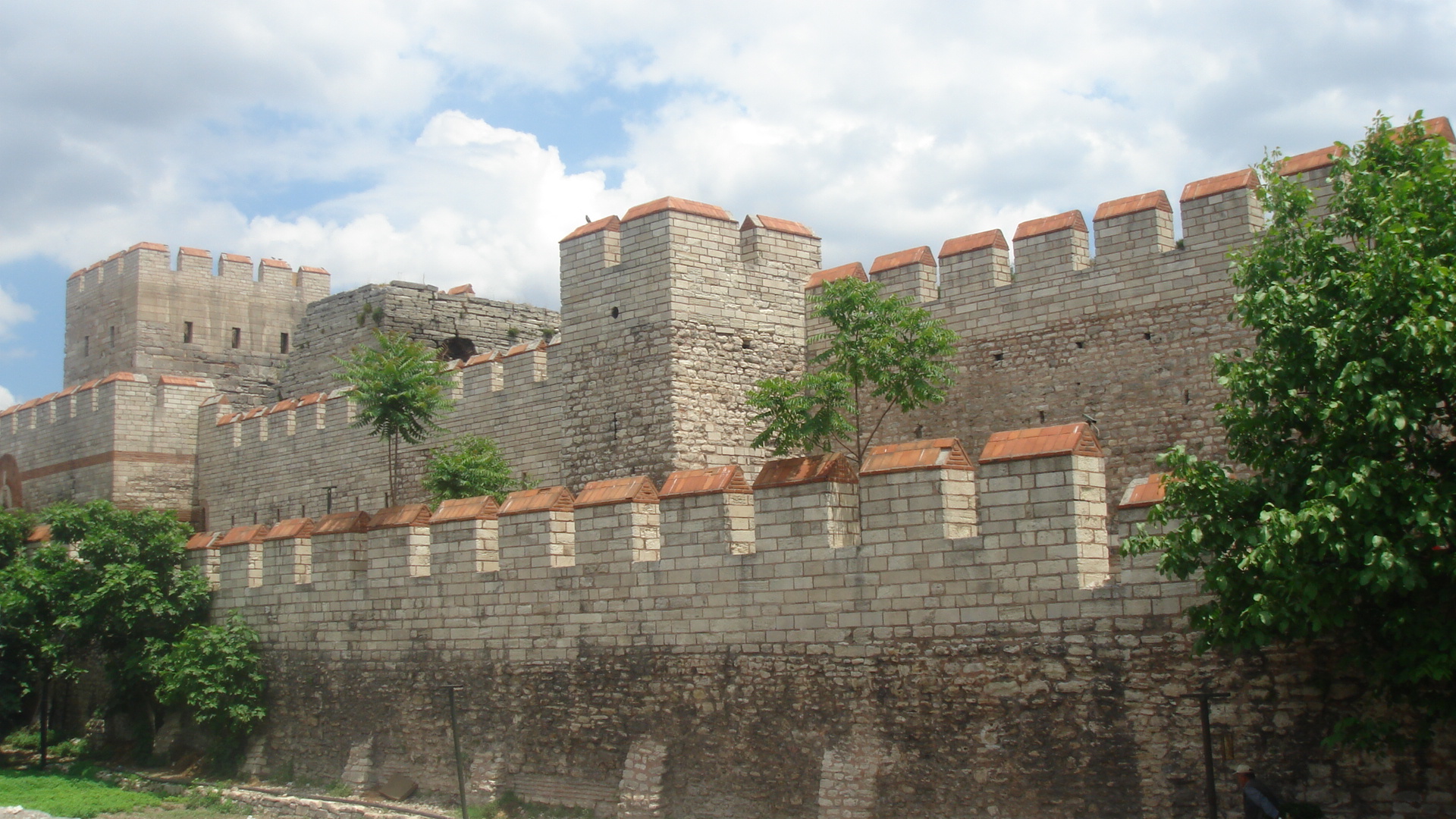 Bigdaddy1204, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Bigdaddy1204, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
What Was Always Lost
It was even suspected that by the time the Fourth Crusade arrived, something had gone wrong with the recipe. It had already been lost, after decades and centuries of being in use. We’ll never know what was really in Greek fire, but historians have a couple of guesses.
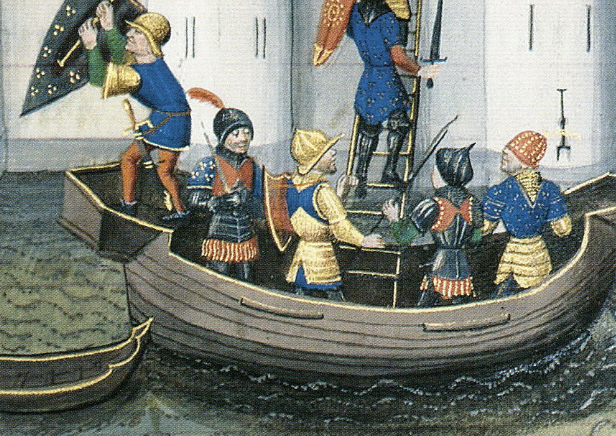 David Aubert (1449-79), Wikimedia Commons
David Aubert (1449-79), Wikimedia Commons
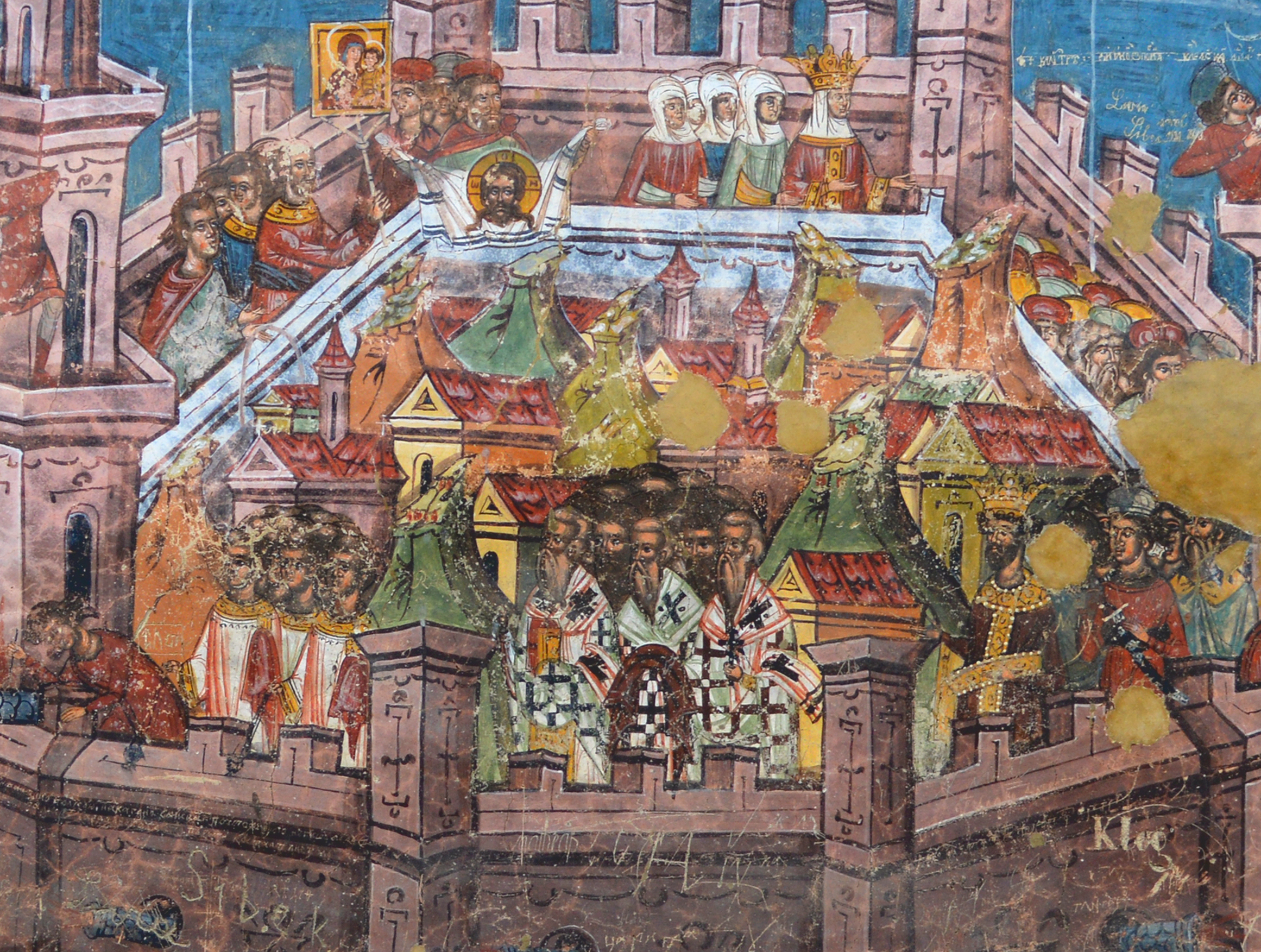
The Descriptions Can’t Begin To Capture Greek Fire
During the Seventh Crusade, the Lord of Joinville described it as “a tail of fire” and that it sounded like “thunder of heaven” in his memoir of the events. But that isn’t the only way he described it.
 Mahiet (illustrator), Wikimedia Commons
Mahiet (illustrator), Wikimedia Commons
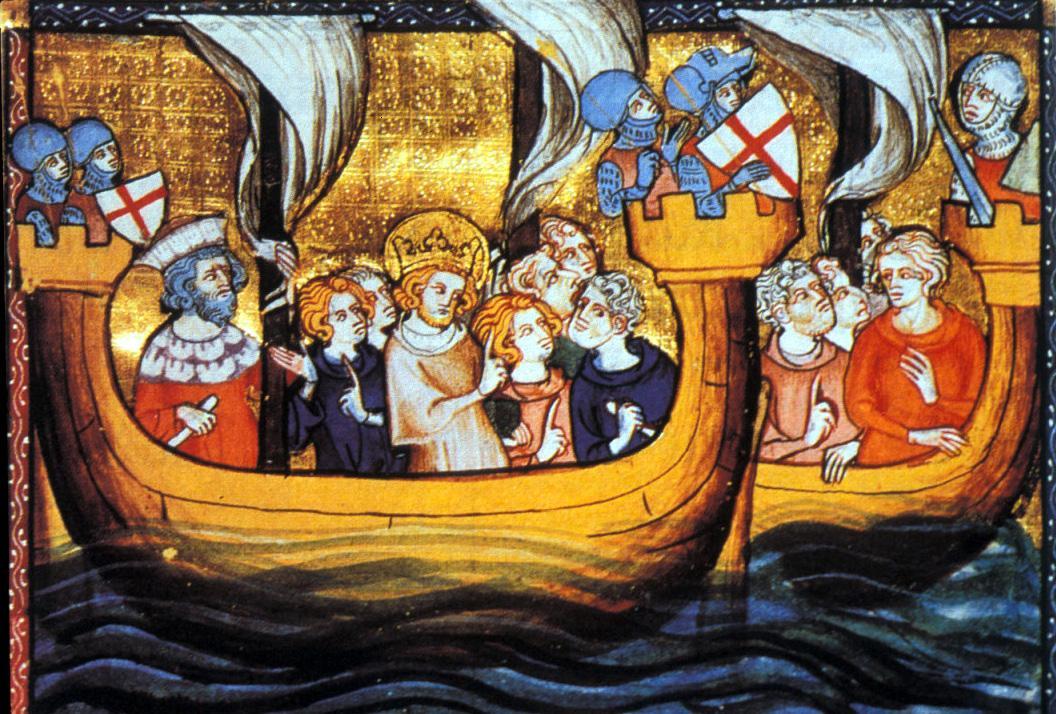
Fantasy Becomes Fact
The Lord of Joinville brought a fantastical description to how he talked about Greek fire. He painted it as “a dragon flying through the air”, with immense, air-shaking flames. At a time without large-scale explosives, this would have been a terrifying sight.
 Guillaume de Saint-Pathus, Wikimedia Commons
Guillaume de Saint-Pathus, Wikimedia Commons
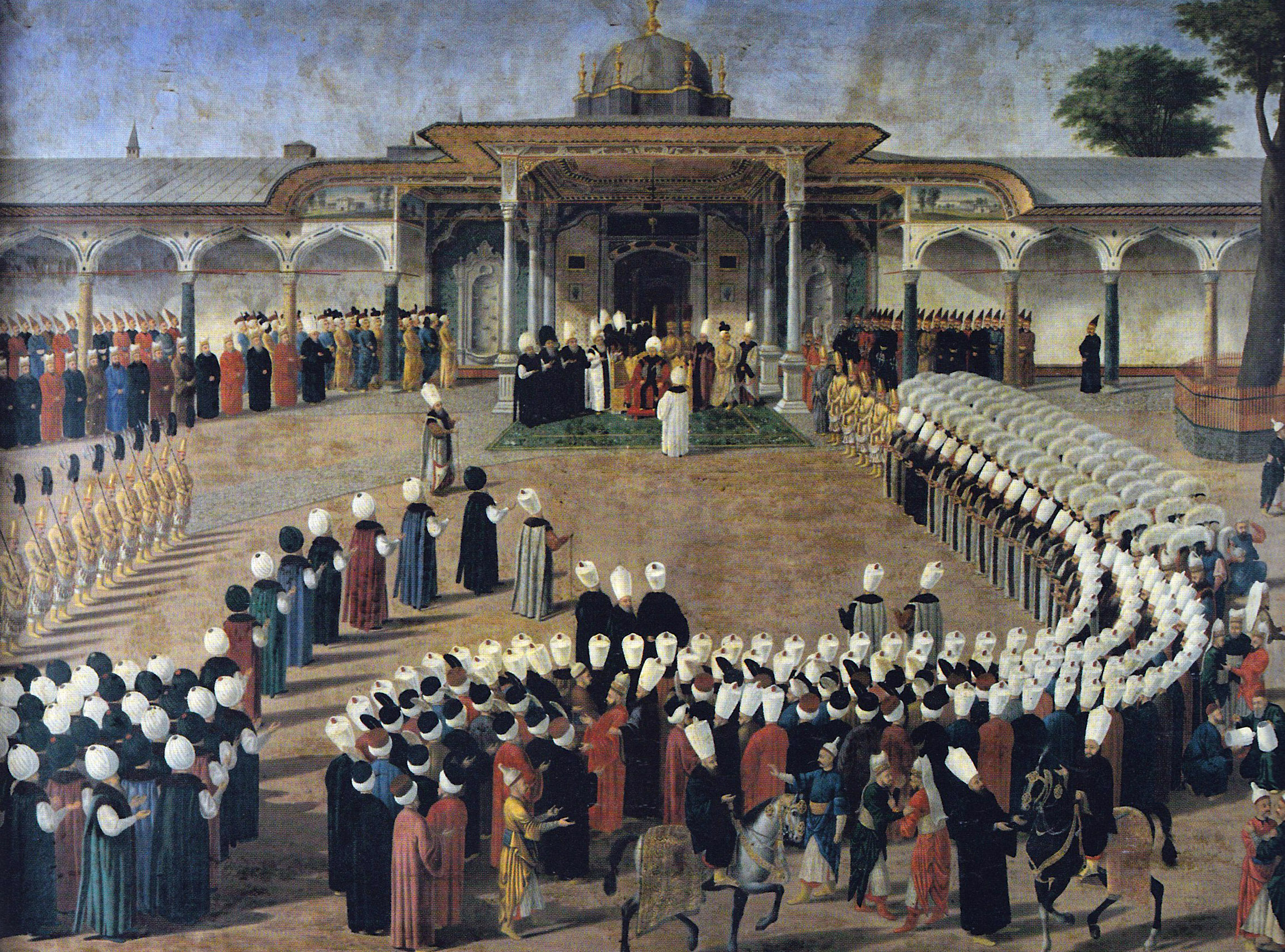
Modern Replication Is Attempted
During the height of the Ottoman Empire in the 19th century, an Armenian man named Kavafian told the Ottoman government that he had rediscovered the recipe. This would have changed the face of conflicts all over the Earth.
 Konstantin Kapıdağlı, Wikimedia Commons
Konstantin Kapıdağlı, Wikimedia Commons
Kavafian Had His Own Requirements
He wouldn’t hand the ingredients over without getting something in return. He told them he wanted to be placed in command of the Greek fire’s use during naval conflicts. But the Ottoman Empire’s response was wildly unexpected.
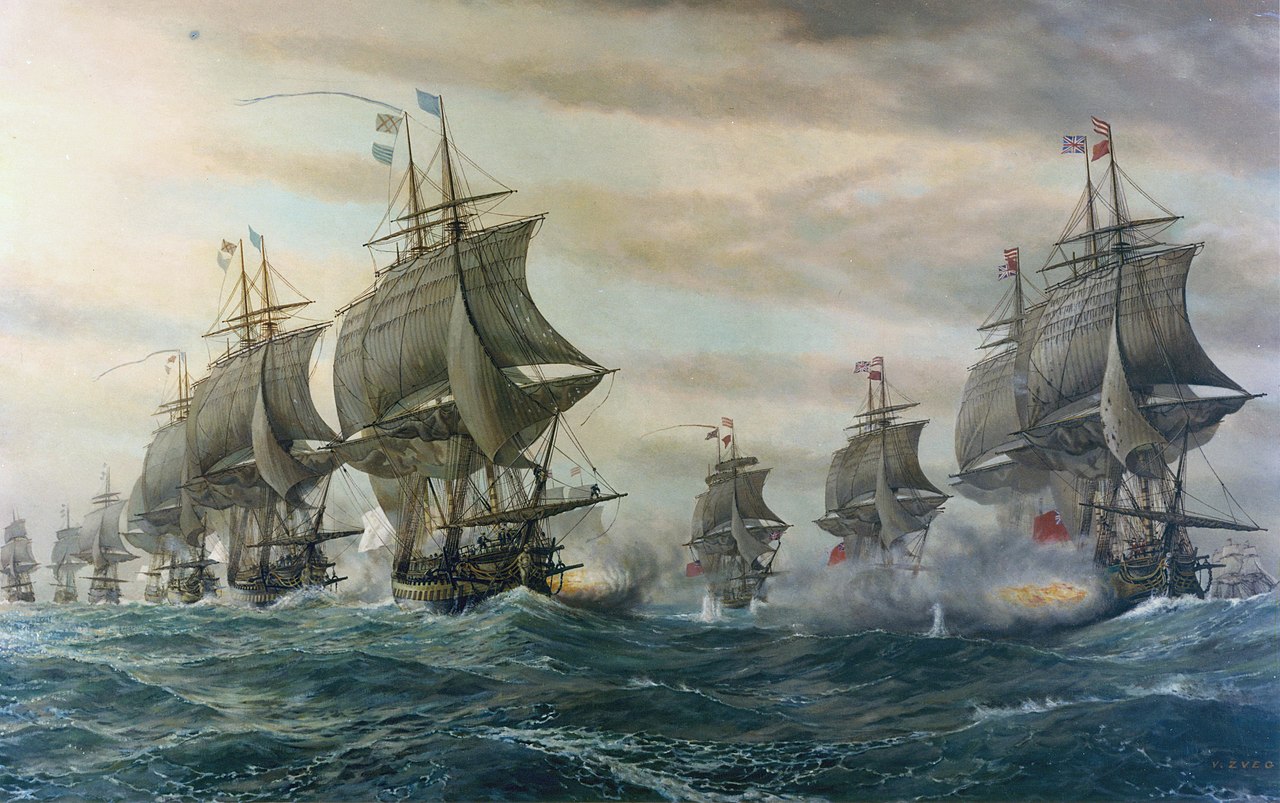 Hampton Roads Naval Museum, Wikimedia Commons
Hampton Roads Naval Museum, Wikimedia Commons
Kavafian’s Shocking End
Even though the imperial forces hadn’t acquired Kavafian’s secrets, they had to act before someone else was offered the recipe. Kavafian was poisoned, and whether or not he actually rediscovered the recipe was lost.
 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
The Downfall Of Secrecy
There was one major consequence to keeping the recipe in so few hands. As those who knew the ingredients were lost to time, so were the ingredients, and so was the recipe for Greek fire. It has been a source of speculation ever since.
Greek Fire Had Lots Of Requirements
There were a lot of different components that went into carrying and launching Greek fire. It had special requirements needed in order to be effective.
It Needed These Special Accommodations
Ships that carried Greek fire had special launching mechanisms attached to the prows. These mechanisms needed specially trained operators to launch—they wouldn’t want untrained sailors accidentally setting their ship aflame.
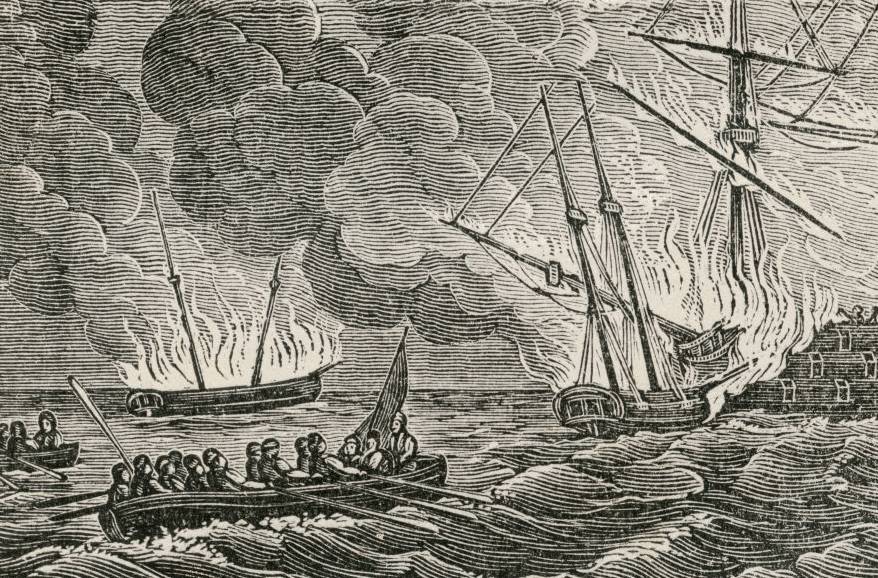 Universal History Archive, Getty Images
Universal History Archive, Getty Images
The Recipe Is Highly Speculated
Many theories have come out about the recipe. With the origins being so mysterious, all modern historians have to go on is what was explosive at the time. This consisted of saltpeter (an early form of gunpowder), sulfur, quicklime, or calcium phosphides (which released phosphine when in contact with water, which spontaneously ignites).
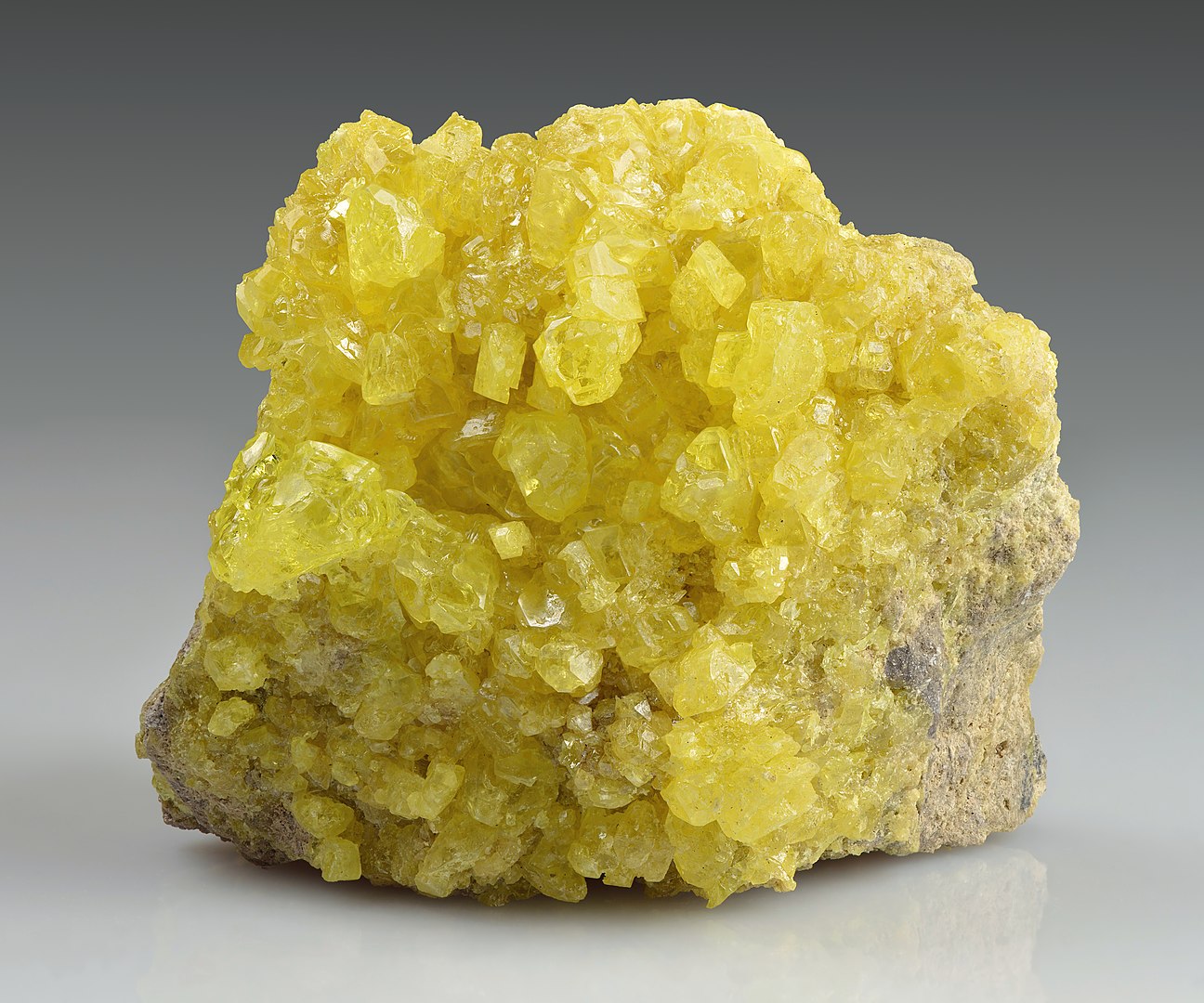 Ivar Leidus, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Ivar Leidus, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
An Italian Recipe Might Hold The Answer
A recipe recorded in the 16th century might detail something close to Greek fire. The ingredients consist of willow tree charcoal, saltpeter, alcohol, sulfur, incense, tar, wool, and camphor. According to the recipe, it was both “beautiful” and able to “burn under water”.
 Tom Murphy VII, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Tom Murphy VII, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Modern Scholars Think Differently
After many debates about the ingredients, it is generally assumed that Greek fire must have been petroleum-based. Some historians think there were resins added, which was comparable to modern napalm.