Famous for great cultural advances in every area of human knowledge, ancient Egypt is still the subject of much fascination. For almost 30 centuries—from its unification around 3100 B.C. to its conquest by Alexander the Great in 332 B.C.—ancient Egypt was the preeminent civilization in the Mediterranean world. From the great pyramids of the Old Kingdom through the military conquests of the New Kingdom, Egypt’s history has long entranced archaeologists and historians and created a vibrant field of study all its own: Egyptology.
The main sources of information about ancient Egypt are the many monuments, objects and artifacts that have been recovered from archaeological sites, covered with hieroglyphs that have only recently been deciphered. The picture that emerges is of a culture with few equals in the beauty of its art, the accomplishment of its architecture or the richness of its religious traditions.
Here are a few things you might not know about ancient Egypt.
53. A Royal Proclamation
Granite blocks used for the King’s chamber of the Great Pyramid weighed as much as 60-80 tons each and were quarried nearly 500 miles away. The exact way the massive blocks were used is unknown. Egyptologists think the massive blocks were floated down the Nile river as much as possible. Legend says that there were some Egyptians who were so devoted to the King that they would walk 500 miles, and they would have walked 500 more, just to be the man to bring the King a block to build a lovely door.

Ancient quarry in Northern Egypt
52. We’re Blushing
Both men and women in ancient Egypt were known to wear copious amounts of makeup which they believed gave them the protection of the gods Horus and Ra. They believed that the makeup had magical healing powers. In fact, research did show that the lead-based cosmetics worn along the Nile helped stave off eye infections.
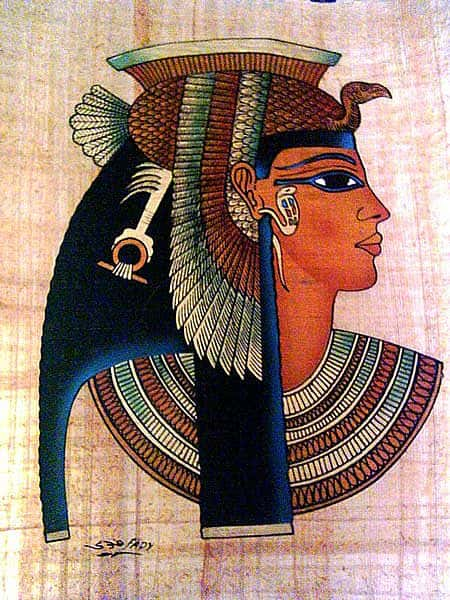

51. Thank You. Sincerely, Tiffany’s
The tradition of exchanging wedding rings goes back to Ancient Egyptian times. That's right, De Beers owes quite a bit to the pharaohs of old.

50. Pick Your Poison
Between the Fourth and Sixth centuries, the main religion in Egypt was Christianity before eventually being supplanted by Islam. Christianity says it’ll make a comeback. We’ve heard that before.

49. Pyramid Scheme
The Great Pyramid of Giza has 8 sides, not 4, distinguishing it from other pyramids. The concavity of the sides was so subtle that it wasn’t noticed until the advent of aviation.
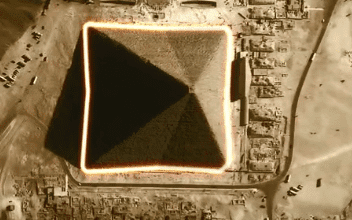
Aerial view of the Great Pyramid of Giza.
48. A Poly Lifestyle
Ancient Egyptians worshiped over 1,400 different gods and goddesses which probably really pissed off the One True God: Bill Murray.

47. Riddle Me This
The Sphinx of Giza is one of the largest single-stone statues in the world, and to this day, nobody knows exactly who built it or why. She is also missing her nose, and while there are theories, it is unknown exactly how that happened. Our theory is that she sneezed too hard because she’s allergic to cats.
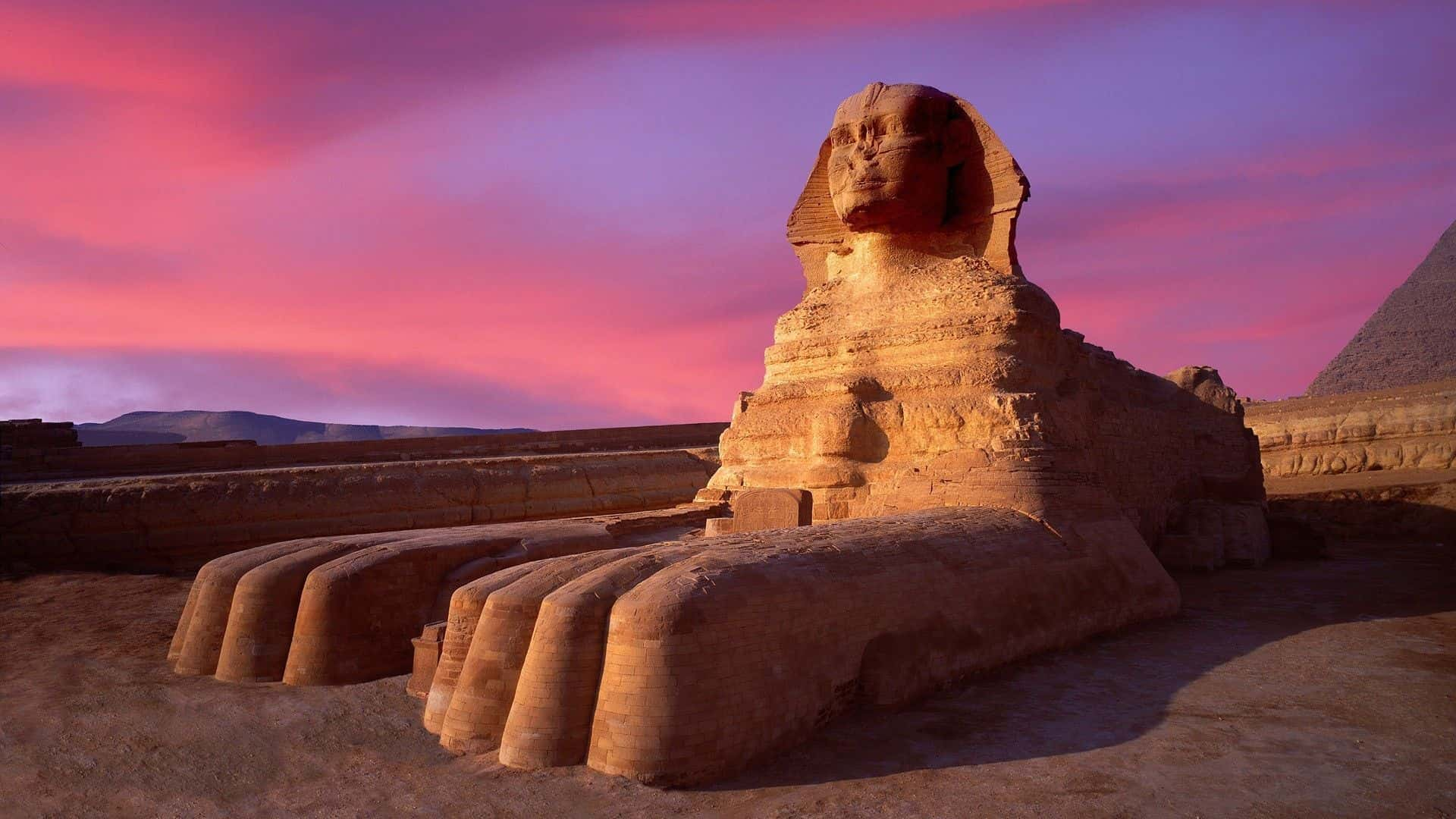

46. Coast to Coaster
Egyptians believed that the earth was flat and round like a pancake and that the Nile flowed through the center of it.

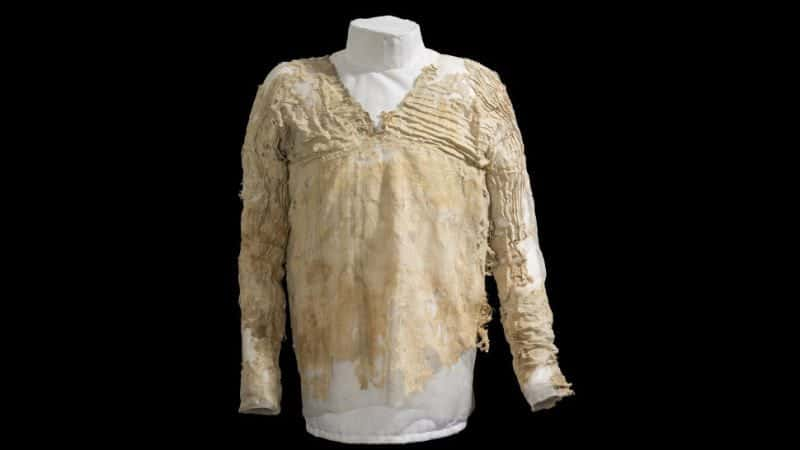
45. Say Yes to the Dress
The world’s oldest dress was found in Egypt and it is 5,000 years old. Even back then, people were probably arguing over if it was blue and black or white and gold.


History's most fascinating stories and darkest secrets, delivered to your inbox daily.
44. Naked Truth
Egyptian children wore no clothing until they were in their teens as the warm temperatures made clothing unnecessary.

43. Planting a Flag
On the border between Egypt and Sudan, there is an area of land 795 miles square, called Bir Tawil, that neither country has claimed. Be right back. We’re off to claim it in the name of Factinate.

42. Great Minds Think Alike
Written language was invented independently by the Egyptians, Sumerians, Chinese, and Mayans.

41. The Writing’s on the Wall
The most important form of Egyptian writing was hieroglyphics. These logographic scripts were considered sacred and were not, contrary to popular belief, a comic book about King Tut and his cat Sphinxy.

40. Location Location Location
Sudan has more pyramids than Egypt. We guess the aliens liked Sudan more.

39. Historical Inaccuracies
Recent discoveries have lead experts to believe that it is possible that the pyramids were actually built by paid laborers and not slaves. The latter is a myth perpetuated by Herodotus, the Greek historian who was apparently not a very good historian.

38. Anhotel Was Here
These workers often left graffiti behind near the monuments suggesting that their work crews had humorous names like the “Drunkards of Menkaure” or the “Friends of Khufu.” Might be one of those jokes where you had to be there.

37. Over Their Heads
The lost Egyptian city of Heracleion was found after 1,200 years under the sea. Being submerged 30 feet underwater probably did a real number on property values.

36. Sleep Like a Rock
Ancient Egyptians slept on pillows made of stones. In case you were wondering, the Princess and the Pea was not an ancient Egyptian story.

35. Sail Away
Egypt invented the first sailing boats used to transports people and goods up and down the Nile. This perhaps the most widely used and important transportation system in Ancient Egypt.

34. On Board
Ancient Egyptians loved board games, one of the most popular being a game of chance known as “Senet.” Historians are a little shaky on what the rules of that game were, but there was no doubt it was popular with paintings depicting Queen Nefertiti playing the game and King Tut was buried with a board.
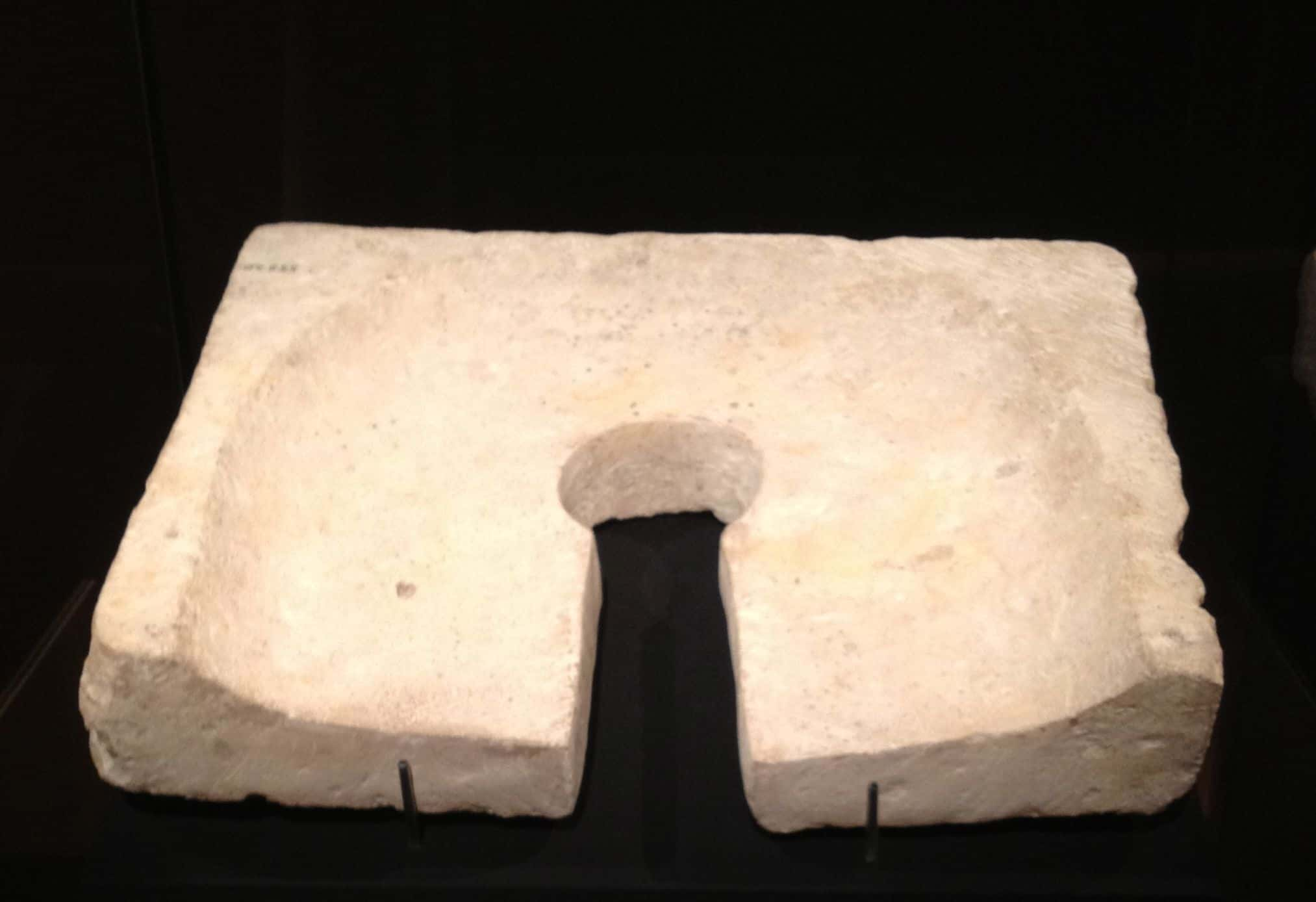
33. When You Gotta Go
Many Egyptian tombs included toilets. Turns out, you CAN take it with you.

32. ¿Dónde está el baño?
There are still unexplored passageways in the Great Pyramid of Giza and we’re sure some of them probably lead to undiscovered toilets. 60% of the time we are right, every time.

31. Egypt by Calvin Klein
Both sexes also wore perfumes made from oil, myrrh, and cinnamon. Given the likelihood that hygiene standards weren’t as high as modern-day, this is probably a good thing.
30. The End of Curiosity
In Ancient Egypt cats were worshiped and killing a cat, even accidentally, was punishable by death. Does that mean they would apply the death penalty nine times?

29. A Close Shave
Ancient Egyptians would shave off their eyebrows in order to mourn the death of their cats. Cats were even mummified so they could live on in the afterlife.

28. Animal House
In addition to cats, Egyptians also had a reverence for hawks, ibises, dogs, lions, and baboons. These animals had a special place in the Egyptian home and were often mummified and buried with their owners after death.
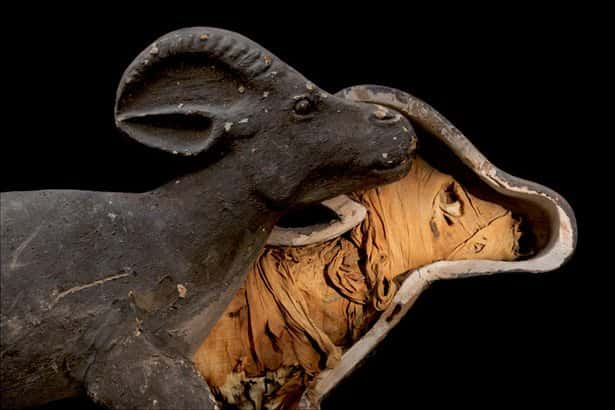

27. The Long Paw of the Law
Ancient Egyptians police officers were known to have trained dogs and monkeys assist them when they were out on patrol. We smell a sitcom.

26. A Periodic Break
In Ancient Egypt, men could take time off of work to care for menstruating wives and daughters.

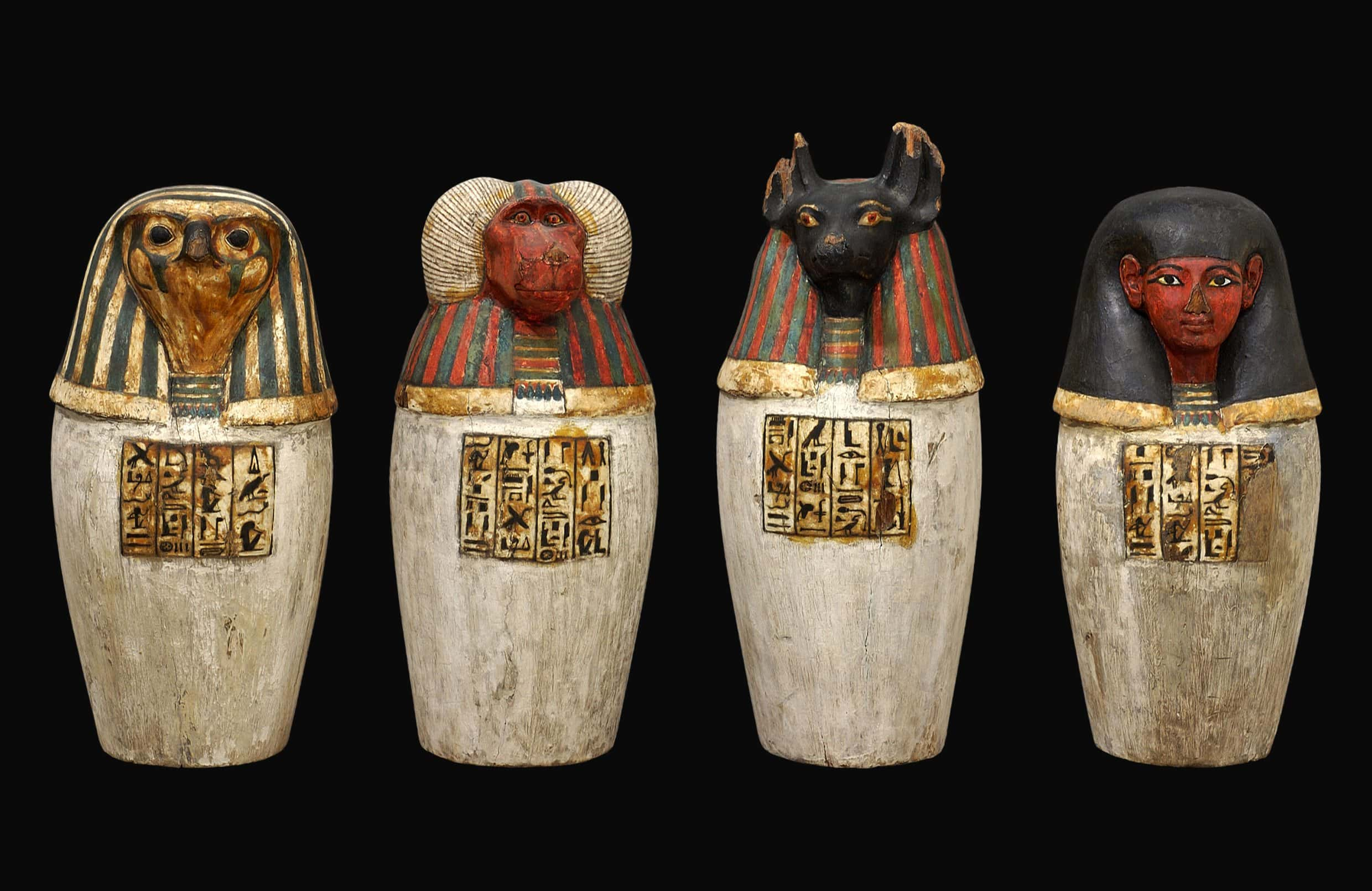
25. We Heart Mummies
When a body was mummified the brain was literally scrambled and removed through one of its nostrils, and each organ was placed in its own canopic jar. The only internal organ that was not removed was the heart as it was considered to be the seat of the soul.

24. Keep it in the Family
Ancient Egyptian King Tutankhamun, or as he is more affectionately known, King Tut, died at the tender age of 18. Some researchers believe he died from genetic disease due to the fact his parents were brother and sister. Ancient Egypt was into Game of Thrones before it was cool.

Possible rendering of King Tut's genetic deformity
23. Hungry Hungry Hippo
Because the body of Tut didn’t include his heart or chest wall, a drastic departure from typical Egyptian embalming practices, other researchers believe that King Tut may have died after a horrific injury, of which one possibility was that he was eaten by a hippo.

King Tut's golden sarcophagus
22. Anatomically Correct
Ancient Egyptian doctors had specialties, often focusing on one part of the human body. Dentists were known as “doctors of the tooth,” while the term for proctologists literally translates to “shepherd of the anus.” We don't want any part of that Shepherd’s Pie.

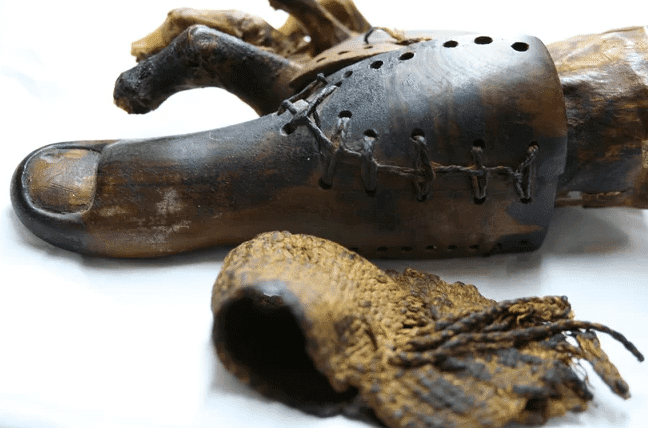
21. This Wooden Piggy
The world’s oldest prosthetic limb belongs to an Egyptian woman who, in approximately 1000 BC, was outfitted with a wooden toe.

20. Tyrion is Pleased
The ancient Egyptians had a very high regard for dwarves, and did not see them as having a physical handicap.
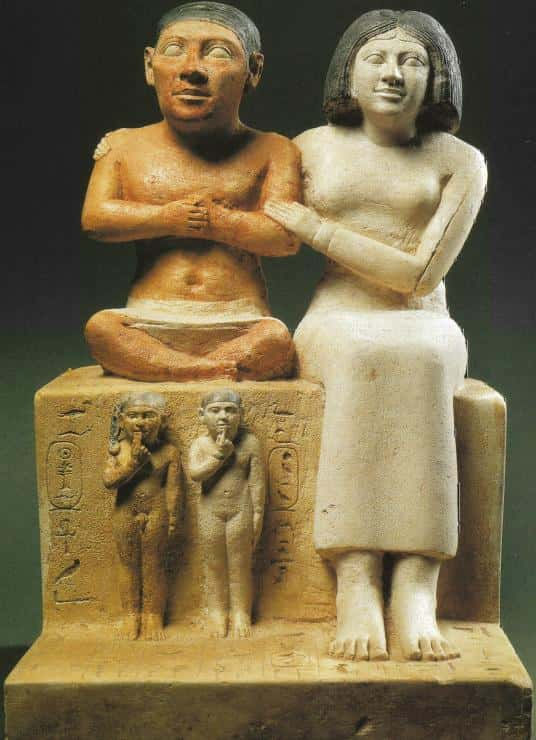

Seneb, overseer of palace dwarves, and his wife
19. It’s All Greek to Me
In the dynasty of Greek rulers of Egypt, Cleopatra was the first who could speak Egyptian.

18. Sweet Relief
In order to keep flies from landing on him, Pepi II of Egypt surrounded himself with naked slaves whose bodies were smeared with honey. Pepi II was a bit of a dick.

17. It’s Good to be the King
Ramses the Great had 8 official wives and nearly 100 concubines. He was over 90 years old when he died in 1212 BC and, no doubt, he died a very happy man.

15. Bundle of Joy
Traces of nicotine and cocaine were found in Egyptian mummies.

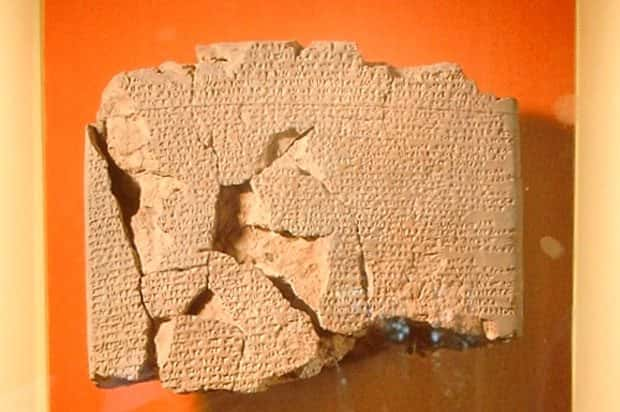
16. Peace Out
The ancient Egyptians and the Hittite Empire were the signatories of one of the earliest surviving peace accords, a copy of which can be seen above the entrance to the United Nations Security Council Chamber in New York.

14. In One Ear…
One ancient Egyptian cure for blindness was to pour mashed-up pig’s eye into the patient’s ear. Luckily, patients who received this treatment couldn’t see the mess it made.

13. If the Mold Fits
While antibiotics weren’t discovered until the 20th century, early Egyptian medicine used moldy bread to treat infections.

12. Crap to the Future
Ancient Egyptians practiced scatomancy, the act of telling the future through someone’s feces. Well, if there’s anyone who can tell us about the future, it’s Doc Brown. We’ll let ourselves out.

11. Gender Studies
Inscribed pottery from the Middle Kingdom of Ancient Egypt lists 3 human genders. Seems like Egypt was way ahead of the curve when it came to their transgendered bathroom policies.
10. Wage Gap? What Wage Gap?
Although Egyptian women typically stayed at home, those who worked outside the home received equal pay for doing the same jobs as men.

9. Strike One
Ancient Egyptian workers were not afraid to protest for better working conditions. The most famous was during the reign of Ramses III when laborers building the royal necropolis did not receive their usual payment of grain. They organized one of the first recorded strikes in history.

8. What’s Mine is Mine
Egyptian couples were known to negotiate ancient prenuptial agreements. These contracts listed all the assets a woman brought into the marriage and guaranteed she would be compensated for it in the event of a divorce.

7. Time for S’Mores
Ancient Egyptians were the first people to make a sweet treat from the marshmallow plant, combining its sap with nuts and honey.

6. A God that Poops
Pharaohs were viewed by the Egyptian people as living gods.

5. Man of the House
The term pharaoh translates to “great house” and originally referred to the royal palace where the pharaohs lived. Eventually, it became the designation for the ruler of Egypt.
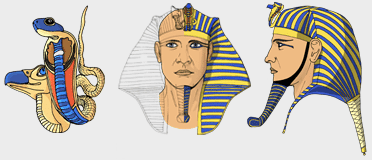
4. Under Wraps
A pharaoh would never let his hair be seen and always wore a crown or a headdress called a nemes. As a result, pharaohs never had a bad hair day.
3. Sweet Tooth
Many Ancient Egyptian Pharaohs were overweight due to a sugary diet of alcohol, bread, and honey.

2. Jabba the Tut
Even though her sarcophagus depicted her as slender and athletic, the legendary Queen Hatshepsut, who lived in 15th century BC, was said to be likely obese and bald.

1. Planned Parenthood
The Egyptian Kahun Papyrus (1850 BC) suggested using crocodile feces either as a contraceptive or as an abortion drug. We’re not doctors, but we’re sure that smearing yourself in poop would deter anyone from wanting to have a baby with you.












