“History isn’t just the story of bad people doing bad things. It’s quite as much a story of people trying to do good things. But somehow, something goes wrong.” —C.S. Lewis
There are certain events which take place in humanity’s history, which shape it and alter it in a most profound way. Discoveries in science, the unveiling of new technologies, immense tragedies, loss of life, and changes in nature all have an impact on human life. Here are some facts about a few of those path-altering events.
Events That Changed Humanity Facts
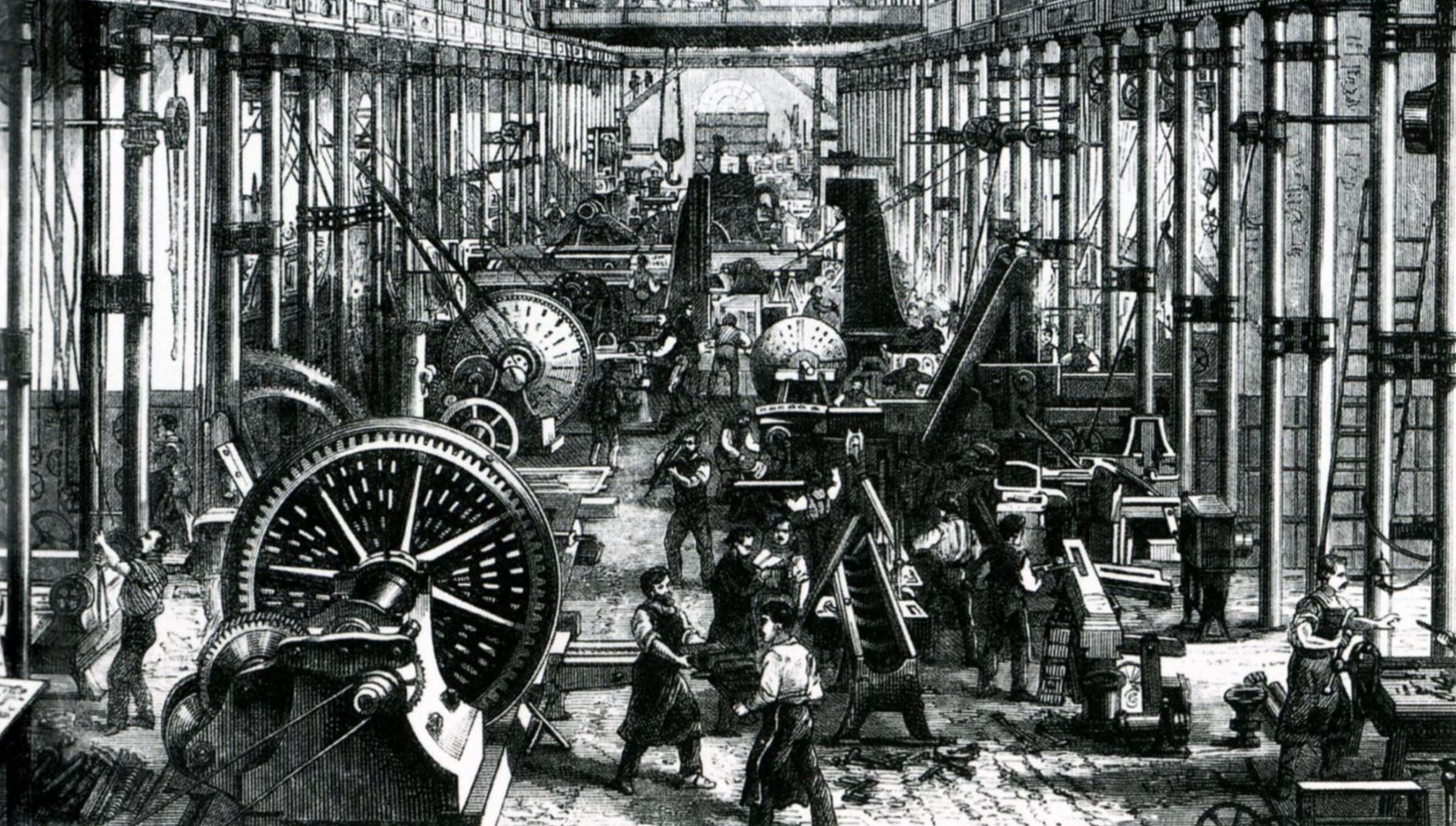
24. The Industrial Revolution
Around 1760, England began to undergo an Industrial Revolution, and other countries soon followed in their footsteps. People were looking to move away from an agricultural-based existence and feudalism as a system of government. This period saw the restructuring of how land, economic power, and labor were distributed. A middle class was created which led to the desire for more goods and services including public transportation and access to healthcare. This turning point essentially led to the creation of modern society.
 Unknown author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown author, Wikimedia Commons
23. The Creation of the Internet
The Creation of the Internet revolutionized how many human beings communicate ideas, gather information, and connect to one another. The ‘world wide web’ first became publicly available on August 6, 1991 and today more than 2.5 billion people use the internet daily. The internet has changed how people buy and sell, work and learn, and even form relationships.
22. The Renaissance
This refers to the period after Europe plunged into the dark ages. During this time, more books were being printed, and education was no longer solely controlled by the Church. Europe developed, enriched its arts and architecture, and sought to embrace logic and curiosity. Thanks to this period in history, the world enjoys the artworks and innovations of icons like Michelangelo and DaVinci.
21. Progress In Medicine
For most of history, humans have had little recourse when it came to illness. Only in recent years have we been able to fight infections, viruses, and diseases. Modern medicine actually has grizzly origins. Early doctors would hire people to dig up fresh graves so they could do experiments and conduct research on real human bodies.
Also, many illegal and immoral experiments performed by doctors in times of war have produced medical research that has gone on to save thousands.
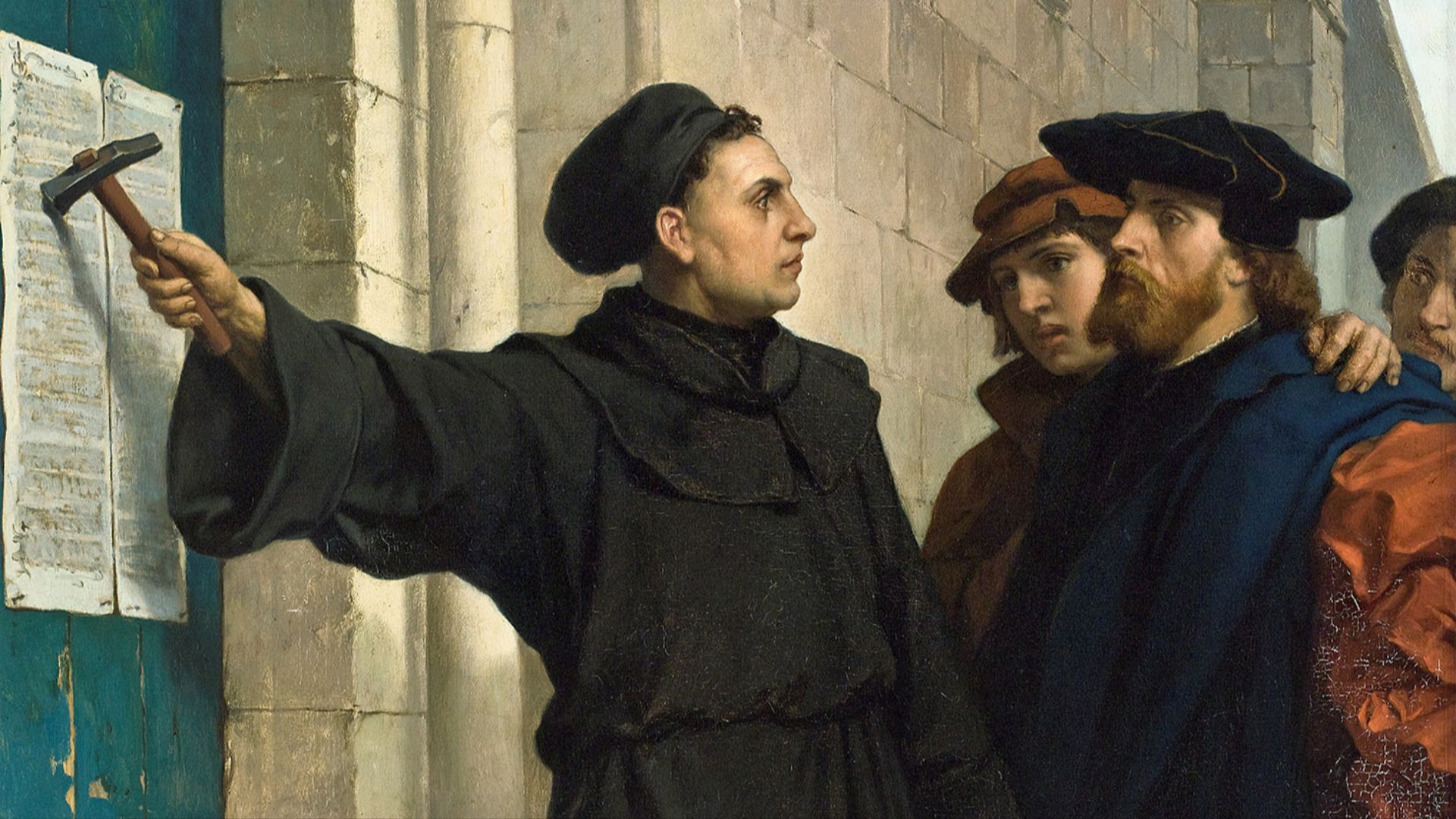
20. The Reformation
In the 16th century, literacy was on the rise and people took an interest in reading books that questioned many popular beliefs of the day. Thanks to Martin Luther’s 95 theses in 1517, which was an exercise in questioning the Roman Catholic Church’s authority and practices, a movement was started. This led to the formation of the Protestants, which in turn caused Europeans to be more skeptical of authority figures and to question traditions.
 Ferdinand Pauwels, Wikimedia Commons
Ferdinand Pauwels, Wikimedia Commons
19. The Black Plague
The bubonic plague, more commonly known as the Black Death, claimed an estimate of over 75 million lives. It arrived on the shores of Europe on October 1347 through rats aboard ships that had sailed through the Black Sea. The horrifically contagious disease had already devastated Egypt, China, India, Persia, and Syria, before eventually consuming Europe. Thanks to the horrors of the plague, better hygiene practices and a push for medical advancements followed.
18. Gutenberg Printing Press
Considered by some to be the most important invention ever, the printing press was invented by Johannes Gutenberg in the mid-15th century. Books of the time were hand made and expensive. Monks and academics were in charge of book creation, so most reading material was typically religious texts or official documents. The printing press made literature, political pamphlets, and other information readily available and affordable for the masses.
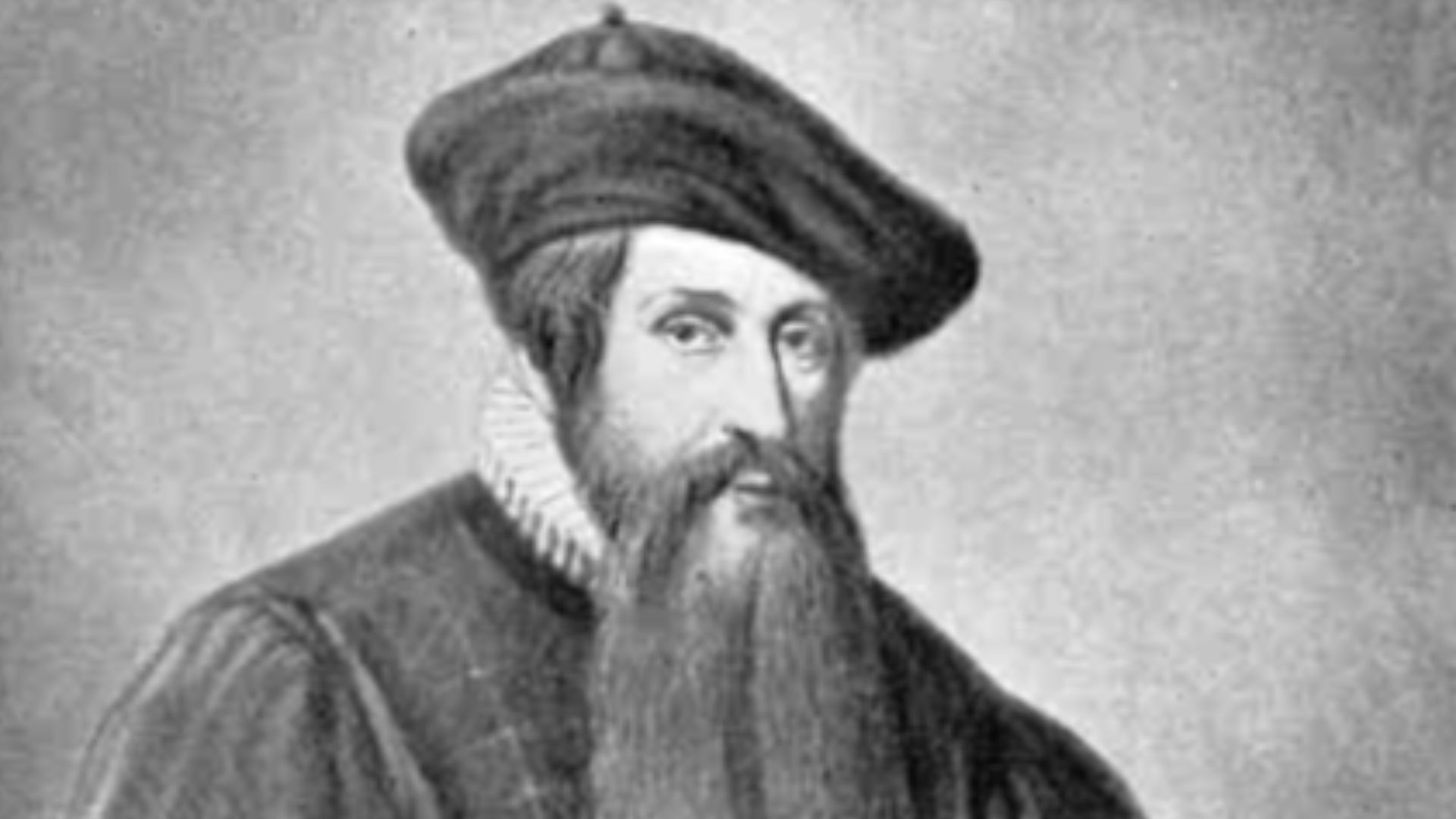 Unknown author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown author, Wikimedia Commons
17. Colonialism
Nations have always sought to expand their borders to access new resources, and display military dominance. European powers raced to control various nations and people in order to extract resources, protect against invasions, and amass wealth. Colonialism largely shaped the political climate of the world we live in today.
16. The Atomic Bomb
During WW2, the first atom bomb (labeled ‘Little Boy’) was dropped on Hiroshima, Japan on August 6, 1945. Never before had the world witnessed the immense power and destruction that weaponized atomic energy could unleash. Many people perished as a result of the bomb immediately, but many people also lost their lives from the bomb’s radioactive after-effects. The atom bomb created a new threat - world domination.
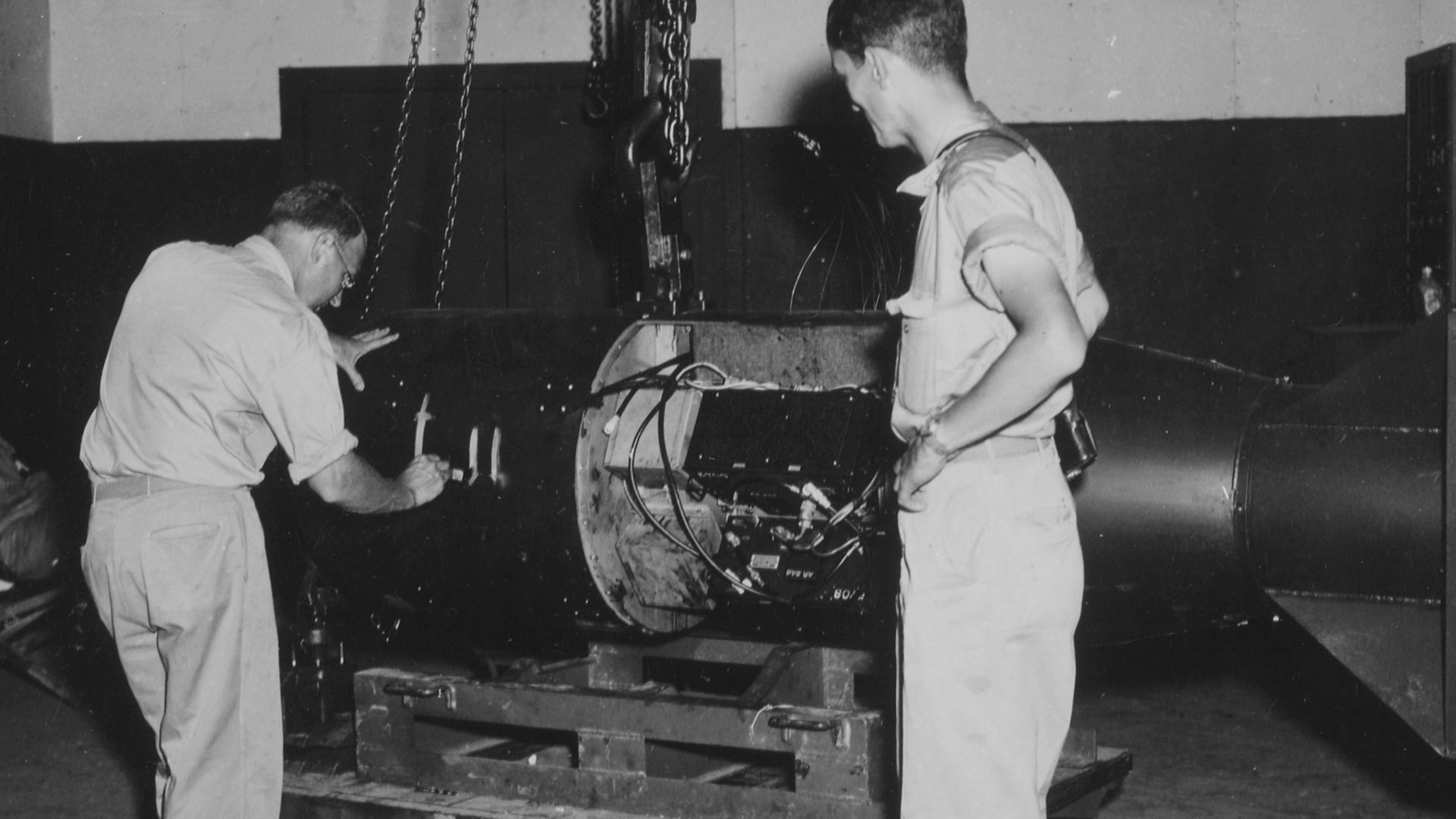 Panoptik~commonswiki, Wikimedia Commons
Panoptik~commonswiki, Wikimedia Commons

History's most fascinating stories and darkest secrets, delivered to your inbox daily.
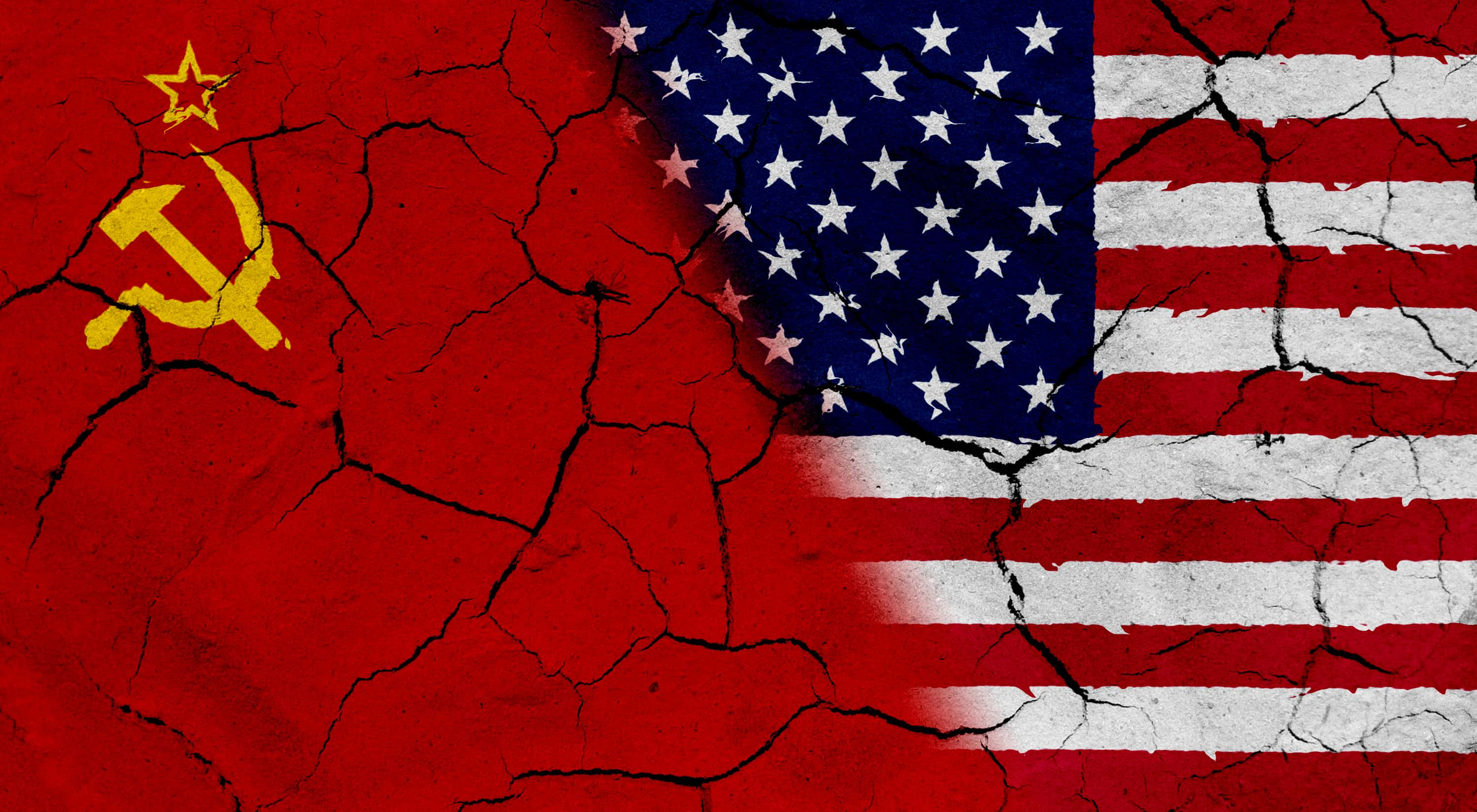
15. The Cold War
During WWII, the Soviet Union and the United states fought together as allies against Axis powers. After the war, the relationship between the nations became tense. The allied powers couldn’t agree on political policy and the US eventually started a ‘containment plan’ for communism. This laid the foundation for what would become the Cold War, resulting in an arms race between the USSR and the USA. Each side created a nuclear arsenal strong enough to destroy the world. The Berlin Wall was famously constructed which literally divided families. The relationship between the US and Russia is still delicate to this day.
14. WWI
The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand was the event that sparked the first World War. This war was a turning point for humanity, as it was the first industrial, modernized war that used chemical weapons, machine guns, and tanks. Approximately 11 million military personnel lost their lives in this time. WWI led to the Austrian monarchy losing power and the founding of the League of Nations.
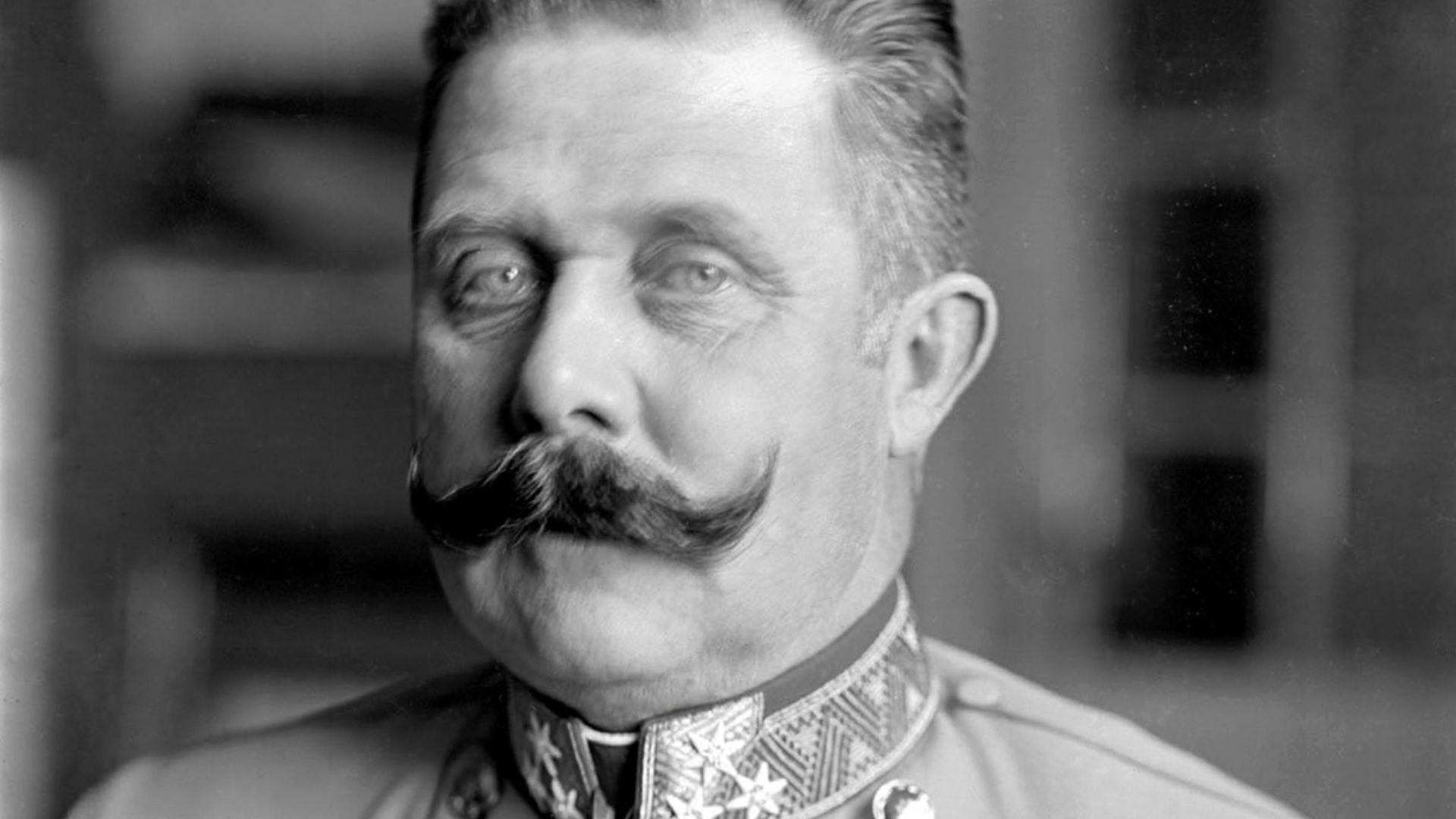 Ferdinand Schmutzer, Wikimedia Commons
Ferdinand Schmutzer, Wikimedia Commons
13. WWII
Germany, unhappy with the terms of the Treaty of Versailles which ended WWI, slowly amassed a powerful mechanized military. Hitler aimed to take over Europe and ultimately the world. The threat of humanity’s ultimate demise arose, with the creation and weaponization of atomic energy. In the end, the United Nations was created which lead to much-needed diplomacy and a place for nations to resolve their disputes.
 Helen Johns Kirtland (1890-1979) and Lucian Swift Kirtland (died 1965), Wikimedia Commons
Helen Johns Kirtland (1890-1979) and Lucian Swift Kirtland (died 1965), Wikimedia Commons
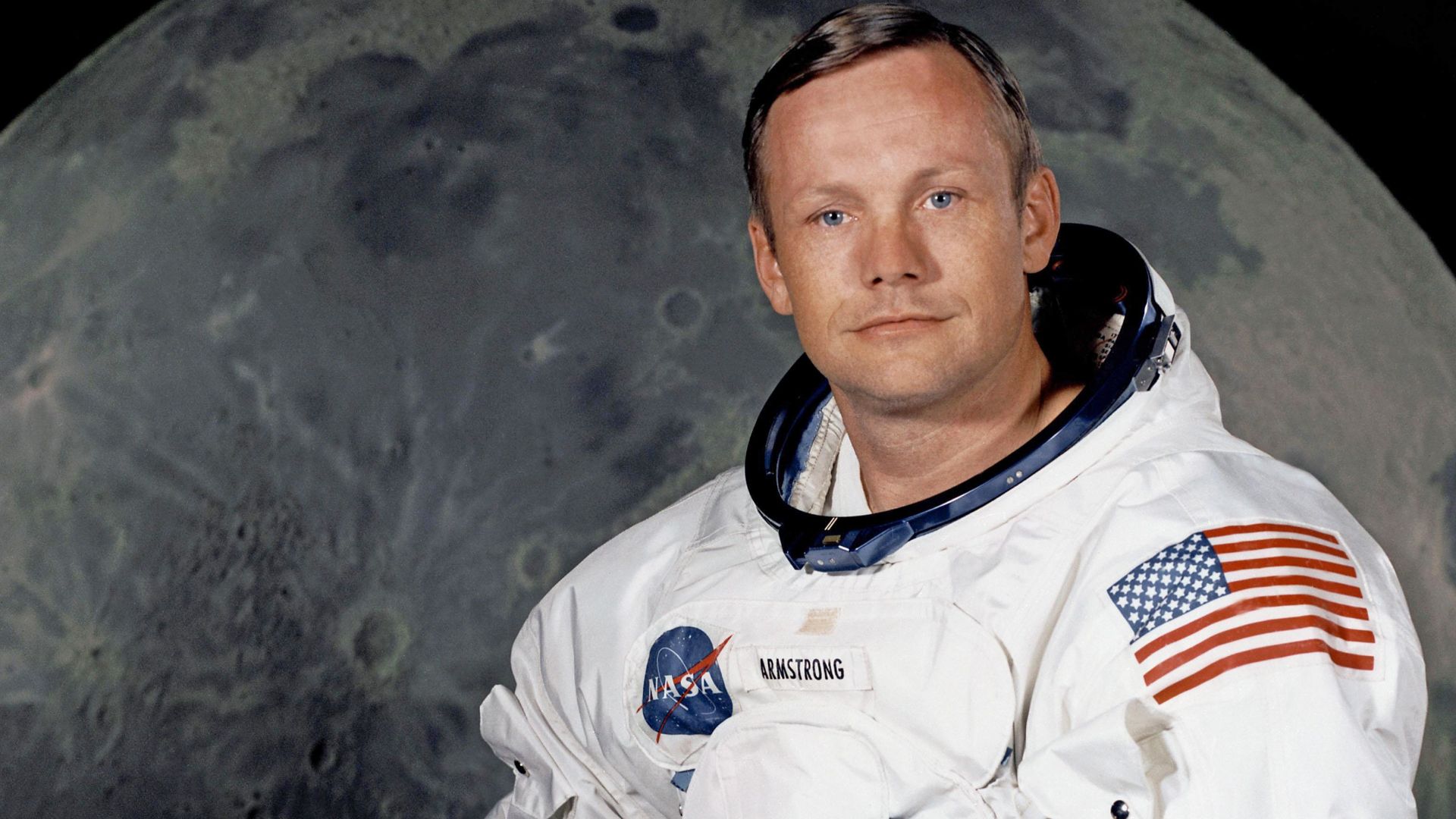
12. Man on the Moon
After mankind discovered that they could survive flight into space for extended periods of time, it was only a matter of time before humans would venture onto the moon. On July 21, 1969, Neil Armstrong made one small step for a man as he walked on the moon. Developments toward space colonization and exploration of neighbouring planets became a possibility.
 Unknown author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown author, Wikimedia Commons
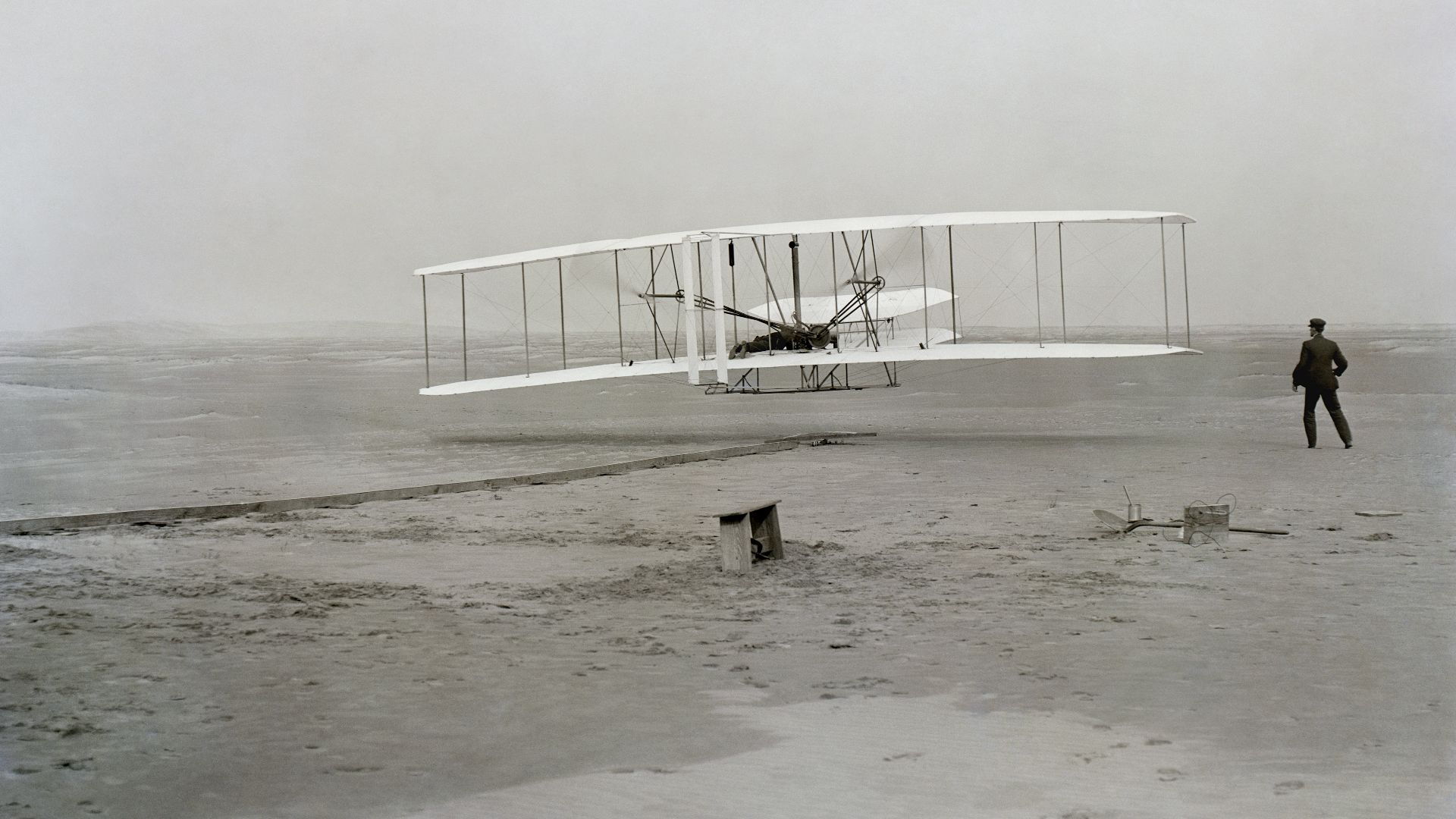
11. Flight
Traveling long distances for most people, involved laborious time-consuming treks via boats, trains, automobiles, or walking. Thanks to two brothers on December 17, 1903, the world marvelled as the first humans took to the sky. Development of more reliable planes followed shortly after. This invention has shrunken the world and made it possible for people and business to expand to all corners of the earth.
 John T. Daniels, Wikimedia Commons
John T. Daniels, Wikimedia Commons
10. Downfall Of The Roman Empire
The fall of the Roman Empire in 476, following the deposition of Romulus Augustulus, led to the end of one of humanity’s largest and most powerful empires. Rome controlled most of Europe, the plains of North Africa, and the fertile Nile river valley. The inception of the Dark Ages is said to be as a result of the destruction of all the cultural and technological progress from Roman culture.
 B. Moerlins, Wikimedia Commons
B. Moerlins, Wikimedia Commons
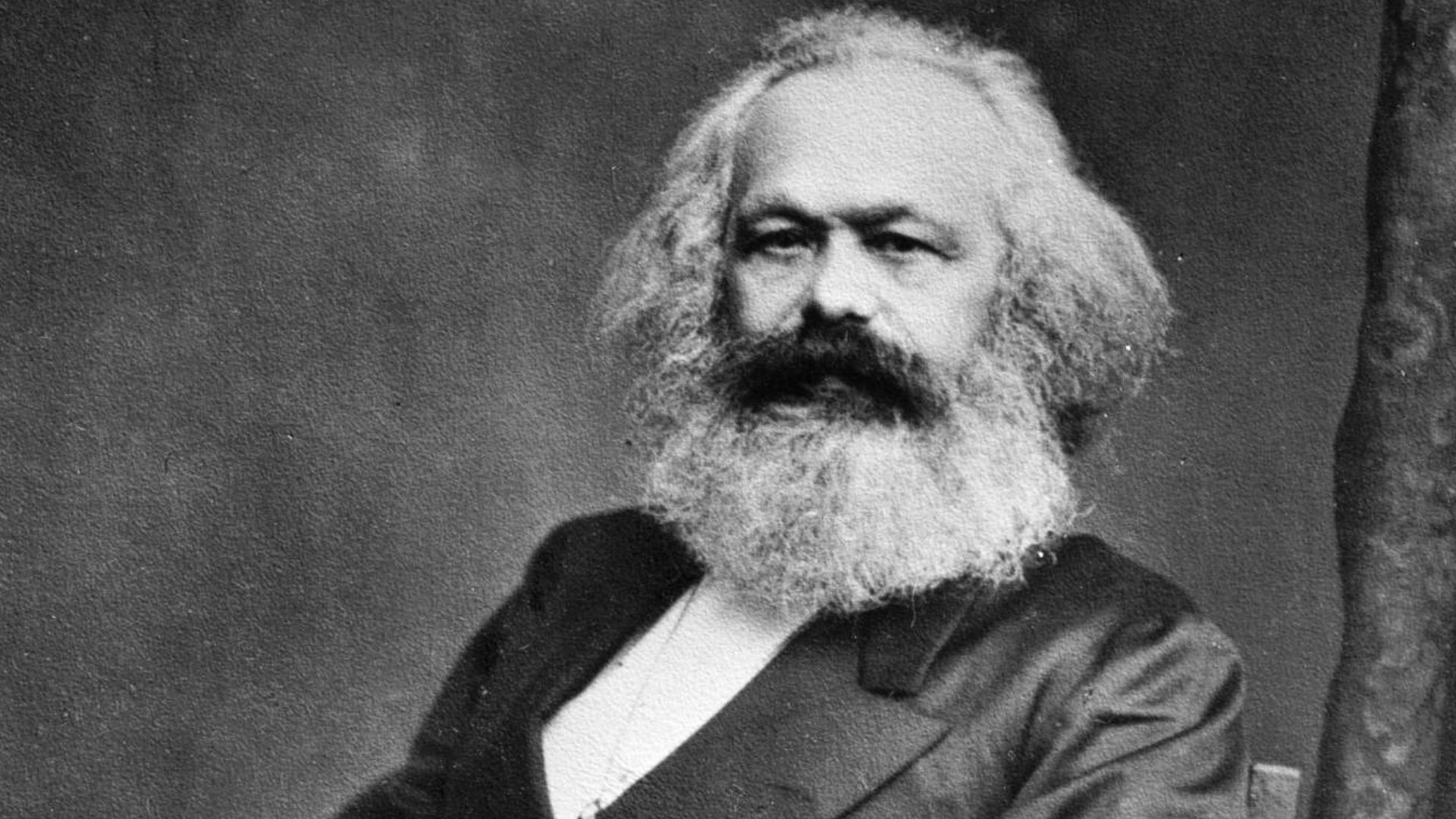
9. Communism
Communism developed as an economic and political philosophy of Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, after the Communist Manifesto was written, published, and distributed in 1848. Thanks to the ideals of these two men, Soviet Russia, China, Cuba, and a handful of other countries adopted this political structure. In theory, these political systems sound ideal but corruption at the highest levels of government has led most communist countries to struggle.
 John Jabez Edwin Mayall, Wikimedia Commons
John Jabez Edwin Mayall, Wikimedia Commons
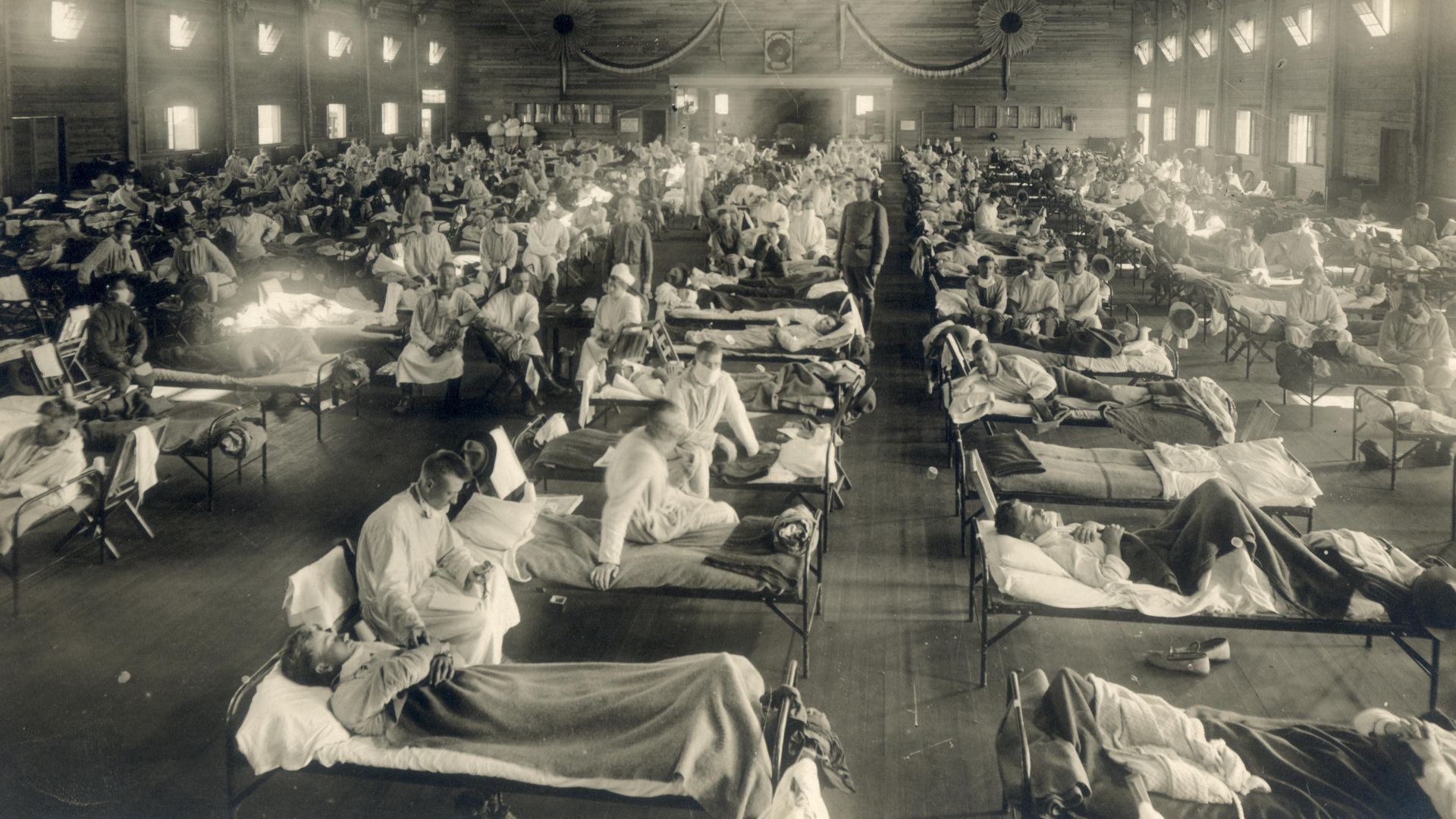
8. Spanish Influenza
The Spanish Influenza became a pandemic on three different occasions. Since the ‘flu’ managed to take as many as 40 million lives between 1918 to 1919, an intense need for medical progress and vaccination development followed as a result. Although a virus can mutate, today people are better prepared to control and combat the spread of viruses thanks to discoveries made as a result of past pandemics.
 Otis Historical Archives, National Museum of Health and Medicine, Wikimedia Commons
Otis Historical Archives, National Museum of Health and Medicine, Wikimedia Commons
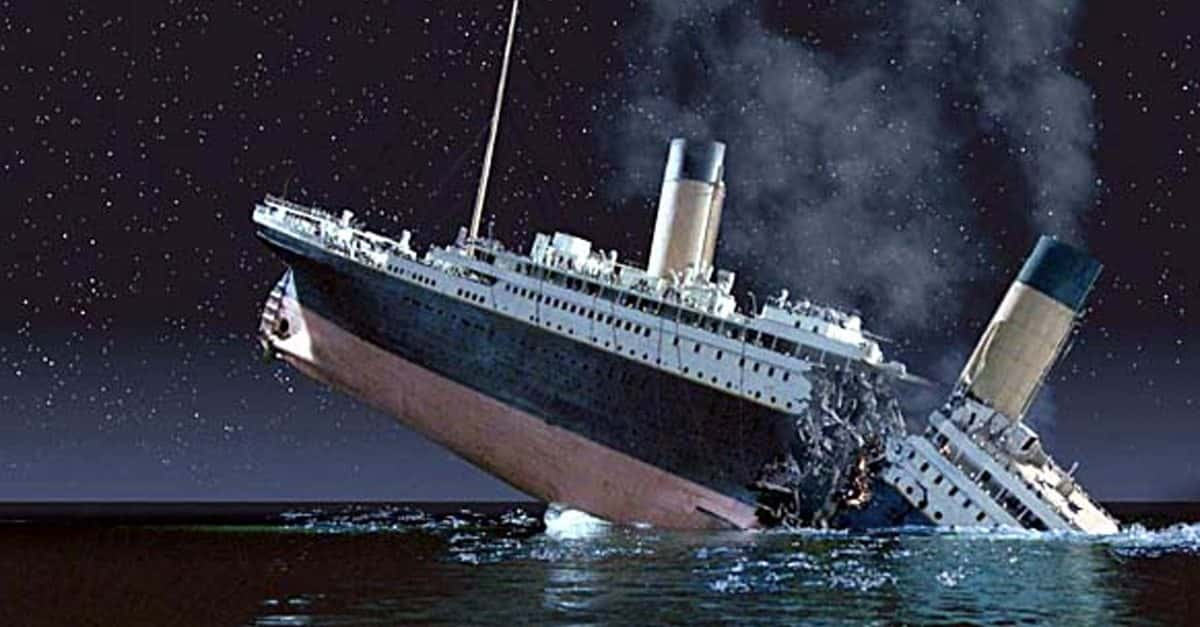
7. The Titanic
The tragedy of the Titanic and the significant loss of life that followed after the ship struck an iceberg, created a lot of changes. The use of radio was crucial in transmitting information about the incident and coordinating the rescue efforts. This tragedy led to the creation of shipping regulations regarding the protocol for the evacuation of a ship, the number of life boats required, and communication equipment required on all major ships.
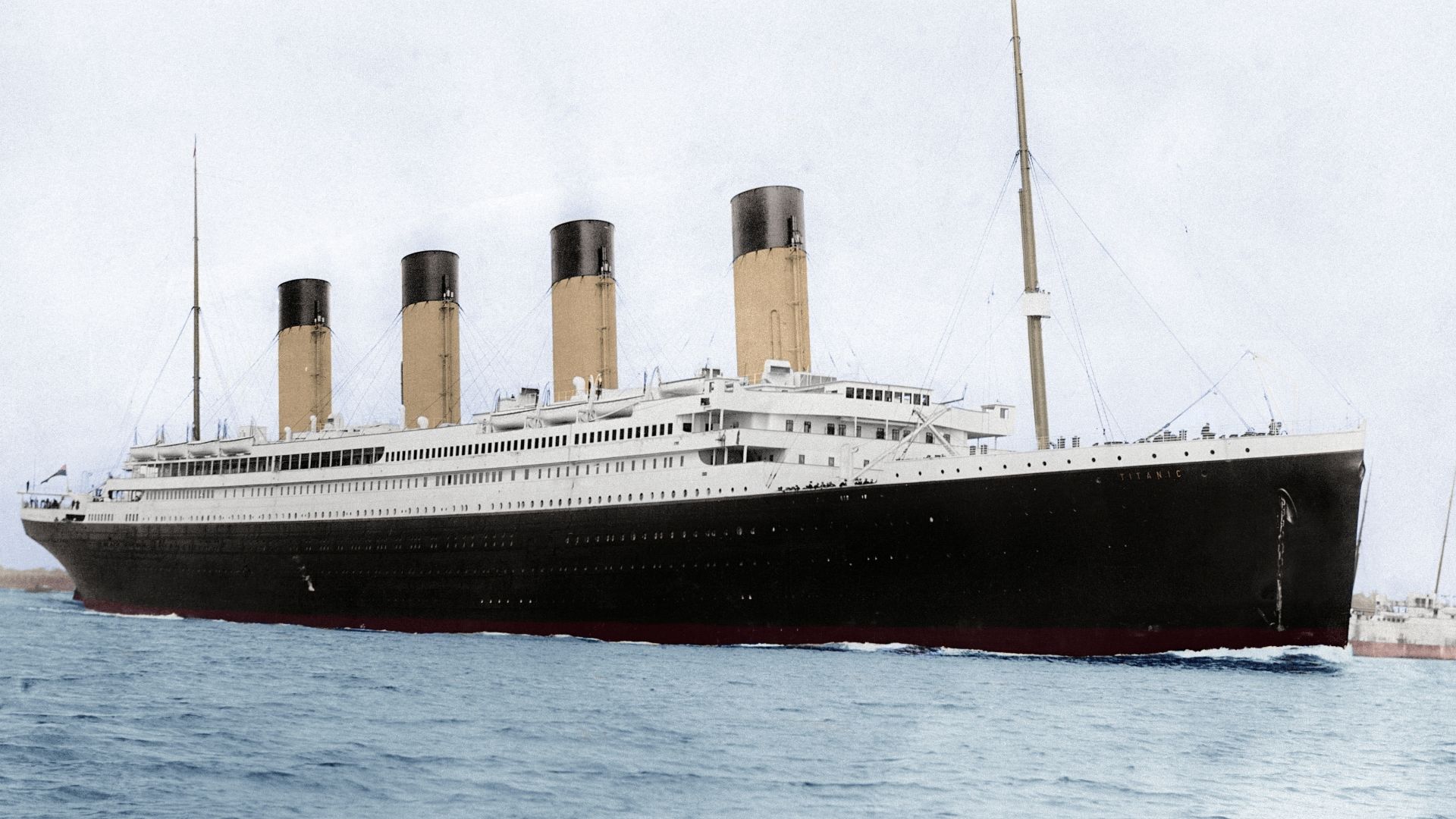 Francis Godolphin Osbourne Stuart, Wikimedia Commons
Francis Godolphin Osbourne Stuart, Wikimedia Commons
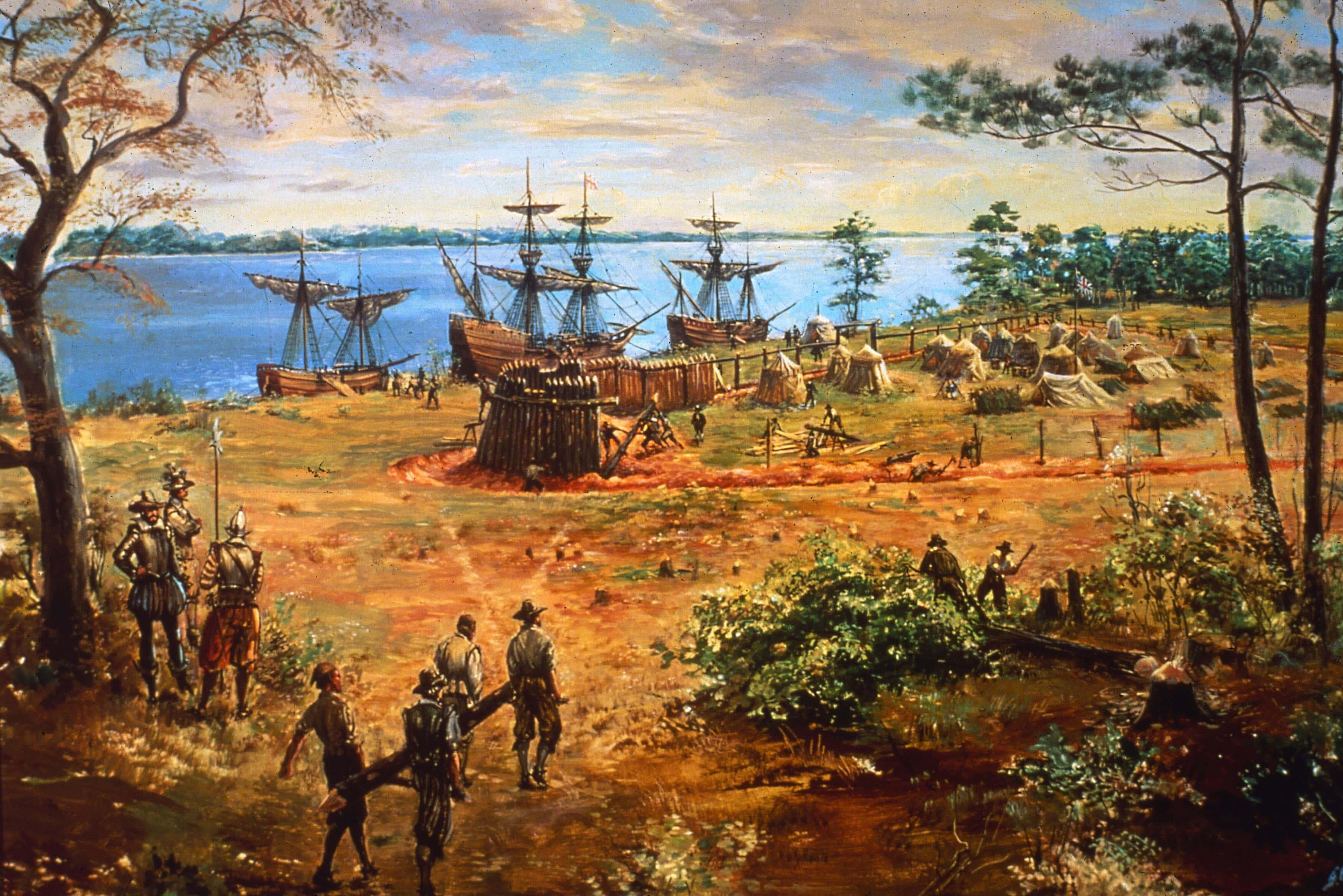
6. New World Discovery
Thanks to the innovations in ship building and navigation, European powers were able to engage in global exploration. They initially wanted to find a quicker route to India to optimize the spice trade. This led to the colonization of the Americas and the creation of a new Western Power.
5. Stock Market Crash and Great Depression
The great stock market crash in 1929 did not solely impact America, but also strained the global economy. After the infamous Black Tuesday stock market crash, the world was plunged into depression, known as the Great Depression, that lasted some ten years. It was the longest lasting economic downturn that the Western world had ever experienced. Thanks to this event, much needed regulations were passed to control how stocks and bonds were traded.
 Associated Press, Wikimedia Commons
Associated Press, Wikimedia Commons
4. Women’s Suffrage in New Zealand
Women’s rights gained a foothold in the world, thanks to New Zealand paving the way as the first country to give women the right to vote on September 19, 1893. The Royal Assent was made by Governor Lord Glasfow, and women had their first involvement with the election process on November 28, 1893. Thanks to New Zealand’s decision, the United States and Great Britain soon granted women the right to vote.
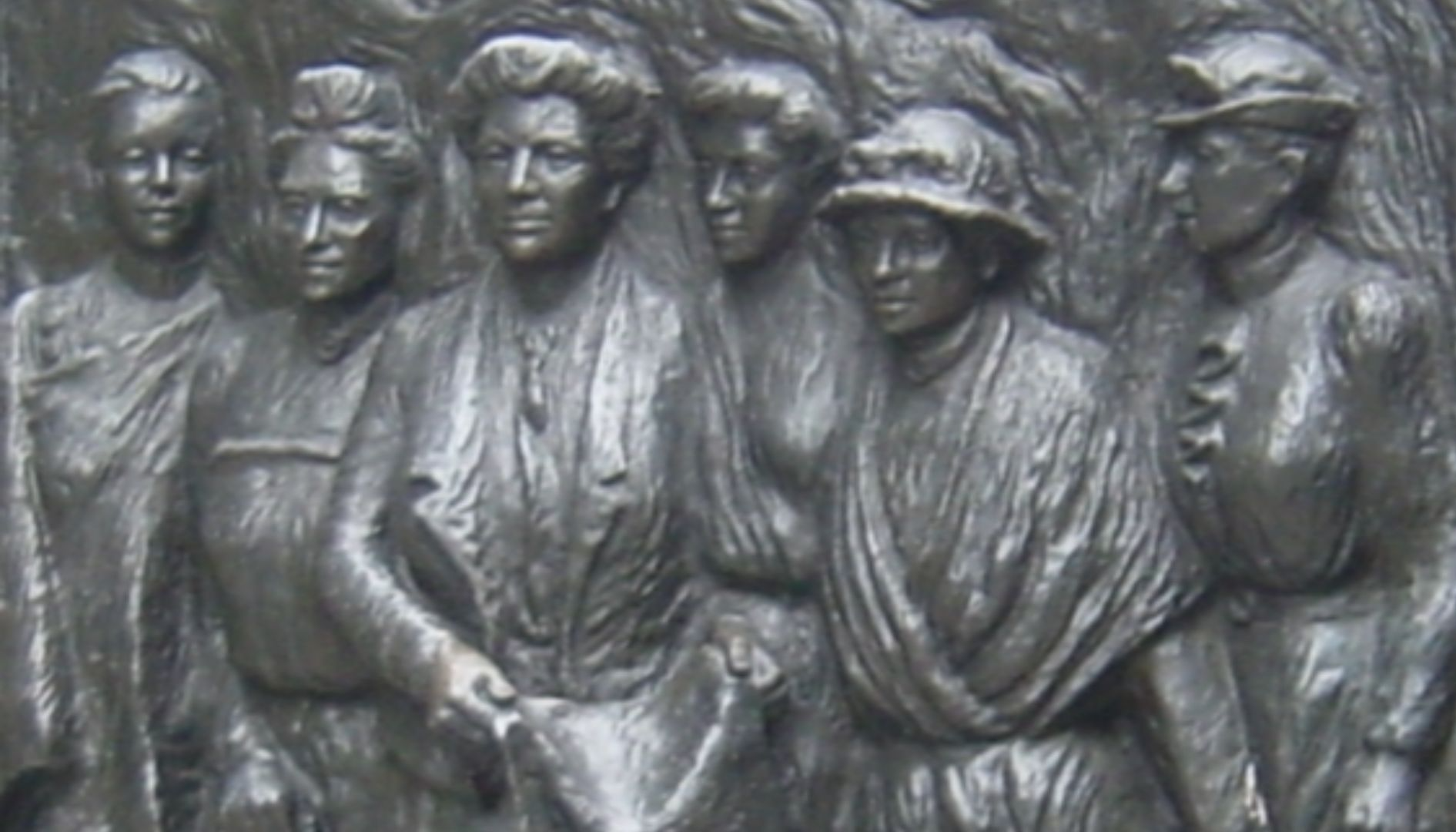 Robert Cutts, Wikimedia Commons
Robert Cutts, Wikimedia Commons
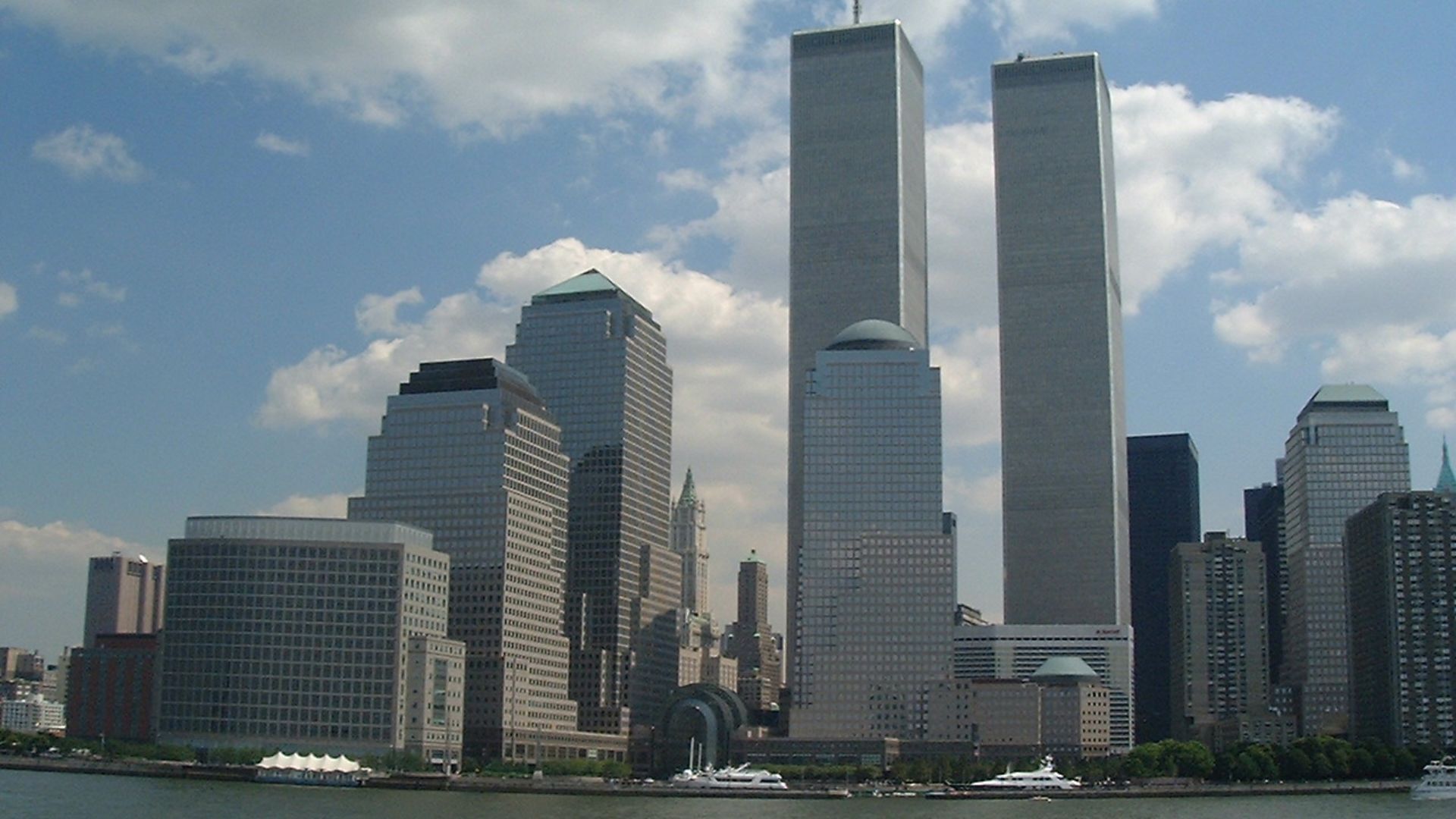
3. September 11th Attacks
September 11, 2001 marks the date of the deadliest terrorist attack ever conducted on American soil. In addition to the destruction of the World Trade Center towers, 3,000 people lost their lives. In response, a Global War on Terrorism started, and many nations introduced anti-terrorism laws and practices to combat global terrorism.
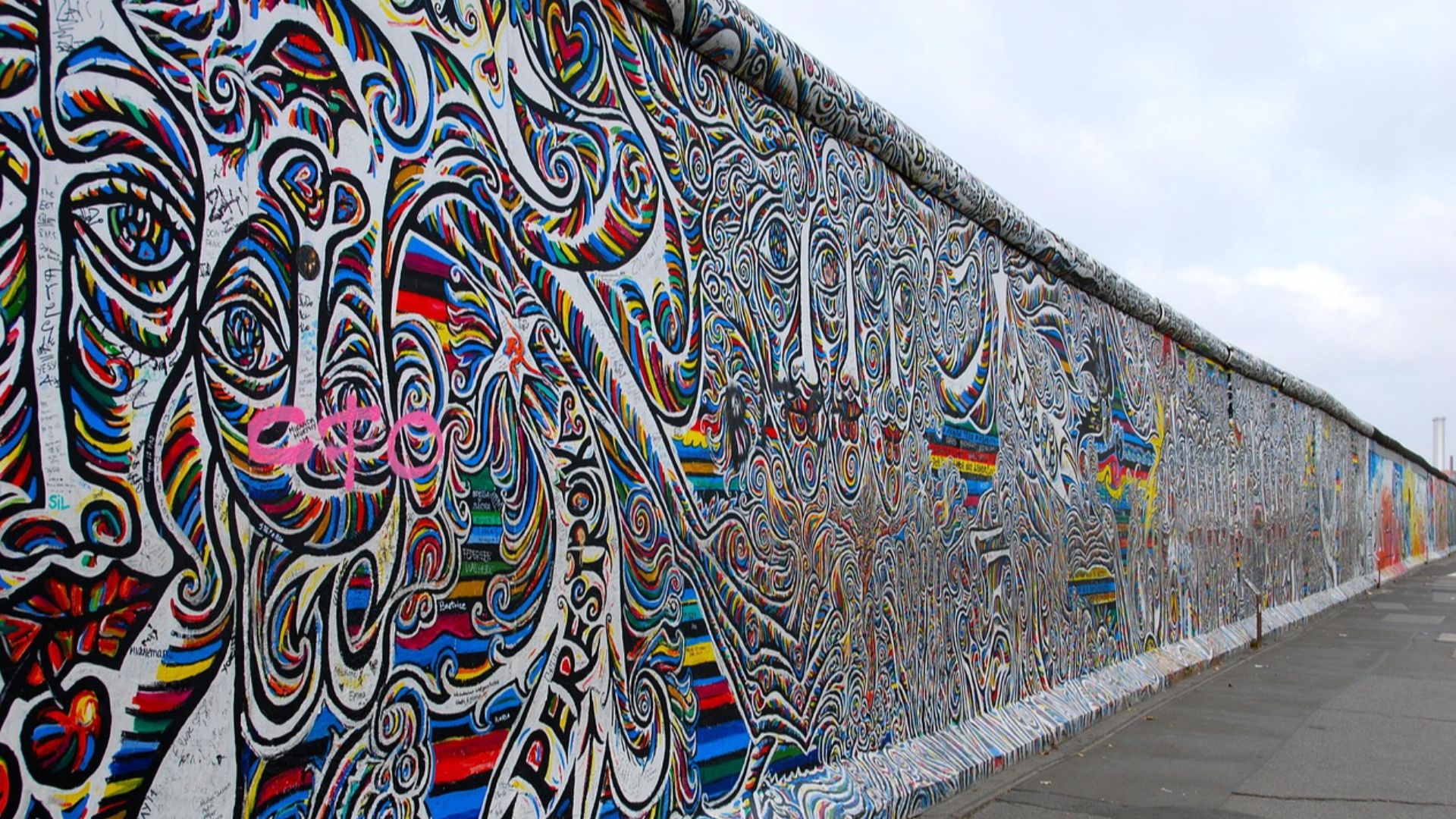
2. Fall of Berlin Wall
The Berlin Wall was a symbol of the split between communism and capitalism, and Western and Eastern Europe. Thanks to the fall of the USSR, and with it the ‘Iron Curtain,’ Germany was able to unify, and the Cold War was finally over. The Soviet Union dissolved and became divided into many sovereign nations. This led to development and progress of Eastern European nations.
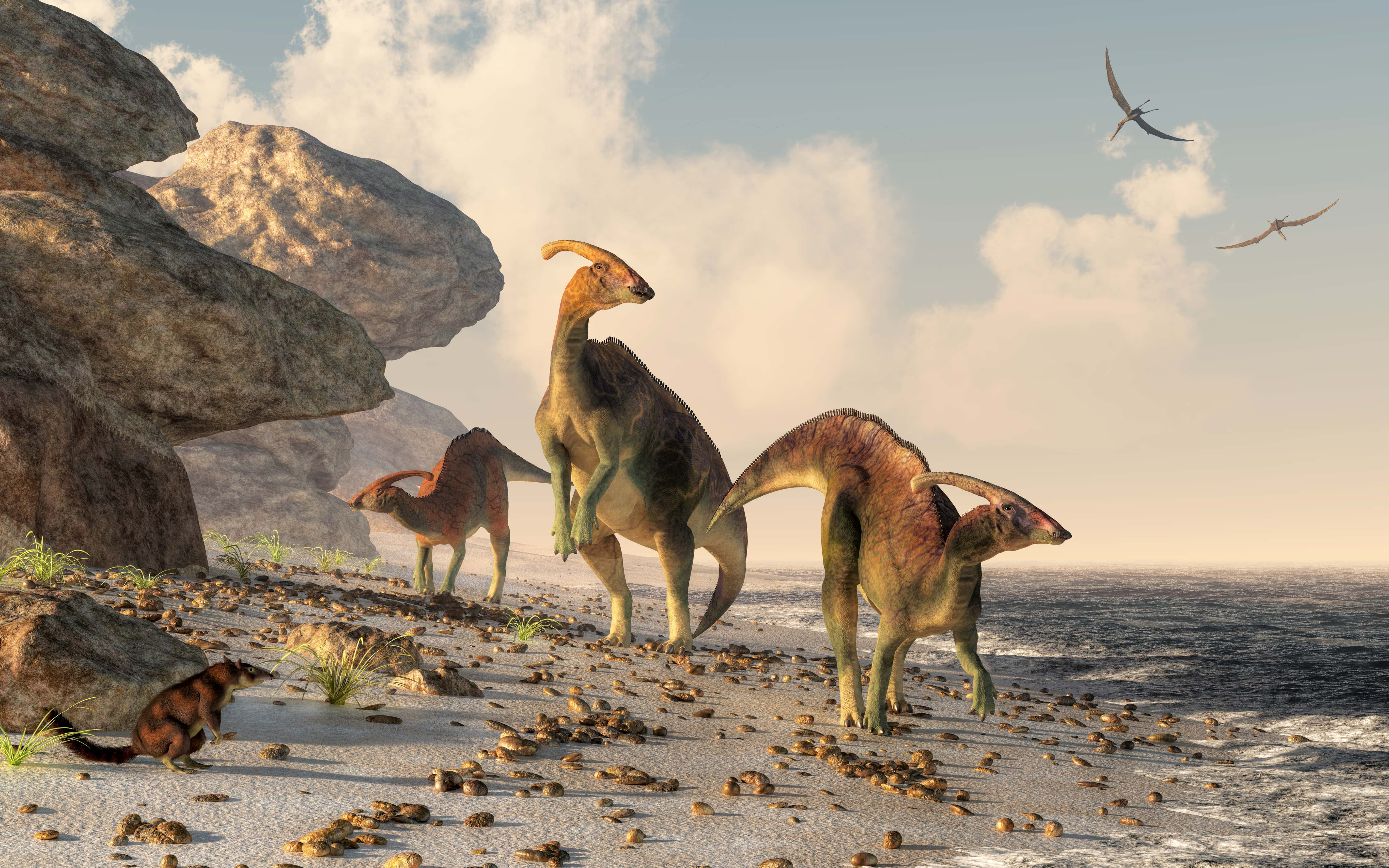
1. Mass Extinction
The single event that most effected the way humanity, and all life on Earth, would develop was the Cretaceous extinction event, also known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary (K–T) extinction. This was a mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth approximately 65 million years ago. With the exception of a few species such as the leatherback sea turtle and crocodiles, no tetrapods, including dinosaurs, weighing more than 25 kilograms (55 lb) survived. It marked the end of the Cretaceous period and with it, the entire Mesozoic Era. This paved the way for the beginning of the Cenozoic Era in which the mammal would become the dominate species.
Sources: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17



















