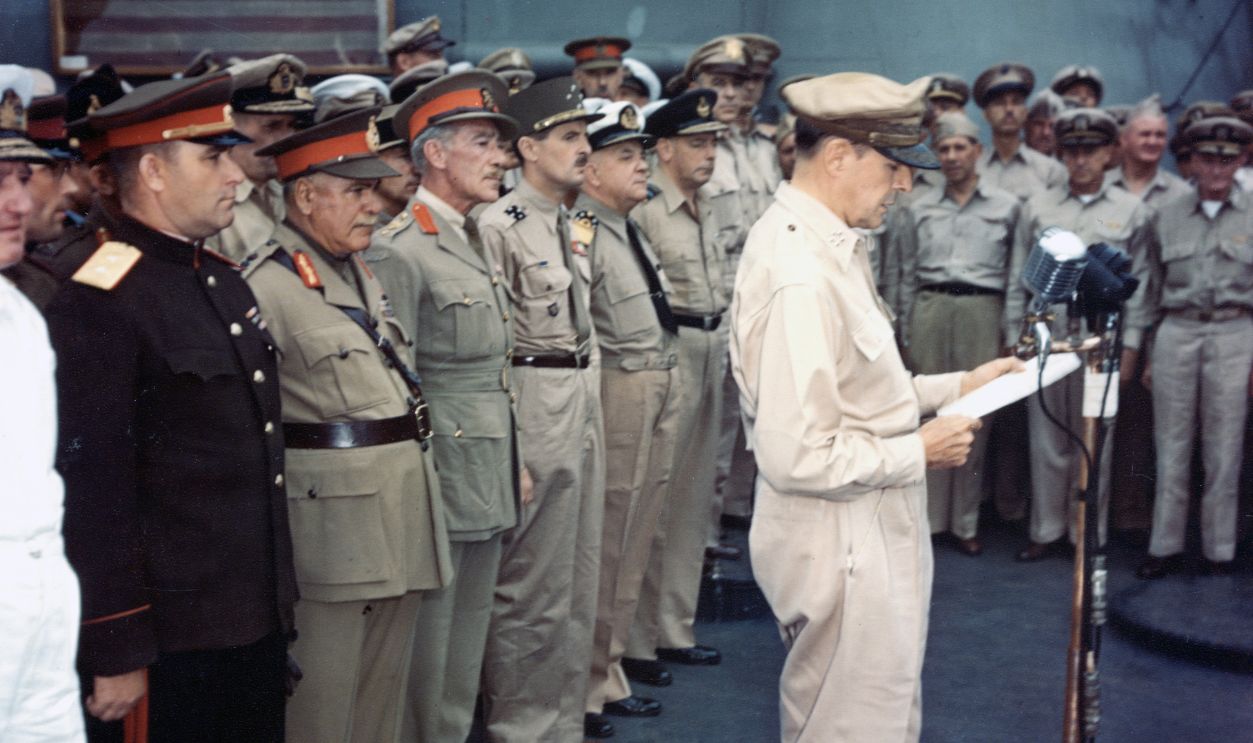
Mushroom Clouds Were Just One Aspect
When Japan announced its surrender in August 1945, the world turned its attention to the devastating atomic attacks of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. While these events were undeniably pivotal, they were not the sole reasons behind Japan's decision to end the armed conflict.

Failing Diplomatic Efforts
Throughout 1945, Japan sought to negotiate an end to the dispute. This was to be done through diplomatic channels, particularly via the Soviet Union, which remained neutral in the Pacific conflict under the 1941 Soviet-Japanese Neutrality Pact. Japanese leaders hoped that Moscow could mediate a peace settlement with favorable terms.
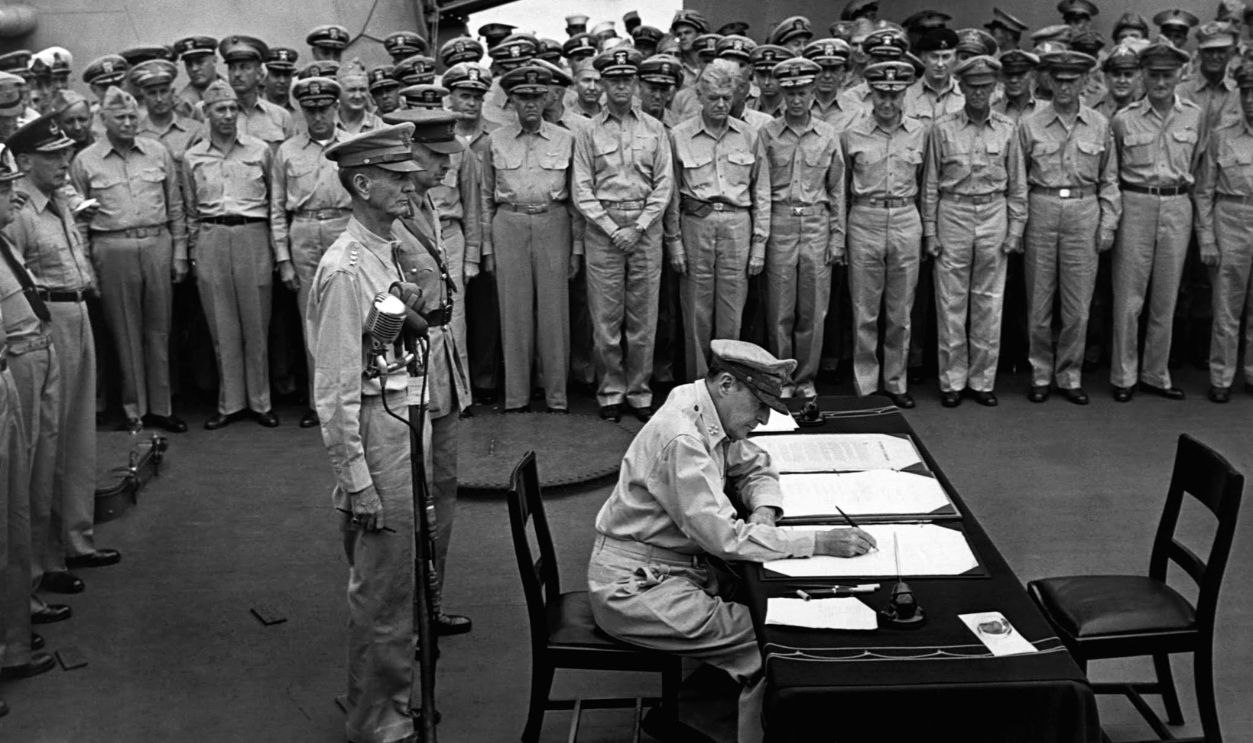 United States Navy, Wikimedia Commons
United States Navy, Wikimedia Commons
Reasons Behind It
However, these efforts failed for two key reasons. First, the Soviet Union was secretly preparing to join the Allies against Japan, as agreed upon at the Yalta Conference in February 1945. Second, the Allies' demand for unconditional surrender left little room for negotiation.
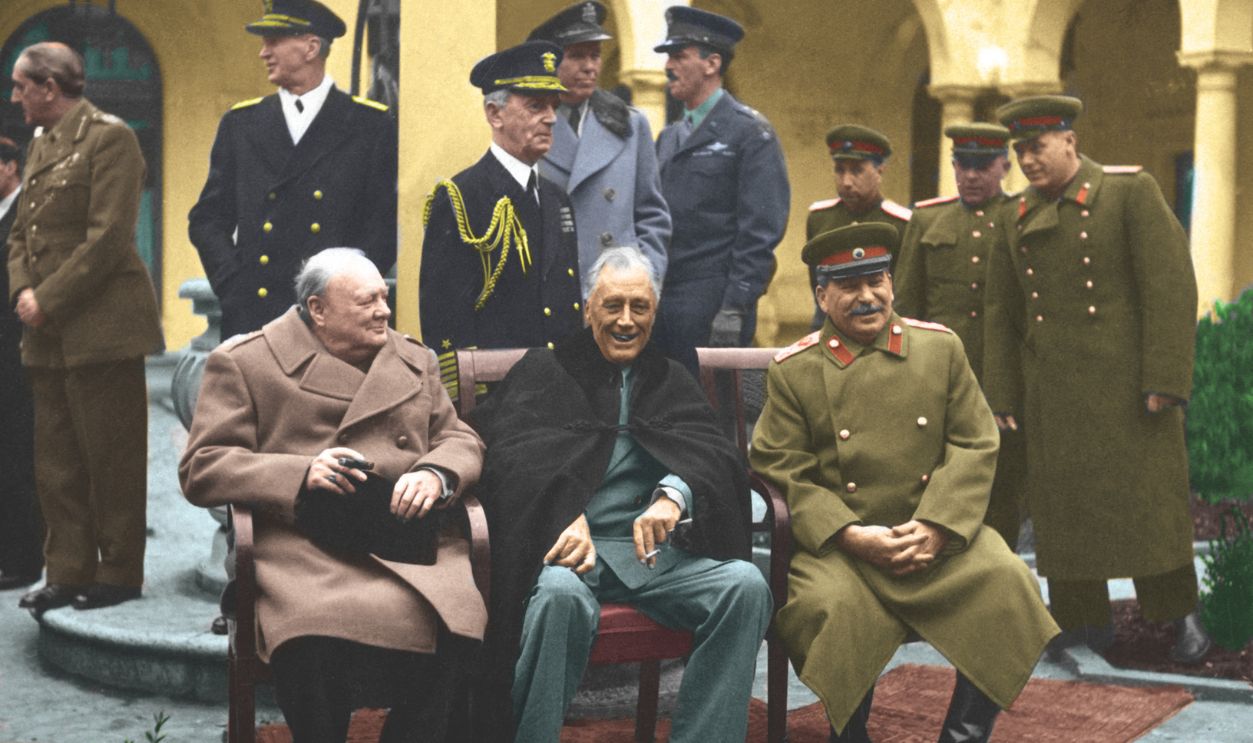 Grambaba, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Grambaba, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
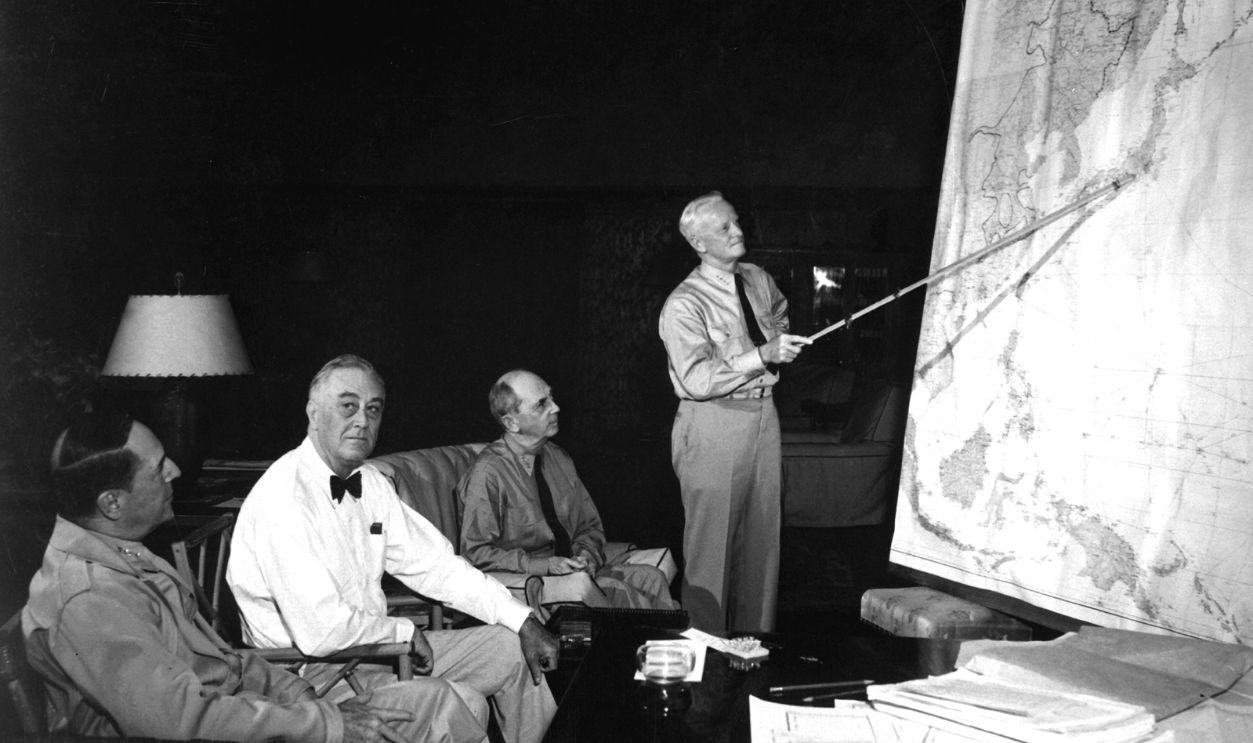
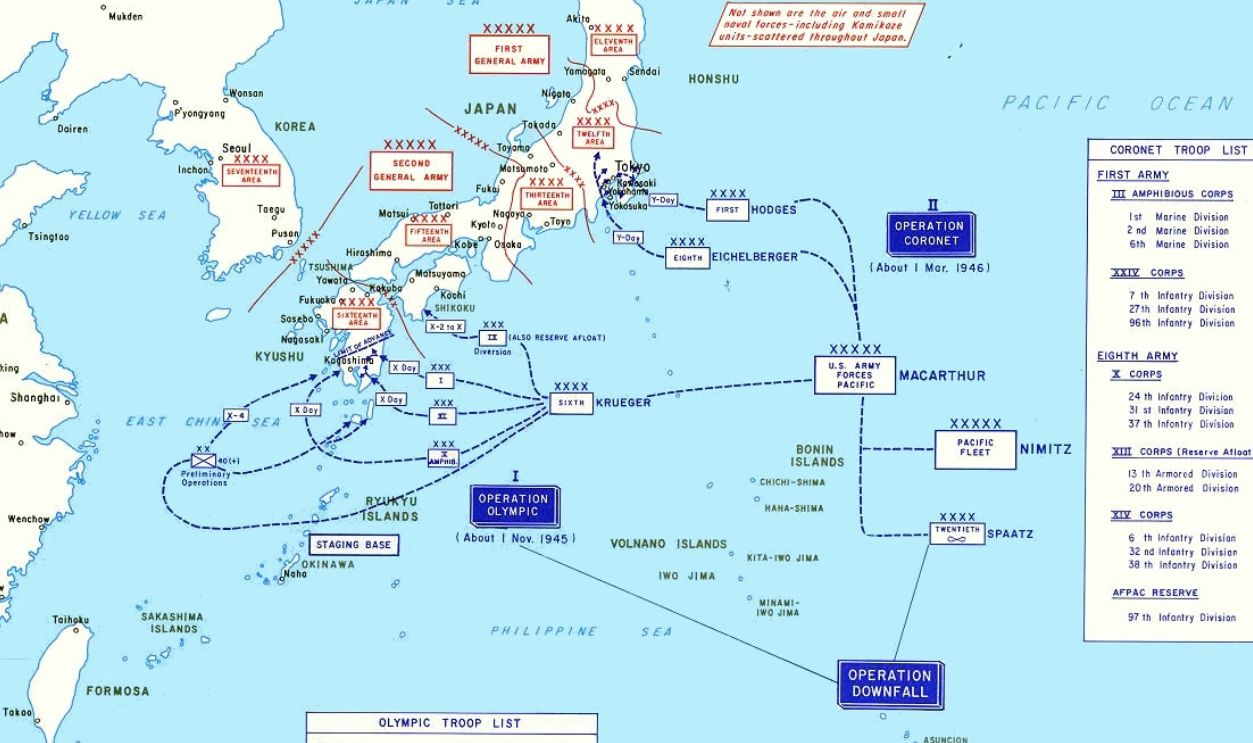
Invasion Threat
The Allies were preparing for Operation Downfall, a massive two-stage invasion of Japan's home islands that was projected to begin in November 1945. The operation consisted of two phases: Operation Olympic, the invasion of Kyushu, and Operation Coronet, the invasion of Honshu.
 U.S. Army, U.S. federal government, Wikimedia
U.S. Army, U.S. federal government, Wikimedia
Great Loss Of Life
Intelligence estimates suggested that Japan would deploy over 2 million troops—for defense. Projected casualties ranged from 1.7 to 4 million for Allied forces, with higher losses expected for Japan. The country fortified its defenses, but the scale of devastation from this invasion made continuing WW2 an increasingly untenable prospect.
Soviet Union's Involvement
Although atomic offensives grabbed global headlines, the Soviet Union's attack on August 8, 1945, profoundly shocked Japan's leadership. Just hours after declaring attack, Soviet forces launched a massive offensive, known as the Manchurian Strategic Offensive Operation, against Japanese-controlled territories in Manchuria, Korea, and Sakhalin Island.
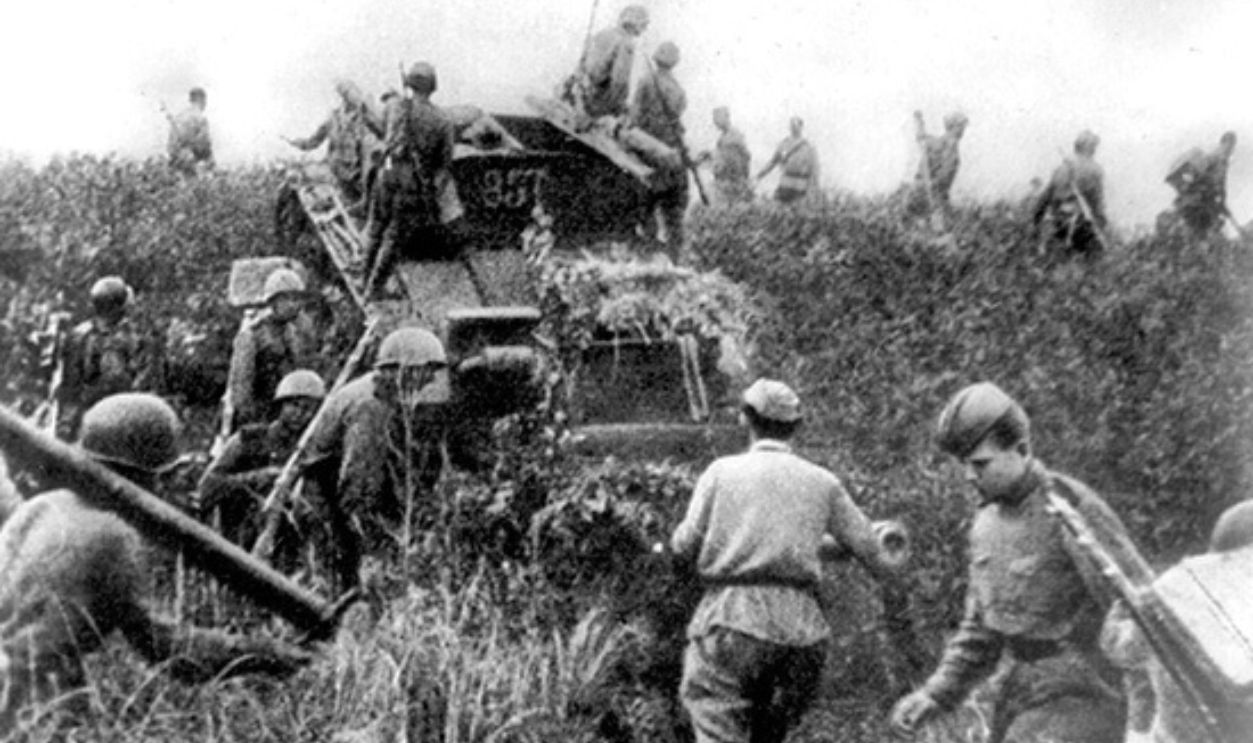 Mil.ru, CC BY 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Mil.ru, CC BY 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
All Major Territories, Captured
The Red Army quickly overwhelmed the Japanese Kwantung Army, which was poorly equipped and vastly outnumbered. Within days, critical territories were captured, and Japan's strategic position in Asia collapsed. The Soviet invasion eliminated any hope that Japan could negotiate peace through Moscow's mediation, which is what Japanese diplomats wanted.
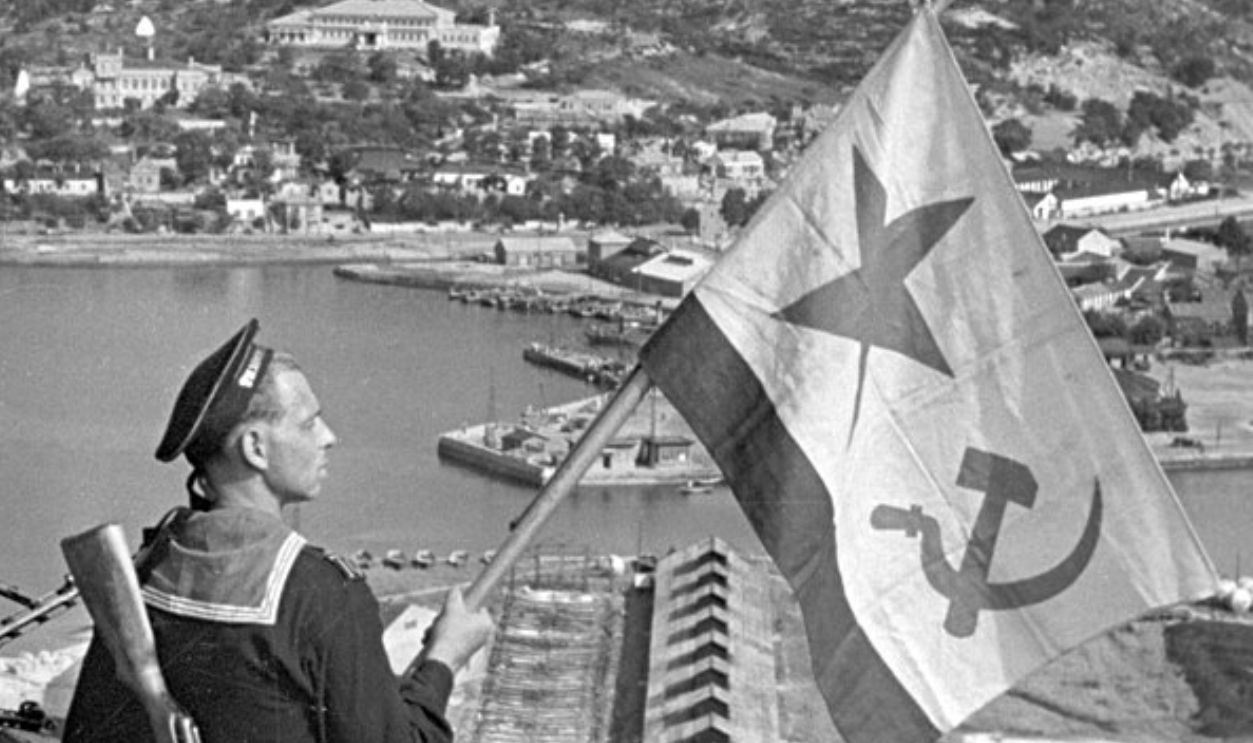 RIA Novosti archive, CC-BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
RIA Novosti archive, CC-BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Diminished Strength
By mid-1945, Japan's military was suffering catastrophic losses. The Imperial Japanese Navy had been decimated in battles such as Leyte Gulf, and Japan's Air Force relied increasingly on desperate kamikaze tactics. On land, the troops were stretched thin in multiple territories from Burma to the Pacific islands.
 U.S. Army Signal Corps officer Gaetano Faillace, Wikimedia Commons
U.S. Army Signal Corps officer Gaetano Faillace, Wikimedia Commons
Isolated And Undersupplied
Many of these forces were isolated and undersupplied due to Allied naval blockades. The loss of Okinawa in June 1945 further highlighted Japan's vulnerability. The island's fall gave the Allies a direct route to Japan's home islands. It was clear Japan could no longer mount an effective defense or counterattack.
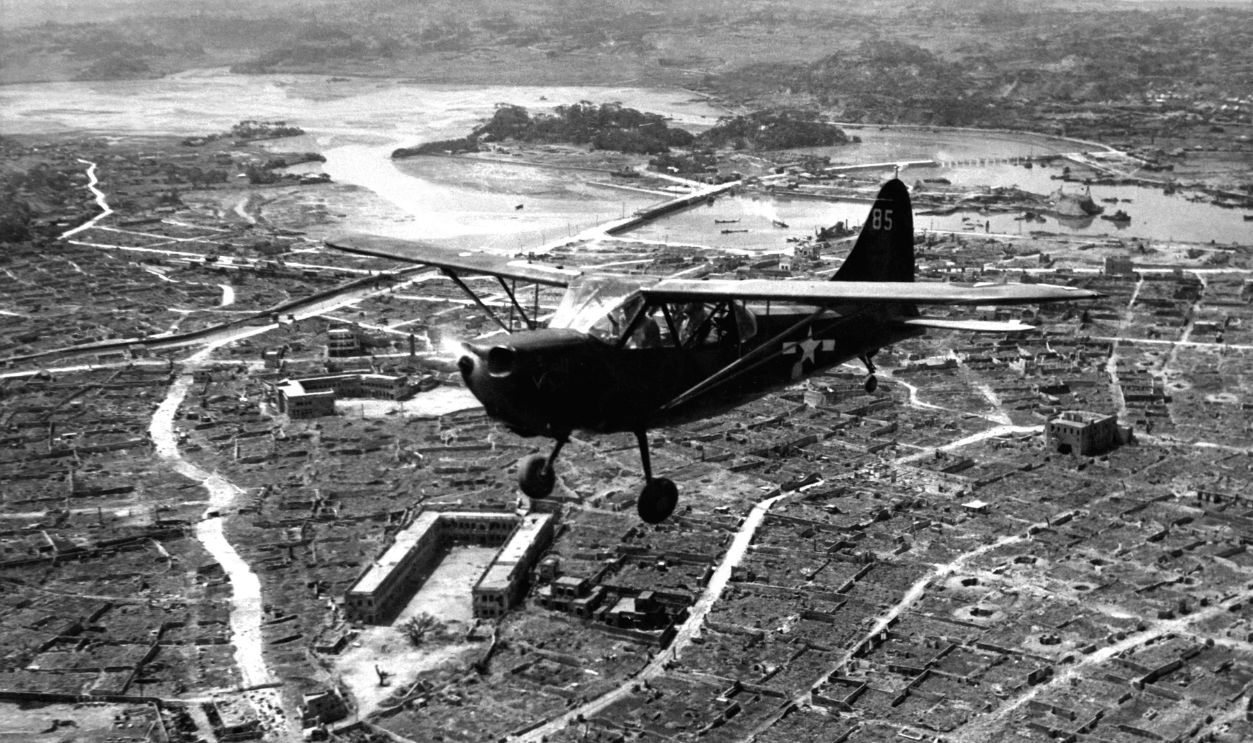 Lt. David D. Duncan, USMC, Wikimedia Commons
Lt. David D. Duncan, USMC, Wikimedia Commons
Allied Blockades
The Allied blockade of Japan, particularly by US submarines, effectively strangled Japan's economy and battle effort. By 1944, American submarines had sunk nearly 5 million tons of Japanese shipping to cut off vital imports of oil, rubber, metals, and other materials. The blockade also disrupted food shipments from Japanese-occupied territories.
Starving Civilians
Civilians faced starvation as agricultural output declined and transportation networks were destroyed by blastings. The blockade's effectiveness was multiplied by the near collapse of Japan's fuel supply. By the summer of 1945, most equipment, vehicles, aircraft, and ships were immobilized due to lack of fuel.
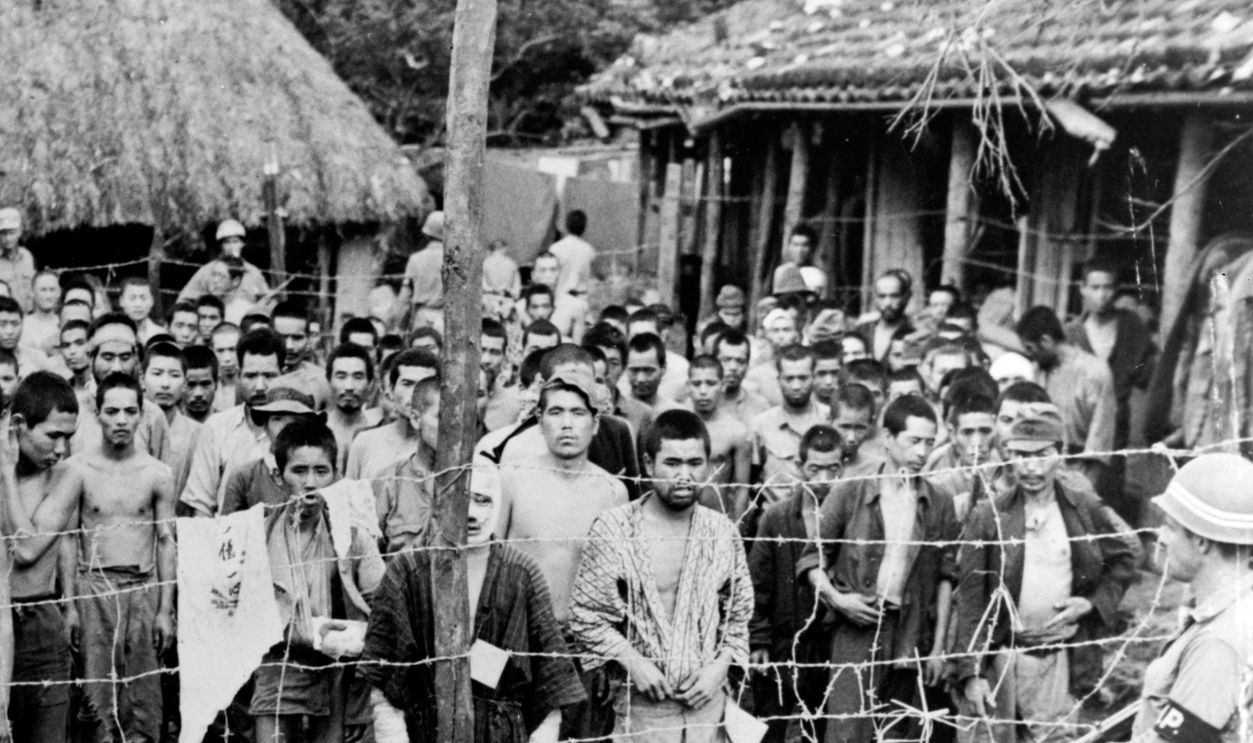 U.S. Marine Corps, Wikimedia Commons
U.S. Marine Corps, Wikimedia Commons
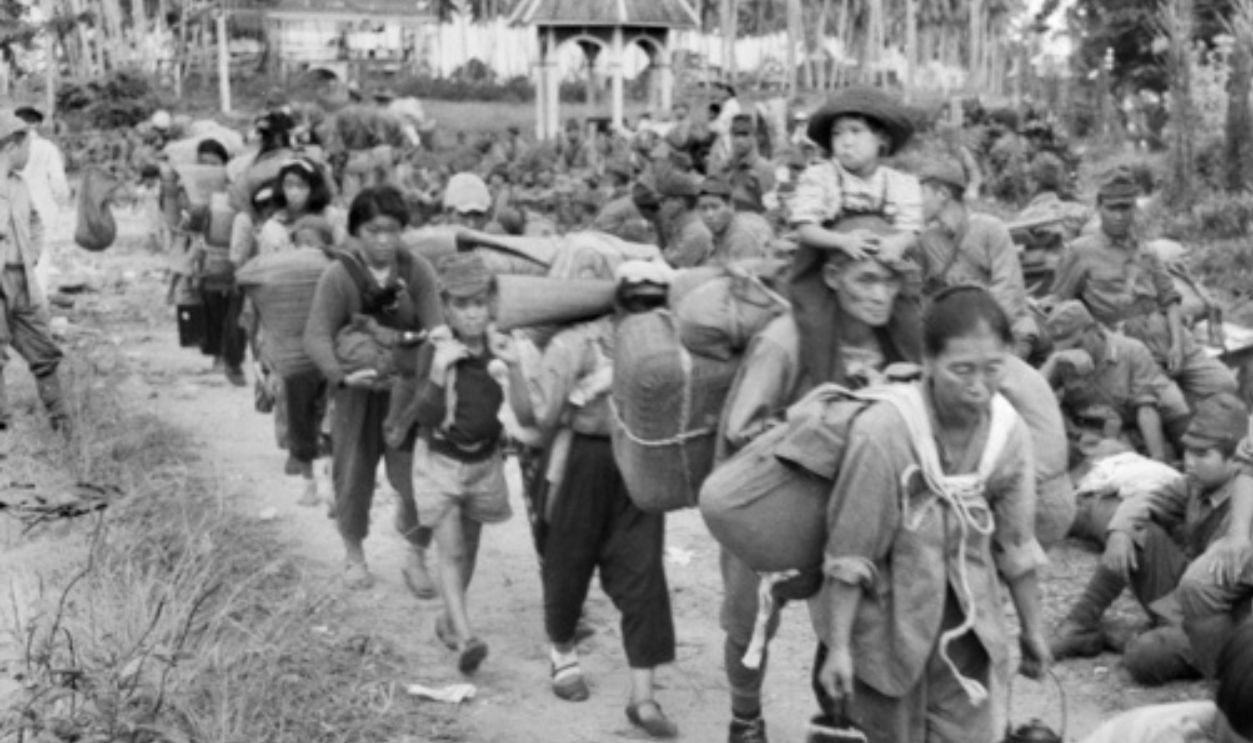
Exhaustion Of Resources
Years of conflict left Japan's supply chains in shambles. Because of the lack of any/all resources and continuous attacks, everything was dedicated to army operations. This meant that other industries and economic segments were neglected, and the whole society suffered as a result.
 Burke, Frank Albert Charles, Wikimedia Commons
Burke, Frank Albert Charles, Wikimedia Commons
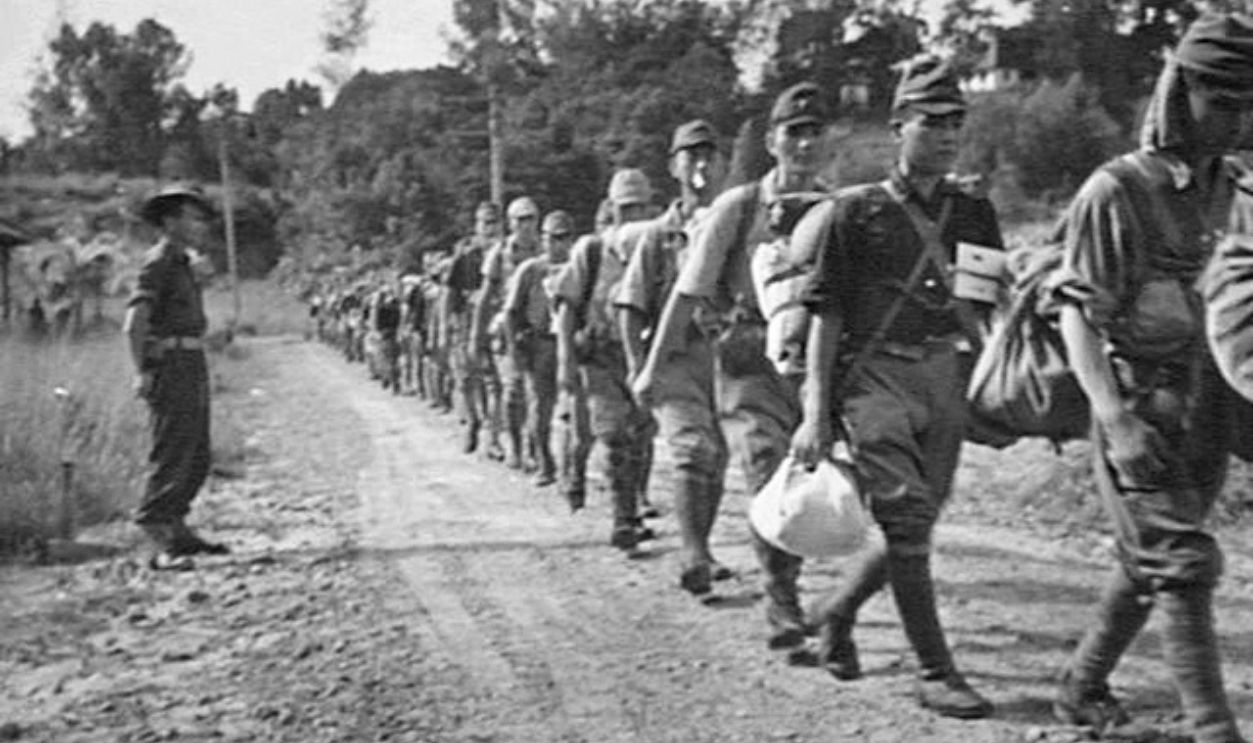
Malnutrition And Diseases On The Rise
Factories struggled to produce necessary goods due to a lack of raw materials. The government imposed rationing on the civilian population. However, it failed to meet basic needs. As a result, malnutrition and diseases became widespread, which directly affected the strength of the troops.
 Sgt F. A. C. Burke, Wikimedia Commons
Sgt F. A. C. Burke, Wikimedia Commons
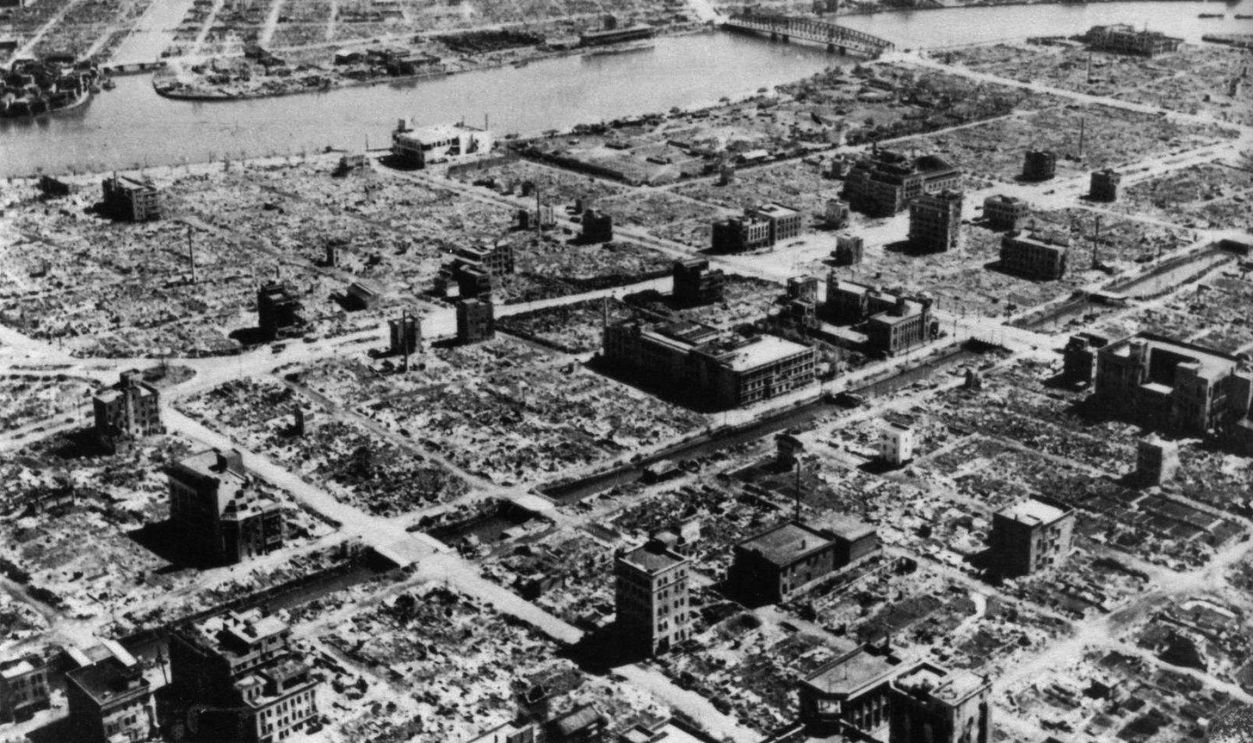
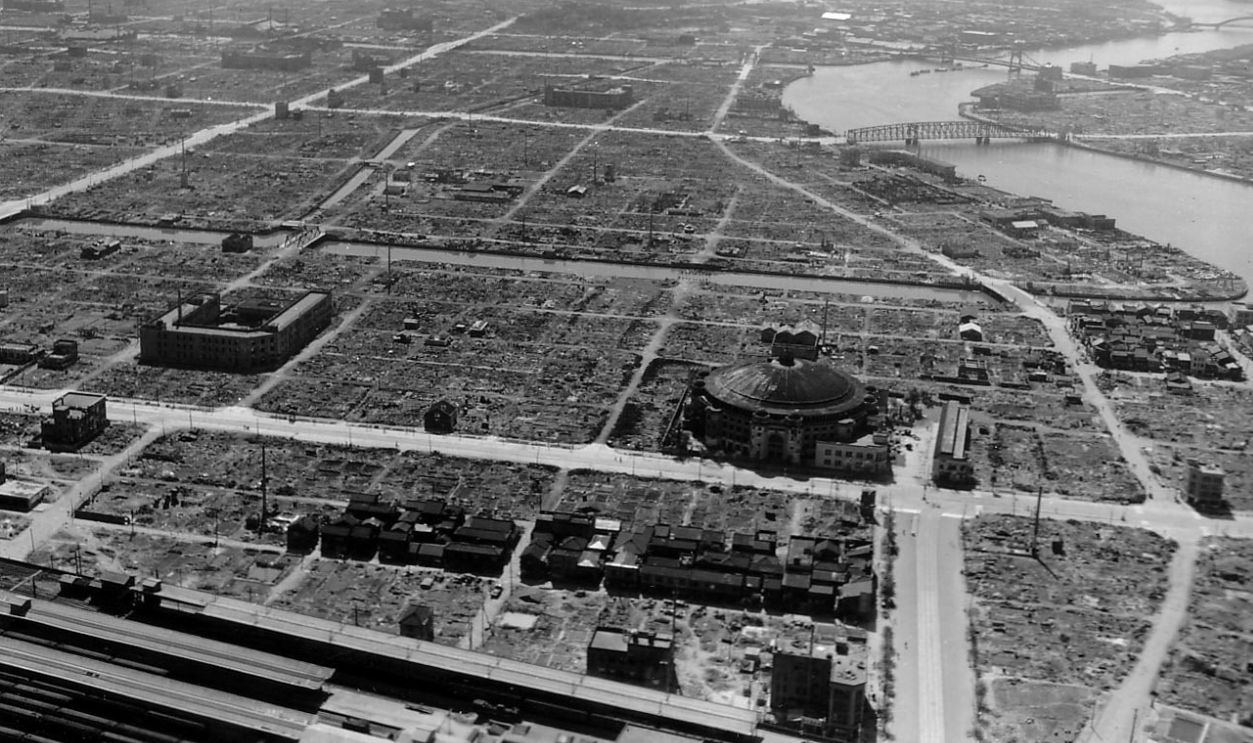
Strategic Campaign
Beginning in 1944, the United States initiated a relentless campaign targeting Japanese cities and infrastructure. These raids included incendiary blastings designed to inflict maximum destruction. One of the most devastating raids occurred on the night of March 9–10, 1945, when approximately 300 B-29s dropped incendiary bombs on Tokyo.
 US Army Signal Corps, Wikimedia Commons
US Army Signal Corps, Wikimedia Commons
Damaged Cities
This operation took out over 100,000 civilians, injured countless others, and left more than a million homeless. Similar attacks on other cities, such as Osaka and Kobe, obliterated urban centers and demoralized its population. By mid-1945, over 60 Japanese cities had been heavily damaged.
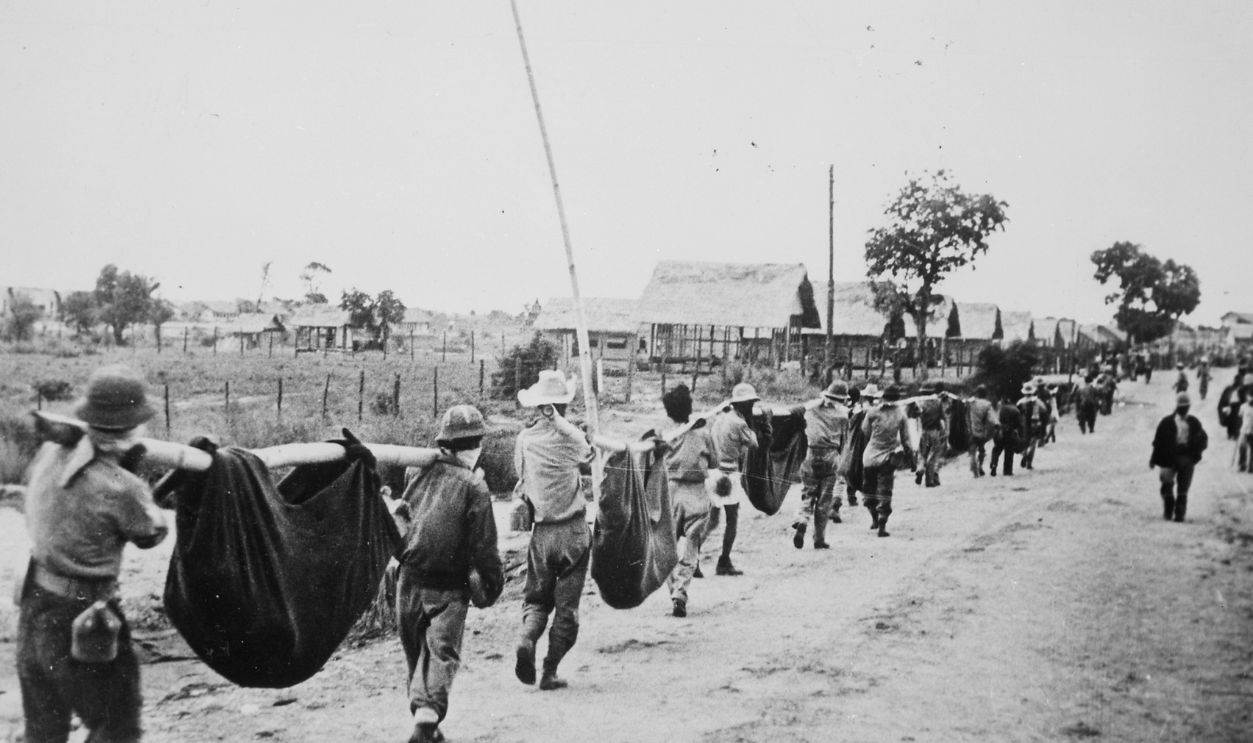
Loss Of Key Territories
Japan's strategy of defending a vast empire across Asia and the Pacific failed as the Allies executed their island-hopping campaign. The loss of key territories such as the Philippines in 1945 dealt a critical hit to Japan's logistical network by cutting off reinforcements to its forces across the Pacific.
 National Archives at College Park, Wikimedia Commons
National Archives at College Park, Wikimedia Commons
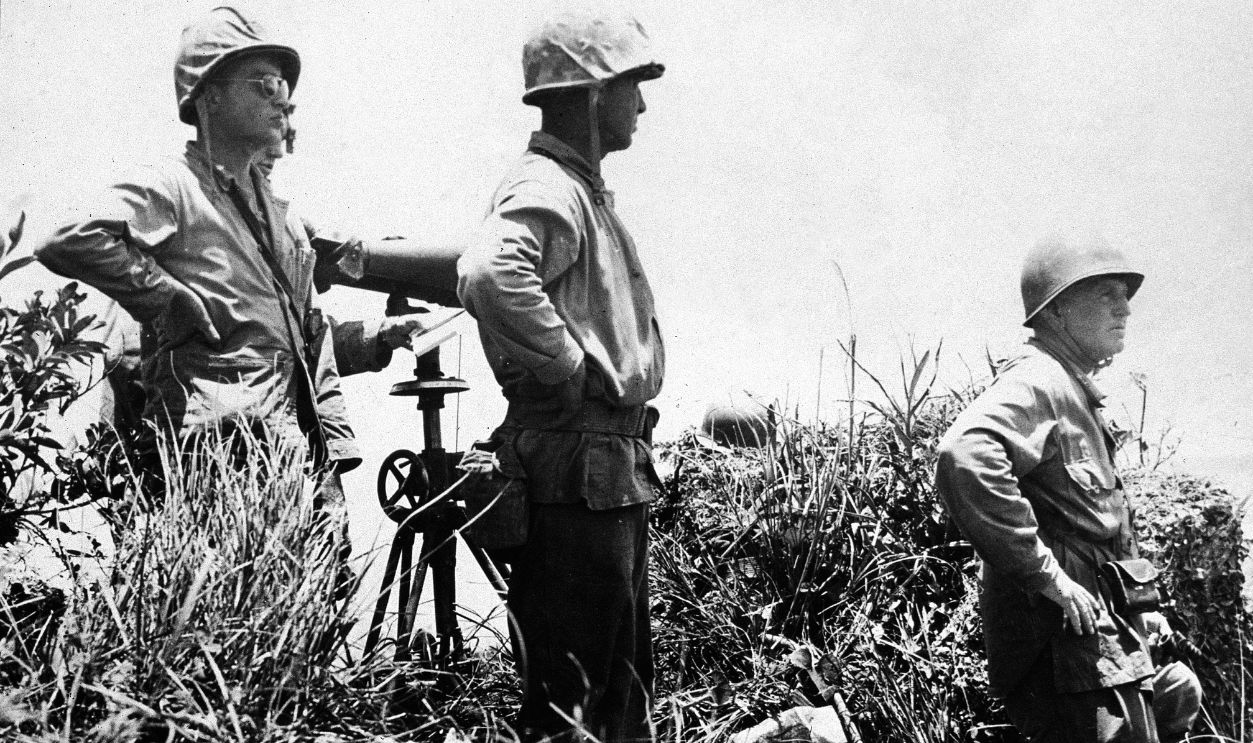
Battle Of Iwo Jima
It wasn't the only one, as the Battle of Iwo Jima, fought from February to March 1945, resulted in the capture of an island critical for launching aerial raids on Japan's home islands. Even more devastating was the fall of Okinawa in June 1945 following a brutal three-month battle.
Decline In Civilian Morale
Civilians were enduring unimaginable hardships. The sustained campaigns, food shortages, multiple defeats, and widespread destruction of cities left people demoralized and desperate. Millions were homeless, and basic necessities were scarce. The shelling of major cities killed thousands and displaced even more.
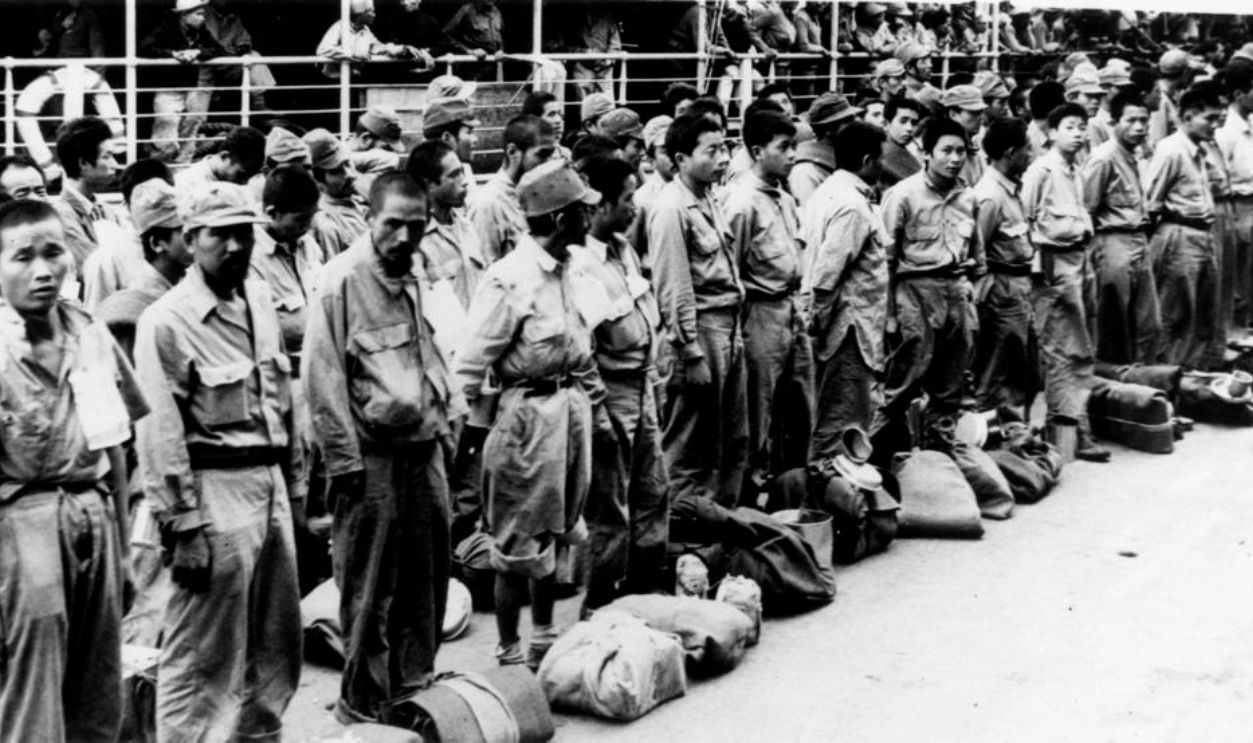 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Plummeting National Spirit
Despite government propaganda, many began to lose faith in the ability of soldiers to protect them. Reports of civilian resistance waned as fear and exhaustion took hold, which eroded the national spirit. The mounting despair among the civilian population urged Japan's leadership to end WW2.
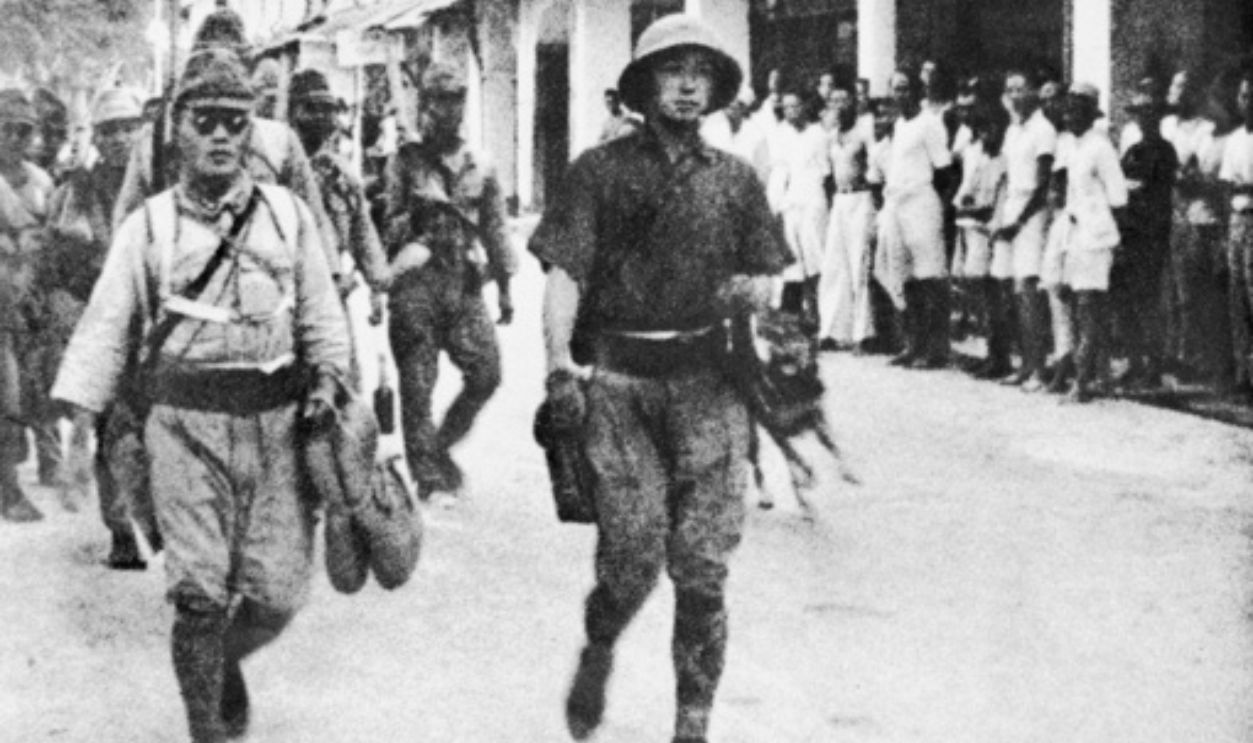 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
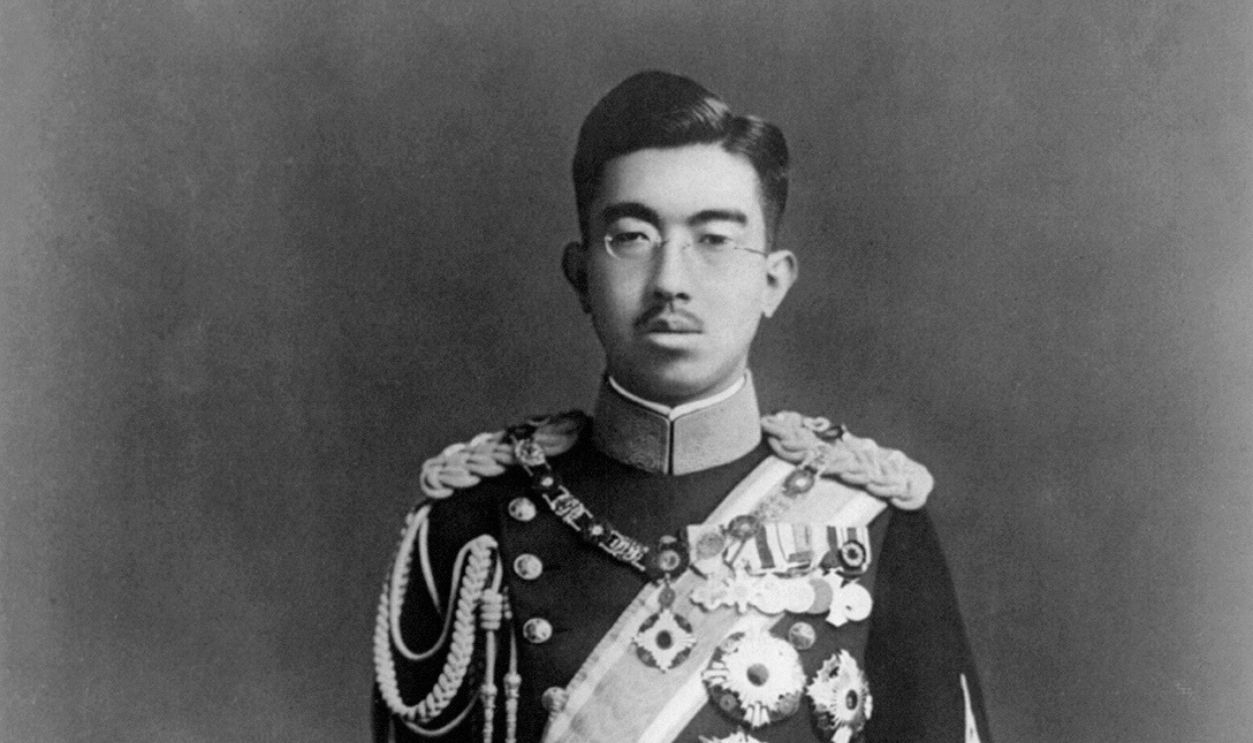
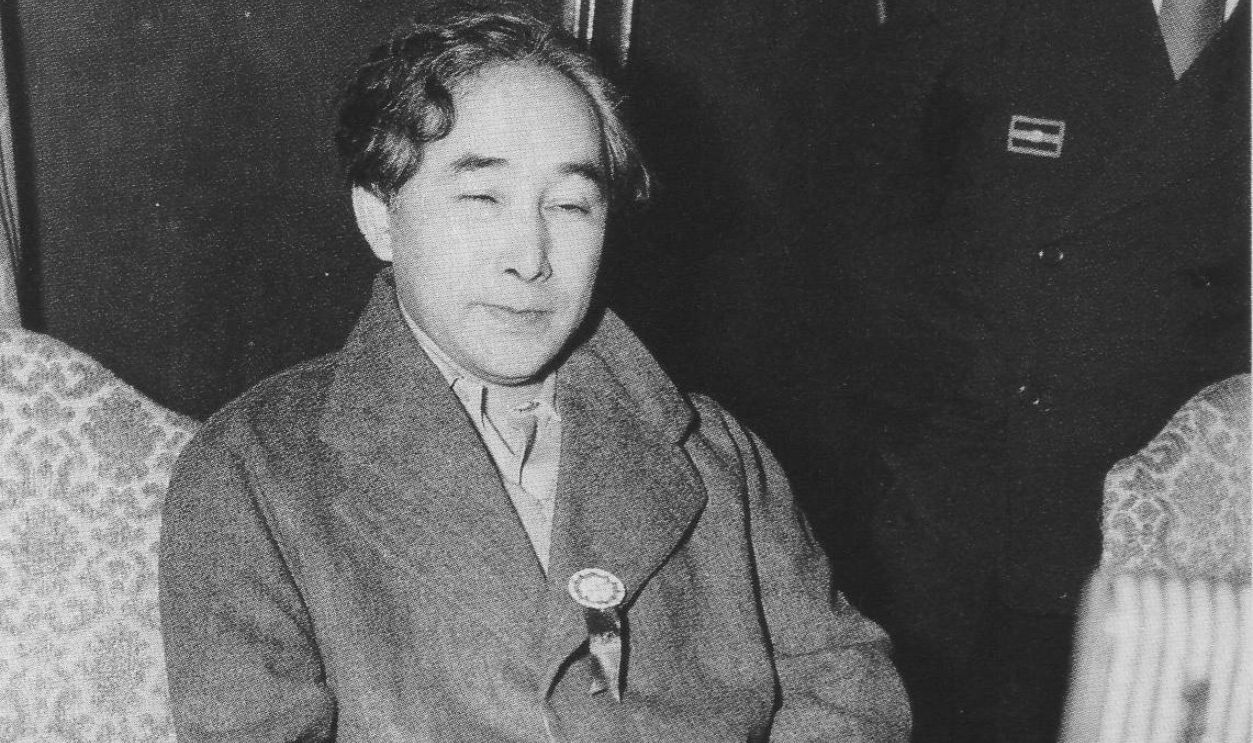
Emperor Hirohito's Influence
Emperor Hirohito played a big role in Japan's surrender despite being a symbolic figurehead during most of the dispute. Members of Japan's Supreme War Council were deeply divided, with hardliners advocating for continued resistance and others seeking a way to end the conflict. Hirohito broke the deadlock by personally intervening.
 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
He Recorded A Radio Broadcast
For years, the emperor's role was merely ceremonial. But on August 14, 1945, Hirohito recorded a radio broadcast known as the Jewel Voice Broadcast, which was played to the nation the following day. His decision to accept the Allies' terms was instrumental in bringing the dispute to a close.
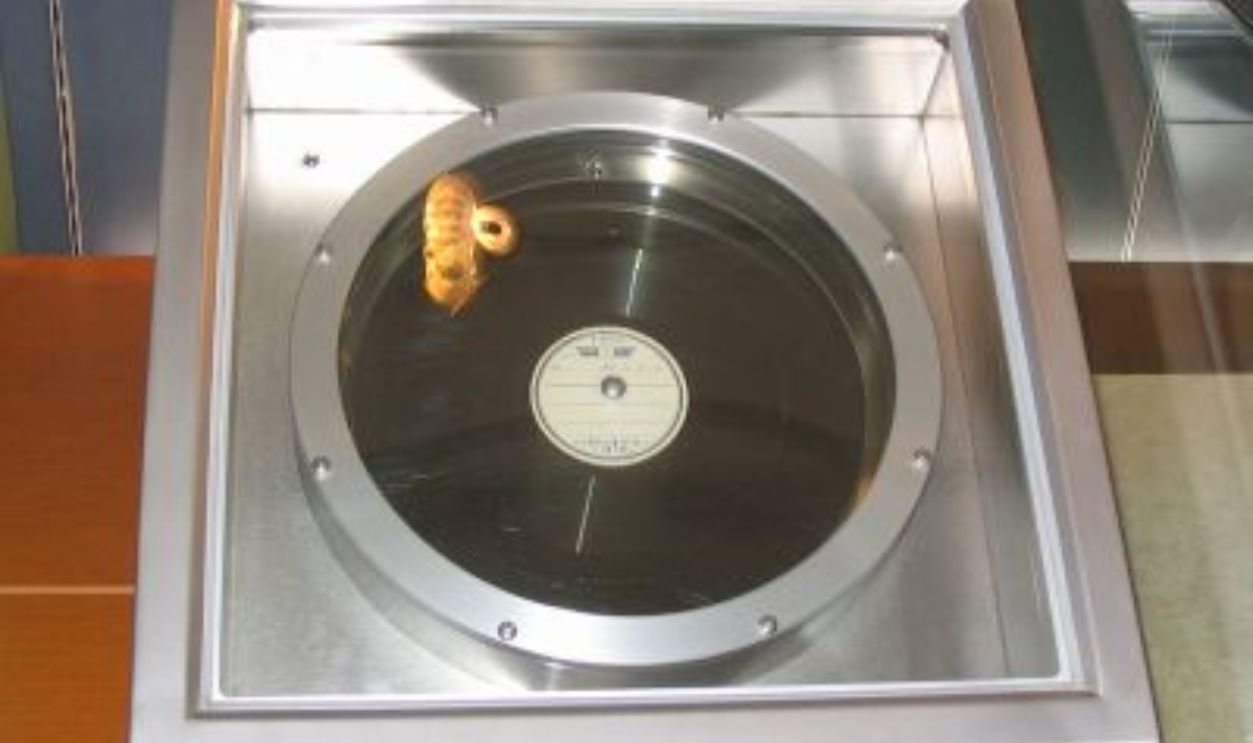 Sphl, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Sphl, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Fear Of Domestic Rebellion
Japan's leadership faced the growing fears of internal unrest. The suffering caused by air assaults and economic collapse impacted civilian morale and weakened the government's authority. People were against the war, and the government lost support, which left it vulnerable on the internal front while dealing with the threat of occupation.
 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Anti-War Ideas
Anti-war sentiment began to surface, with some groups covertly opposing the continuation of the conflict. Japanese leaders feared that further devastation from Allied attacks might spark widespread rebellion or even a collapse of social order. This added urgency to the decision to surrender for domestic stability.
 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
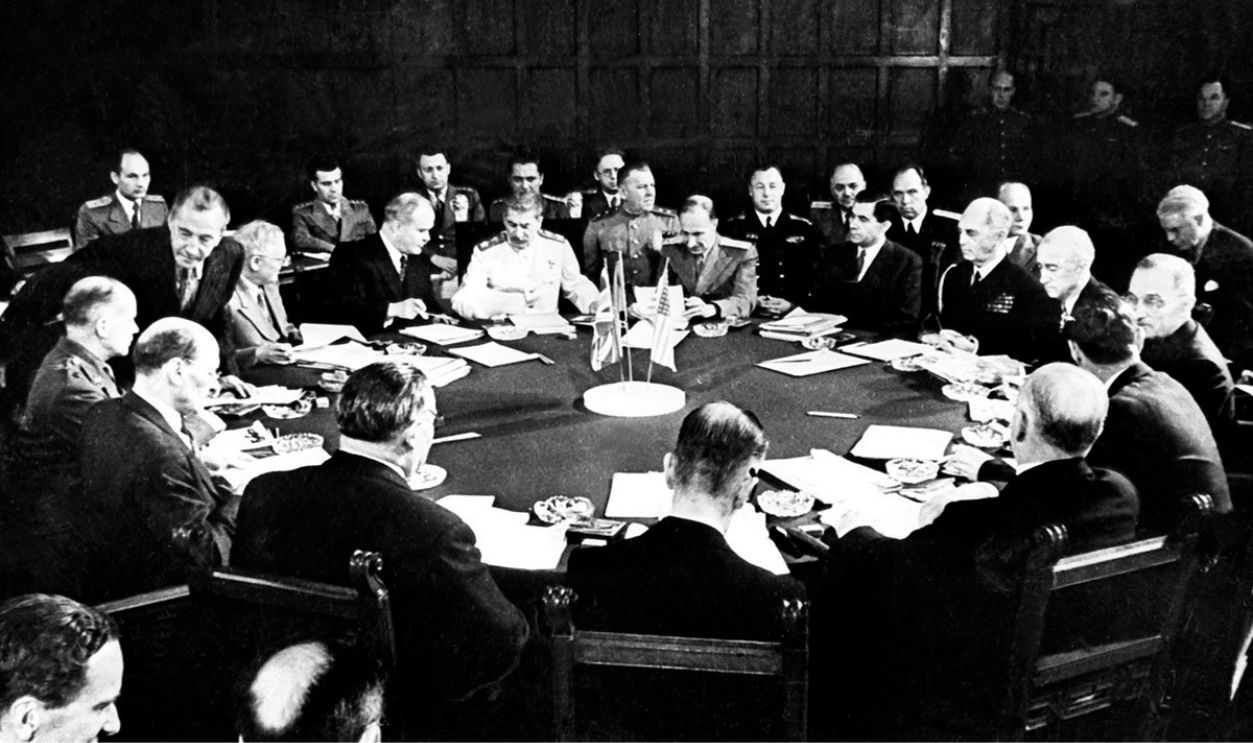
Potsdam Declaration And Allied Ultimatum
The Allies issued the Potsdam Declaration on July 26, 1945, to outline the terms for Japan's surrender. The declaration, signed by the United States, the United Kingdom, and China (with the Soviet Union endorsing it later), demanded Japan's unconditional surrender and warned of utter destruction if it refused.
 Bundesarchiv, CC-BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Bundesarchiv, CC-BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
The Terms
Terms included the disarmament of Japan's military and the occupation of its territory, with no guarantee of the preservation of the emperor. Initially, Japan rejected the ultimatum. However, after the atomic bombardment and the Soviet invasion, the terms of the Potsdam Declaration became the only viable path to survival.















